Session Information
Session Type: Late-Breaking Abstract Session
Session Time: 7:30AM-9:00AM
Background/Purpose: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a fibroinflammatory disease. Remission induction treatment with glucocorticoid (GC) is usually effective, but its tendency of relapse makes the strategy for maintenance treatment a challenge. TheWInS IgG4-RD (withdraw immunosuppressants and steroid in stable IgG4-RD) trial tested whether discontinuation of GC and immunosuppressive agent (IM) were feasible in stable IgG4-RD.
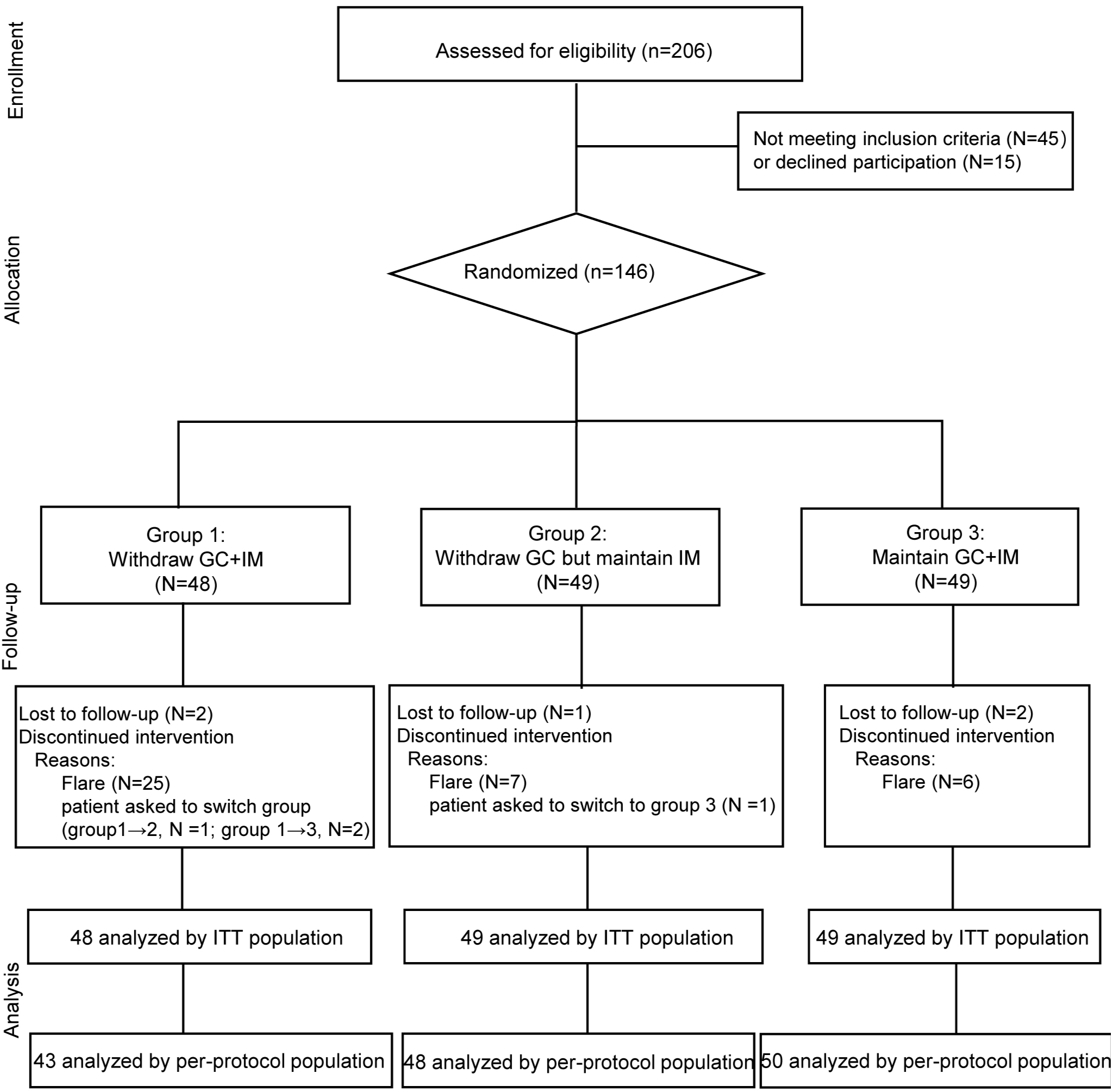
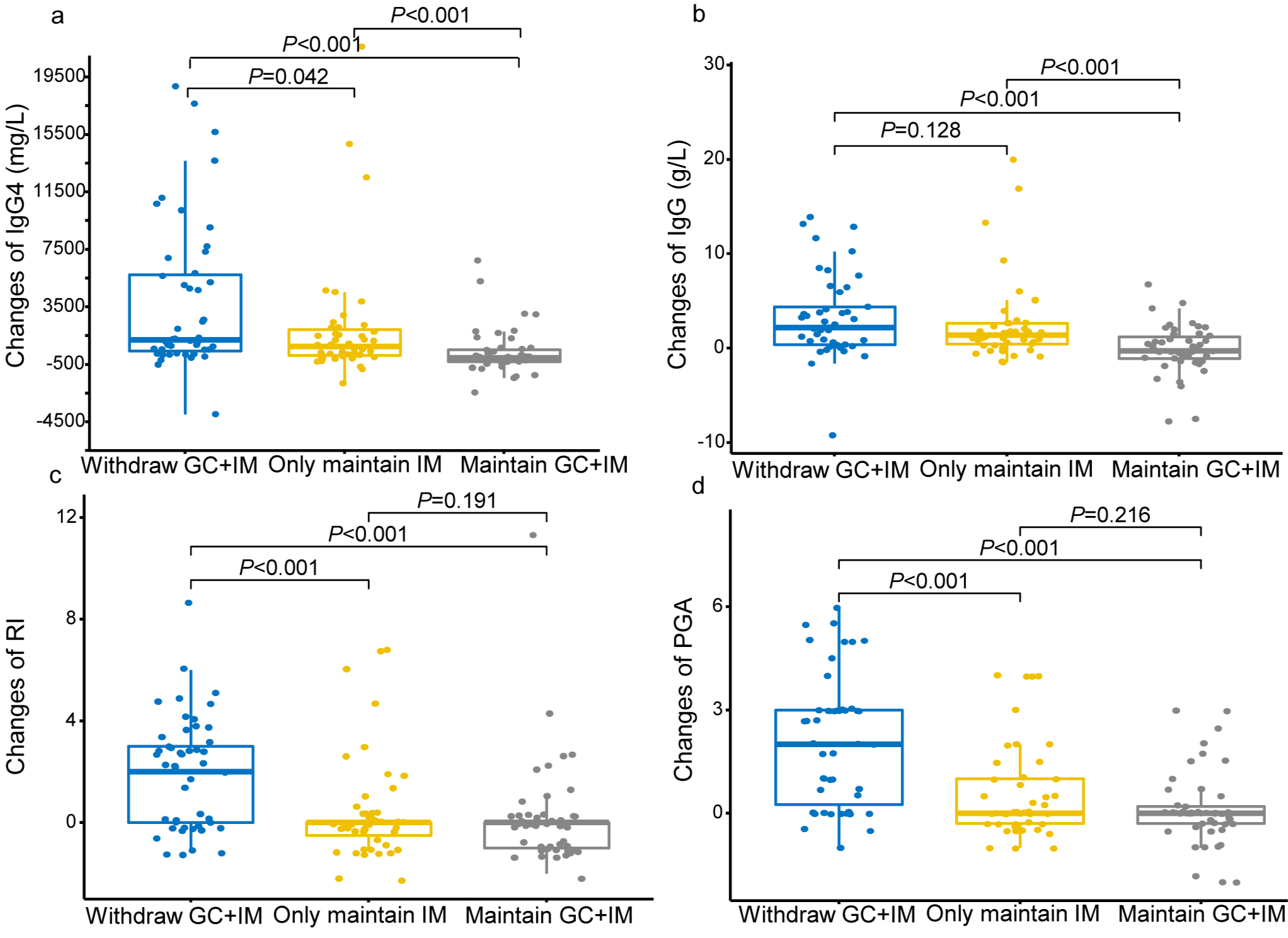
Methods: The WInS IgG4-RD trial was a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. IgG4-RD patients receiving GC+IM as maintenance treatment with clinically quiescent disease for at least 12 months were randomised (1:1:1) into three groups: (1) Group 1: withdraw GC+IM; (2) Group 2: withdraw GC but maintain IM; (3) Group 3: maintain GC+IM. The primary endpoint was the relapse rate of disease within 18 months. The secondary endpoints include the changes of responder index (RI), physician’s global assessment (PGA), serum IgG4 and IgG, as well as adverse events.
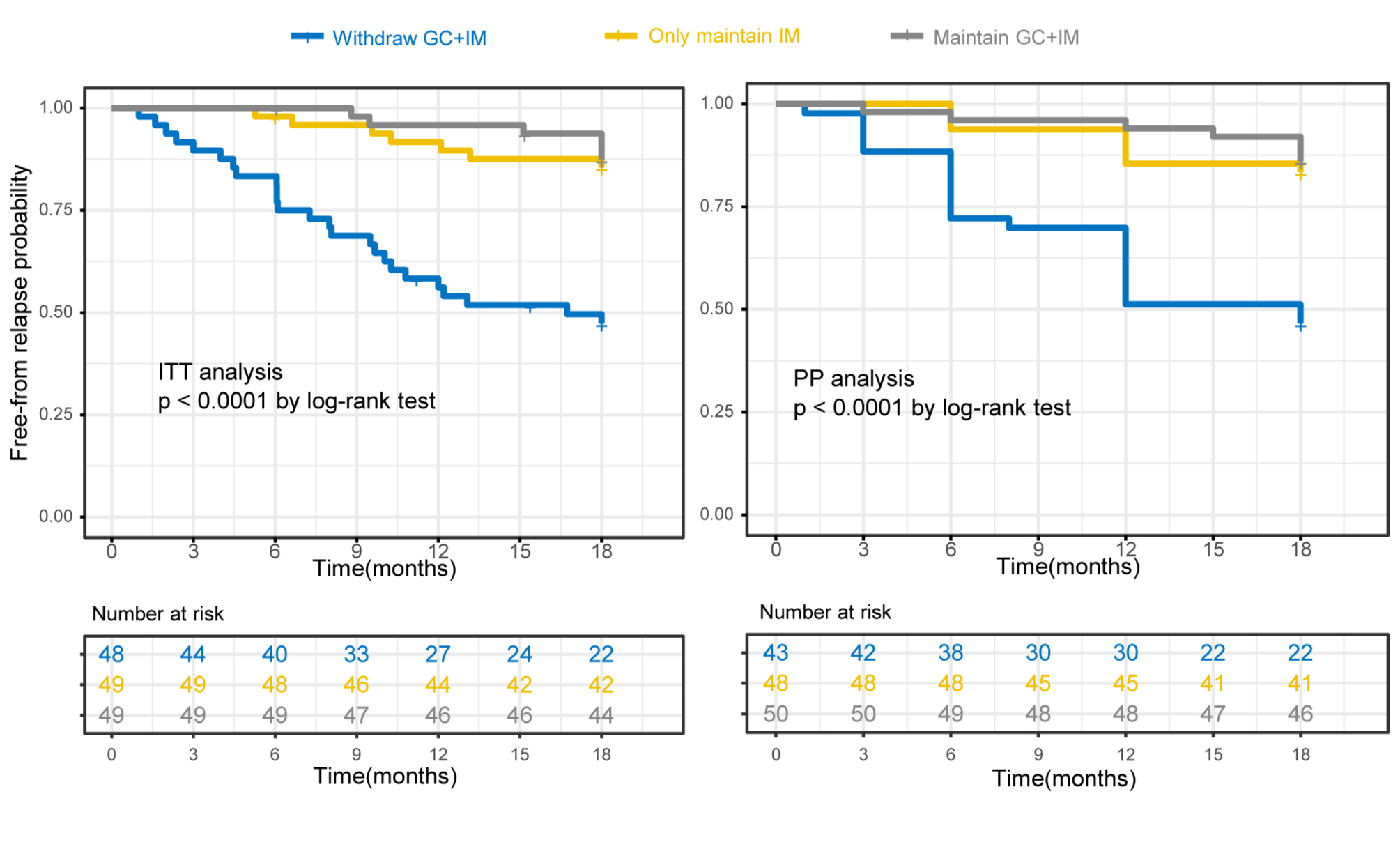
Results: One hundred and forty-six patients were randomised, with 48 patients in Group 1, and 49 patients in Group 2 and Group 3 respectively. Within the 18-month follow-up period, disease relapse occurred in 25/48 (52.1%) patients in Group 1 versus 7/49 (14.2%) in Group 2 and 6/49 (12.2%) in Group 3 (p< 0.001). The changes in RI and PGA were significantly higher in Group 1 than Group 2 (p< 0.001) or Group 3 (p< 0.001).
Conclusion: The maintenance of IMs, with or without low-dose GC, was found to be superior to withdraw GC+IM in preventing relapse for long-time stable IgG4-RD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Peng L, nie Y, Zhou J, Wu L, Wang F, Chen X, Li J, Peng Y, Lu H, Zhao L, Li M, Zhao Y, Zeng X, Fei Y, Zhang W. Withdrawal of Immunosuppressant and Low-dose Steroids in IgG4-RD Patients with Stable Disease (WInS IgG4-RD): An Investigator-initiated, Multi-center, Open-label, Randomized Controlled Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/withdrawal-of-immunosuppressant-and-low-dose-steroids-in-igg4-rd-patients-with-stable-disease-wins-igg4-rd-an-investigator-initiated-multi-center-open-label-randomized-controlled-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/withdrawal-of-immunosuppressant-and-low-dose-steroids-in-igg4-rd-patients-with-stable-disease-wins-igg4-rd-an-investigator-initiated-multi-center-open-label-randomized-controlled-trial/