Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1264–1307) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: RA is a chronic disease that can lead to irreversible damage and functional decline with delayed or inadequate treatment.1 Abatacept + MTX is effective for many patients (pts) with RA2,3 and may better preserve functional status when introduced early in the disease course4. The HAQ-disability index (DI) is a pt-reported outcome delineating physical function impacted by RA.3,5 This study assessed the relationship between baseline (BL) disease duration after initiating abatacept + MTX and improved physical function using HAQ-DI scores in RA over 8 yrs.
Methods: This pooled analysis included data from 15 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) in pts with RA (ACR/EULAR 2010 criteria6) treated with abatacept + MTX. Included pts had data available on BL disease duration, HAQ-DI scores (0–3 scale), and demographic characteristics. Trends in mean HAQ-DI and mean change in HAQ-DI from BL over time were modelled using mixed-effect linear regression models, fitted to BL disease duration and the log of treatment duration as fixed effects and subject identities as random effects. Analyses were repeated in subgroups categorized by age, sex, race, and BMI.
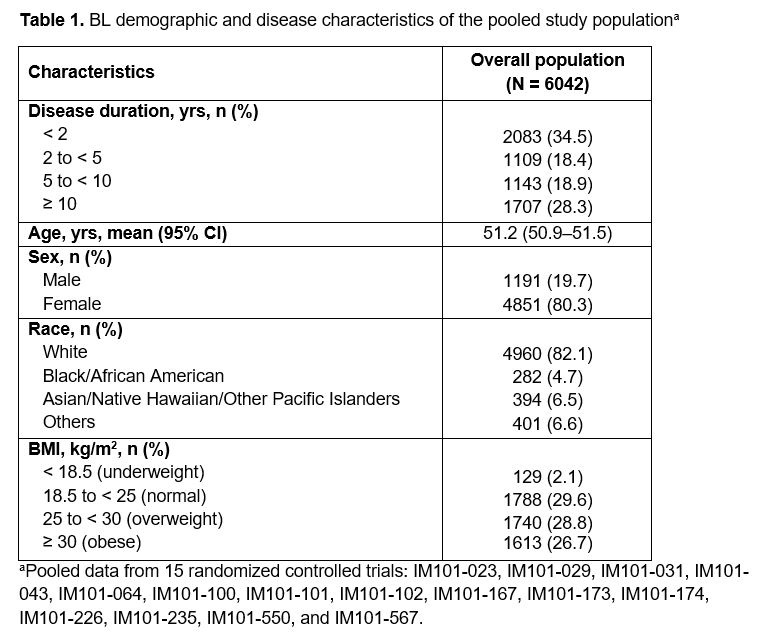
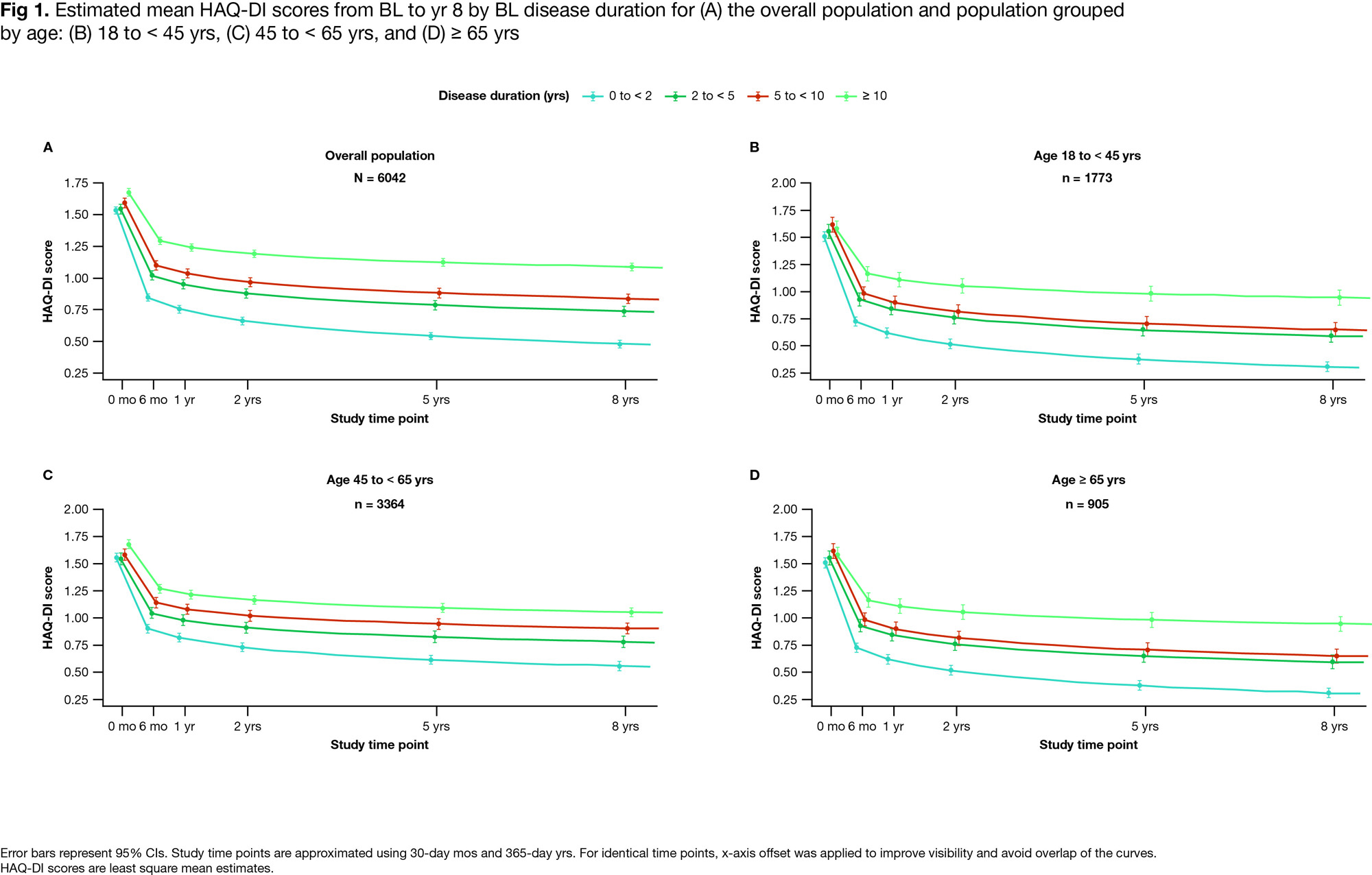
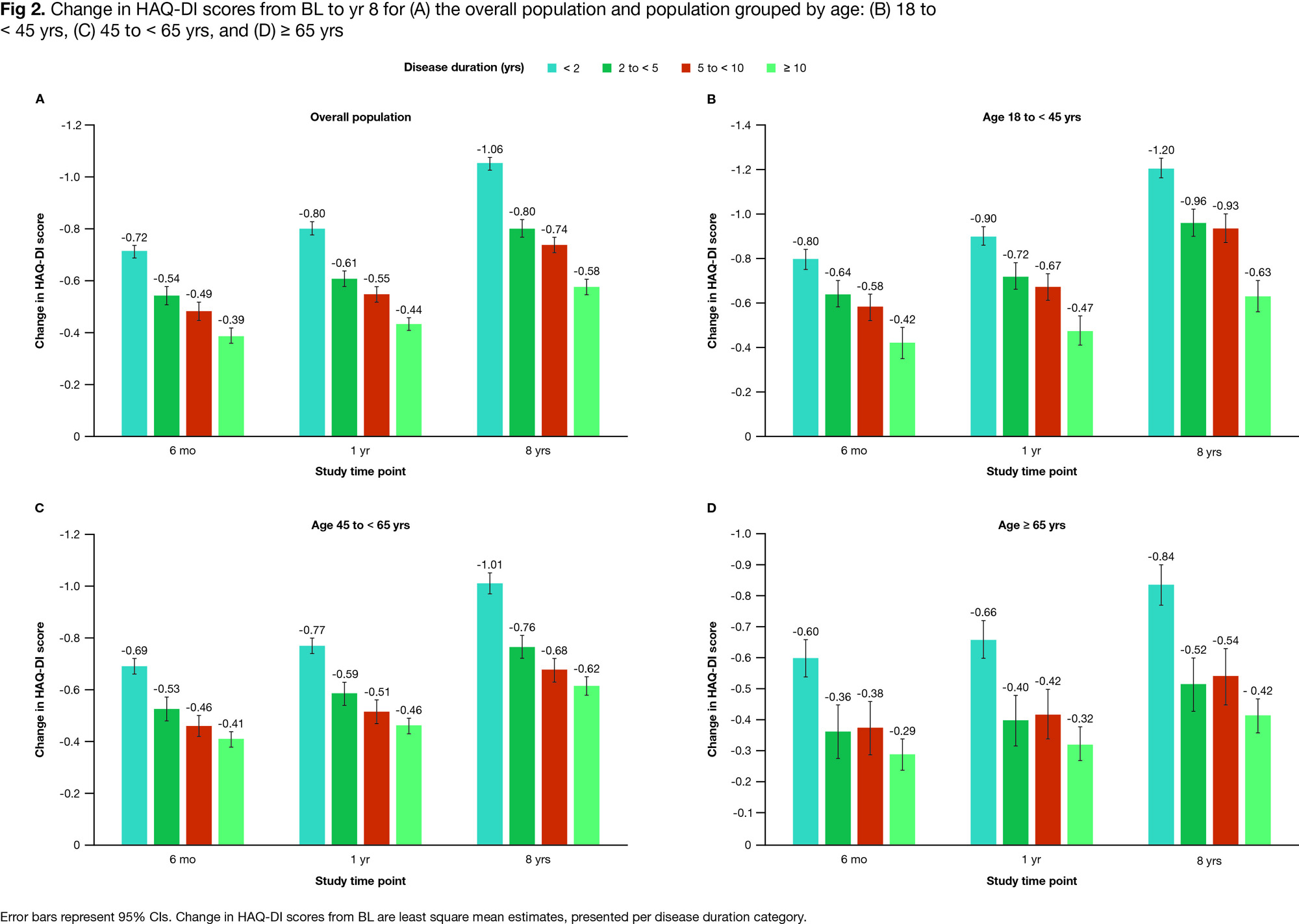
Results: Of the 6042 pts included, most had a disease duration < 2 yrs (34.5%), a normal BMI of 18.5 to < 25 kg/m2 (29.6%), were of female sex (80.3%) and White (82.1%) (mean age: 51.2 yrs; Table 1). In the overall population, HAQ-DI decreases were associated with shorter disease duration (Fig 1A): the magnitude of changes in HAQ-DI scores decreased as disease duration increased at all time points (Fig 2A). A similar trend was observed for subgroups categorized by age (Figs 1B–D, 2B–D), sex, race, and BMI (data not shown). BL HAQ-DI scores for all disease duration categories were higher among females (95% CI: 1.6–1.7 vs 1.3–1.5 in males), and the trend in HAQ-DI reductions was more gradual in male versus female pts (data not shown). In the overall population and subgroups categorized by age, the greatest reduction in HAQ-DI scores occurred between BL and 6 mo, followed by gradual reductions until 8 yrs (Figs 1, 2). Differences between disease duration categories were notable from 6 mo and increased with follow-up time (Figs 1, 2). The largest reductions in HAQ-DI scores were reported by pts with RA disease duration < 2 yrs and the smallest reductions, by those with RA disease duration ≥ 10 yrs (Fig 2A).
Conclusion: Pts with RA receiving earlier abatacept treatment (within 2 yrs of diagnosis) reported greater improvements in and better maintenance of physical function over time. In all groups analyzed, pts with the shortest disease duration at BL who received abatacept + MTX had the best outcomes. Among currently available RA treatments, abatacept + MTX notably improves physical function in pts with early RA. Our findings support the need for prospective RCTs to evaluate abatacept + MTX as an early-line treatment for RA.
References
- Quinn MA, et al. Rheumatology(Oxford) 2001;40:1211–20.
- Westhovens R, et al. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2014;32:553–62.
- Cagnotto G, et al. Arthritis Res Ther 2020;22:15.
- Aletaha D, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2008;67:238–43.
- Pope JE, et al. J Rheumatol 2009;36:254–9.
- Aletaha D, et al. Arthritis Rheum 2010;62:2569–81.
Medical writing: Candice Dcosta (Caudex), funded by Bristol Myers Squibb.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bykerk V, Castrejon I, Strand V, Dahan S, Castellanos-Moreira R, Chen L, Little W. Window of Opportunity to Achieve Better Functional Outcomes in Patients with RA: Effectiveness of an Early Treatment Strategy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/window-of-opportunity-to-achieve-better-functional-outcomes-in-patients-with-ra-effectiveness-of-an-early-treatment-strategy/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/window-of-opportunity-to-achieve-better-functional-outcomes-in-patients-with-ra-effectiveness-of-an-early-treatment-strategy/