Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a severe complication of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Abatacept (ABA) has demonstrated efficacy in the treatment of RA-ILD. Our objective is to compare the efficacy of ABA in RA-ILD patients according to ILD duration.
Methods: National multicenter study of 526 RA-ILD patients treated with ABA. Patients with ABA initiation early in the disease (during the first 6 months since ILD diagnosis) were compared to those in whom ABA was started after 2 years of ILD diagnosis (“early” vs. “late” group, respectively). We analyzed in the 2 groups the following outcomes: a) forced vital capacity (FVC), b) diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide (DLCO), c) chest high resolution computed tomography (HRCT), d) dyspnea (modified Medical Research Council scale), and e) arthritis activity (DAS28-ESR or clinical records).
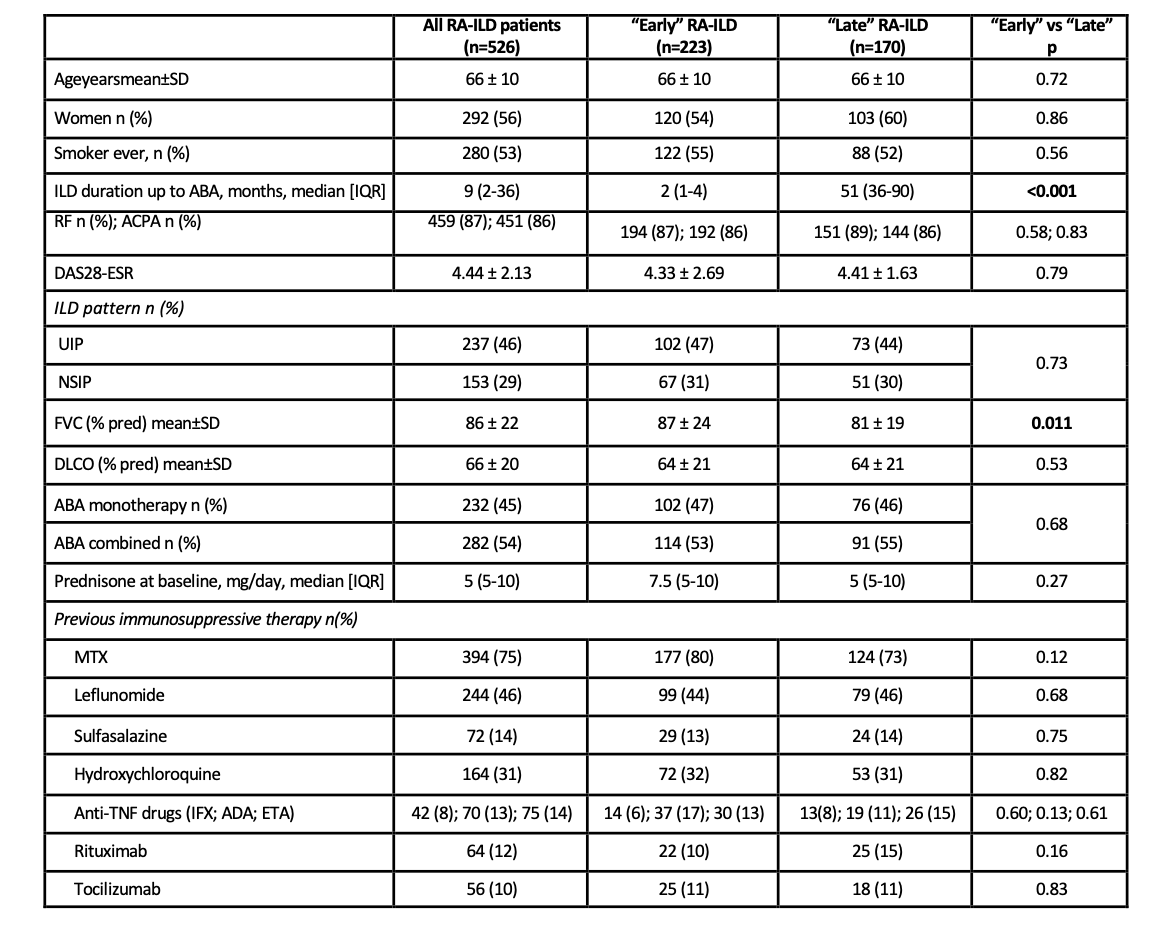
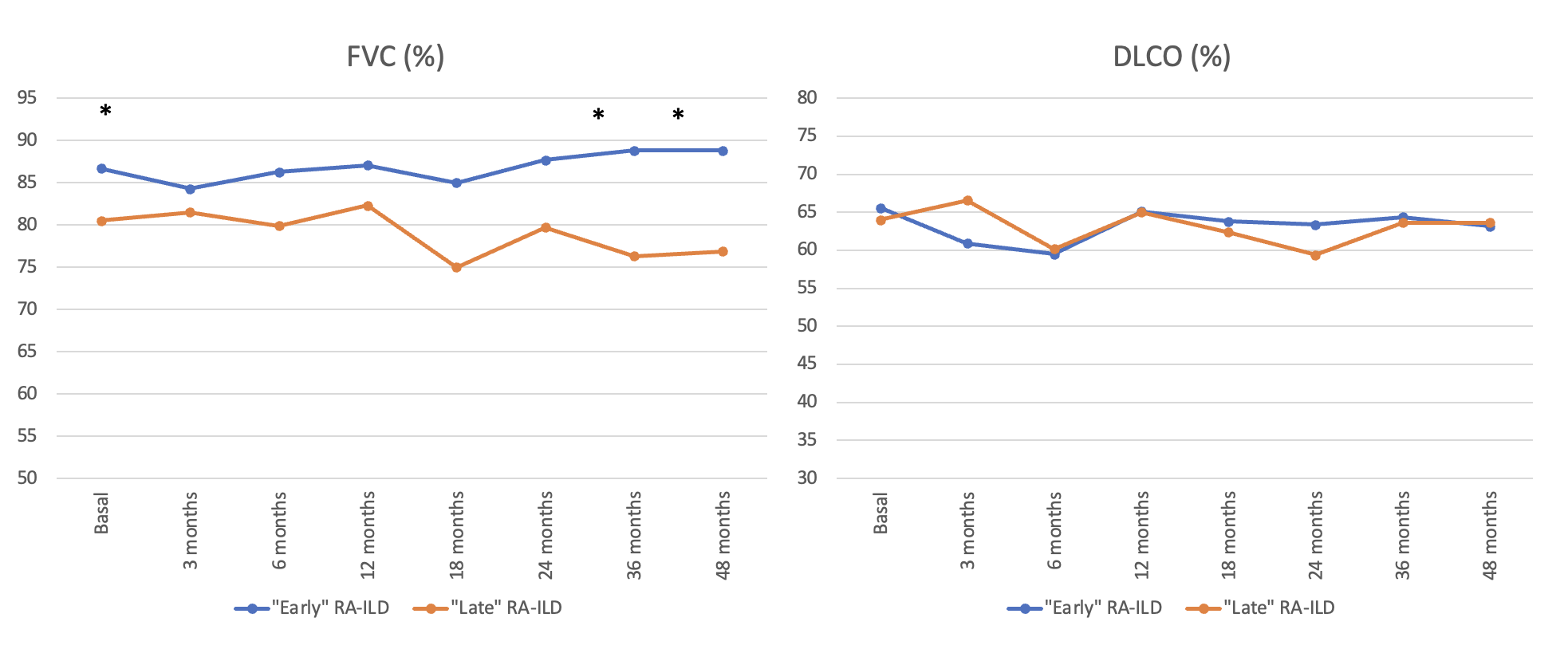
Results: A total of 223 patients were included in the “early” group and 170 patients in the “late” group. Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics are shown in Table. Mean baseline values of FVC were significantly higher in the “early” group. The evolution of FVC and DLCO for 48 months is shown in Figure. Both parameters remained stable during 48 months of ABA therapy, with statistically significant differences found in case of FVC (although lower stable values of FVC in the “late” group). Available chest HRCT images improved/ stabilized in 74% and 57% of patients in the “early” and “late” group, respectively. Stabilization or improvement of dyspnea was found in most patients of both groups.
Conclusion: Treatment with ABA at any time of the course in the ILD seems to prevent interstitial lung progression. However, our results suggest that the same treatment (ABA) prescribed early in RA-ILD, may be preferable to preserve lung function (“window of opportunity”).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Serrano-Combarro A, Atienza-Mateo B, Ibarrola Paino L, Casafont-Sole I, Loarce J, Blanco Madrigal J, Castañeda S, Ortega-Castro R, Mena Vázquez N, Vegas Revenga N, Domínguez Casas L, Peralta Ginés C, Retuerto Guerrero M, Pérez Albadalejo L, López Sánchez R, MANZANO CANABAL M, Brandy-Garcia A, Lopez Viejo P, Bonilla G, Maíz Alonso O, Carrasco-Cubero C, Garijo Bufort M, Urruticoechea Arana A, Ordoñez S, González Montagut C, García-Valle A, De Dios J, Martín López M, Vázquez Rodríguez T, Fernández-Lozano D, Brana Abascal I, Melero-Gonzalez R, Giner E, Ruiz-Esquide V, Ventin Rodriguez C, Rodriguez M, Andújar-Brazal P, Fernandez Melon J, López-Núñez L, LAMUA RIAZUELO J, Pamies Corts A, Fernández Díaz C, Loricera J, Ferrer D, Blanco-Alonso R. Window of Opportunity in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis – Interstitial Lung Disease with Abatacept. National Multicenter Study of 526 Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/window-of-opportunity-in-the-treatment-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-interstitial-lung-disease-with-abatacept-national-multicenter-study-of-526-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/window-of-opportunity-in-the-treatment-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-interstitial-lung-disease-with-abatacept-national-multicenter-study-of-526-patients/