Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster II: Psoriatic Arthritis I (1329–1363)
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease characterized by musculoskeletal and skin inflammation. Selective inhibition of Janus kinase 1 (JAK1) has the potential to simultaneously block multiple inflammatory pathways and alleviate pathology. In the recently completed EQUATOR study, filgotinib (FIL), a preferentially JAK1 selective inhibitor, showed significant improvements in clinical signs and symptoms of PsA versus placebo.1 In this study, whole-blood RNA-Seq data analysis was performed to evaluate the impact of FIL on gene expression and biological pathways in the EQUATOR study.
Methods: EQUATOR (Clinicaltrials.gov identifier: NCT03101670) was a phase 2 double-blind, placebo (PBO)-controlled study in 131 patients with active moderate-to-severe PsA and insufficient response or intolerance to ≥1 conventional synthetic DMARD. Patients were randomized 1:1 to receive FIL 200 mg or PBO orally once daily for 16 weeks. Whole blood samples from patients were collected at baseline and weeks 1, 4 and 16. Illumina TruSeq Stranded mRNA was generated for 452 samples from 121 patients. Gene-level quantification of RNA-seq counts and transcripts/million was conducted using Salmon (v0.8.2, and gencode GRCh38.p7 v25). Pathway analysis was performed using single sample gene set enrichment analysis based on Hallmark 50 pathways (v7.0) from the MSigDB. Treatment effect was evaluated using differential expression analysis by limma. Twelve factors were extracted from the union of genes significantly affected by FIL treatment compared to PBO at either week 1, 4 or 16. An effect of FIL on Factor scores was evaluated with mixed effect linear models for repeated measures.
Results: At baseline, Spearman rank correlation analyses showed a number of inflammation-associated genes and immune related Hallmark 50 pathways significantly correlated with CRP, Disease Activity in Psoriatic Arthritis score (DAPSA) and patient reported pain. Several of these pathways were decreased with FIL treatment including IL6_JAK_STAT3 and Inflammatory Response. Differential gene expression analysis comparing PBO-corrected samples from FIL-treated patients revealed significant changes in individual gene expression across weeks 1, 4 and 16 such as downregulation of the CRP-associated gene FAM20A and the JAK-STAT pathway members SOCS2 and CISH.
The pharmacodynamic effects of FIL can be described by changes in 8 factors derived from latent variables resulting from Exploratory Factor Analysis (Figure 1). These factors are split into two distinct categories: changes in circulating cell composition (% total B cells, % effector B cells, % T cells, % monocytes) and changes in transcriptional pathways (Complement, Type I Interferon, Inflammation, SOCS2/CISH).
Conclusion: Treatment with FIL rapidly downregulates inflammatory and immune pathways associated with PsA disease activity as a result of changes in inflammatory gene expression and alterations in circulating cellular composition.
Reference
1. Mease P, Coates LC, Helliwell PS, et al. Lancet. 2018;392(10162):2378-2387.
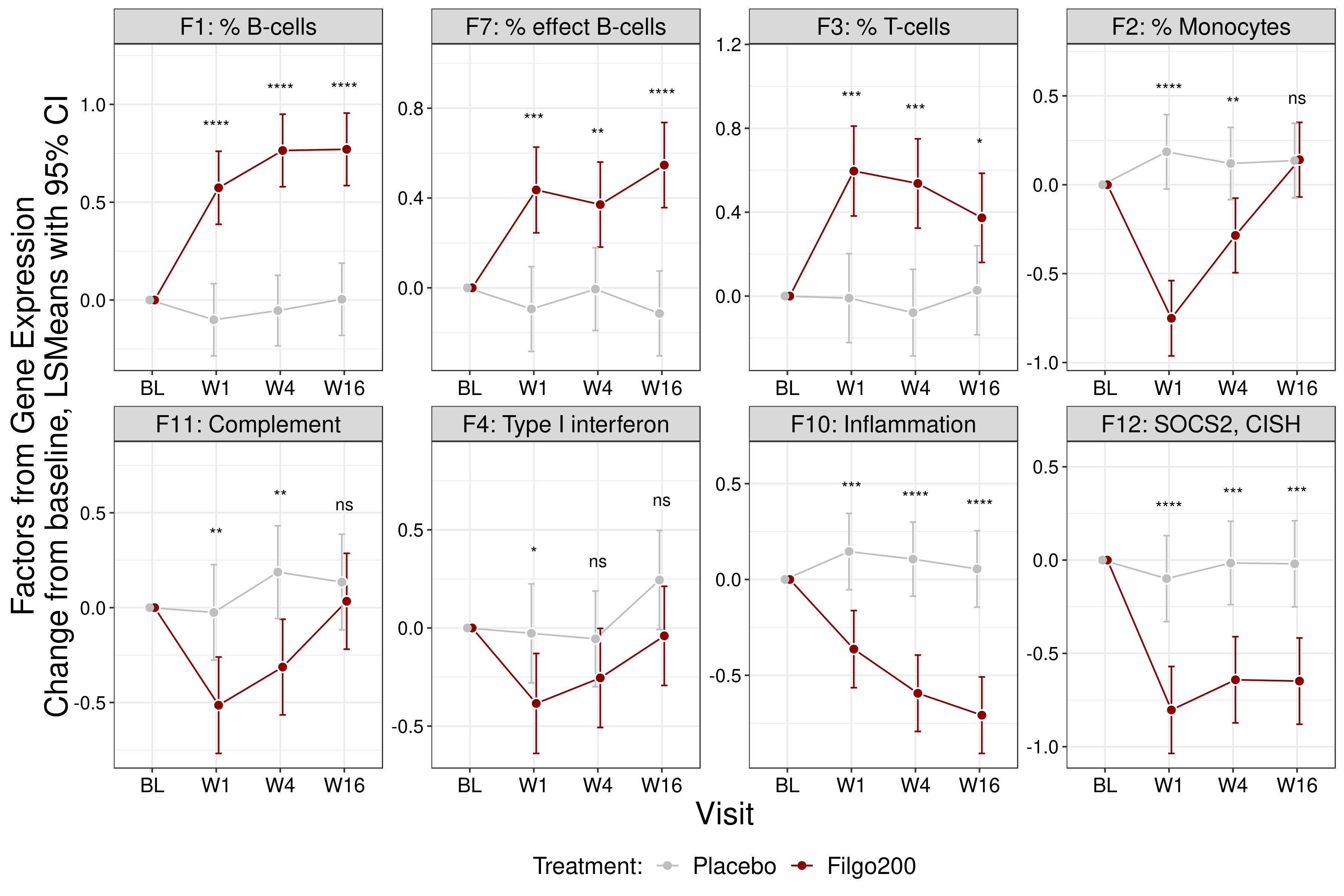 Figure 1. Pharmacodynamic gene expression changes observed during 16 weeks of treatment with FIL or PBO. Exploratory Factor Analysis was performed using the union of gene signatures (FIL vs PBO) at BL and Weeks 1, 4 and 16. Eight derived factors showed significant changes with FIL treatment as compared to PBO with FDR < 0.05. Changes in circulating cell composition (Factor 1: % B cells, Factor 7: % Effector B cells, Factor 3: % T cells, Factor 2: % Monocytes) and changes in transcriptional pathways (Factor 11: Complement, Factor 4: Type I Interferon, Factor 10: Inflammation, Factor 12: SOCS2,CISH) were observed. * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001, **** p ≤ 0.0001.
Figure 1. Pharmacodynamic gene expression changes observed during 16 weeks of treatment with FIL or PBO. Exploratory Factor Analysis was performed using the union of gene signatures (FIL vs PBO) at BL and Weeks 1, 4 and 16. Eight derived factors showed significant changes with FIL treatment as compared to PBO with FDR < 0.05. Changes in circulating cell composition (Factor 1: % B cells, Factor 7: % Effector B cells, Factor 3: % T cells, Factor 2: % Monocytes) and changes in transcriptional pathways (Factor 11: Complement, Factor 4: Type I Interferon, Factor 10: Inflammation, Factor 12: SOCS2,CISH) were observed. * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001, **** p ≤ 0.0001.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gladman D, Liu Y, Yoon O, Trivedi M, Galien R, Besuyen R, Malkov V, Hertz A, Chandran V. Whole Blood Transcriptional Changes Following Treatment with Filgotinib in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/whole-blood-transcriptional-changes-following-treatment-with-filgotinib-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/whole-blood-transcriptional-changes-following-treatment-with-filgotinib-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/
