Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The satisfaction of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients with their pharmacological therapy is a relevant patient reported outcome which influences treatment adherence and continuation. However, it has not been investigated frequently, and almost never in large studies. The aim of this study was to assess factors exerting a potential influence on the satisfaction with the pharmacological treatment and to quantify the strength of their association.
Methods: The German register RABBIT is a prospective longitudinally followed cohort of RA patients enrolled with a new start of a DMARD after at least one conventional synthetic (cs)DMARD failure. This analysis comprises patients who were enrolled with start of a DMARD between 01/2009 and 10/2018, who were observed for at least 12 months and had been on the therapy prescribed at enrolment for at least six months.
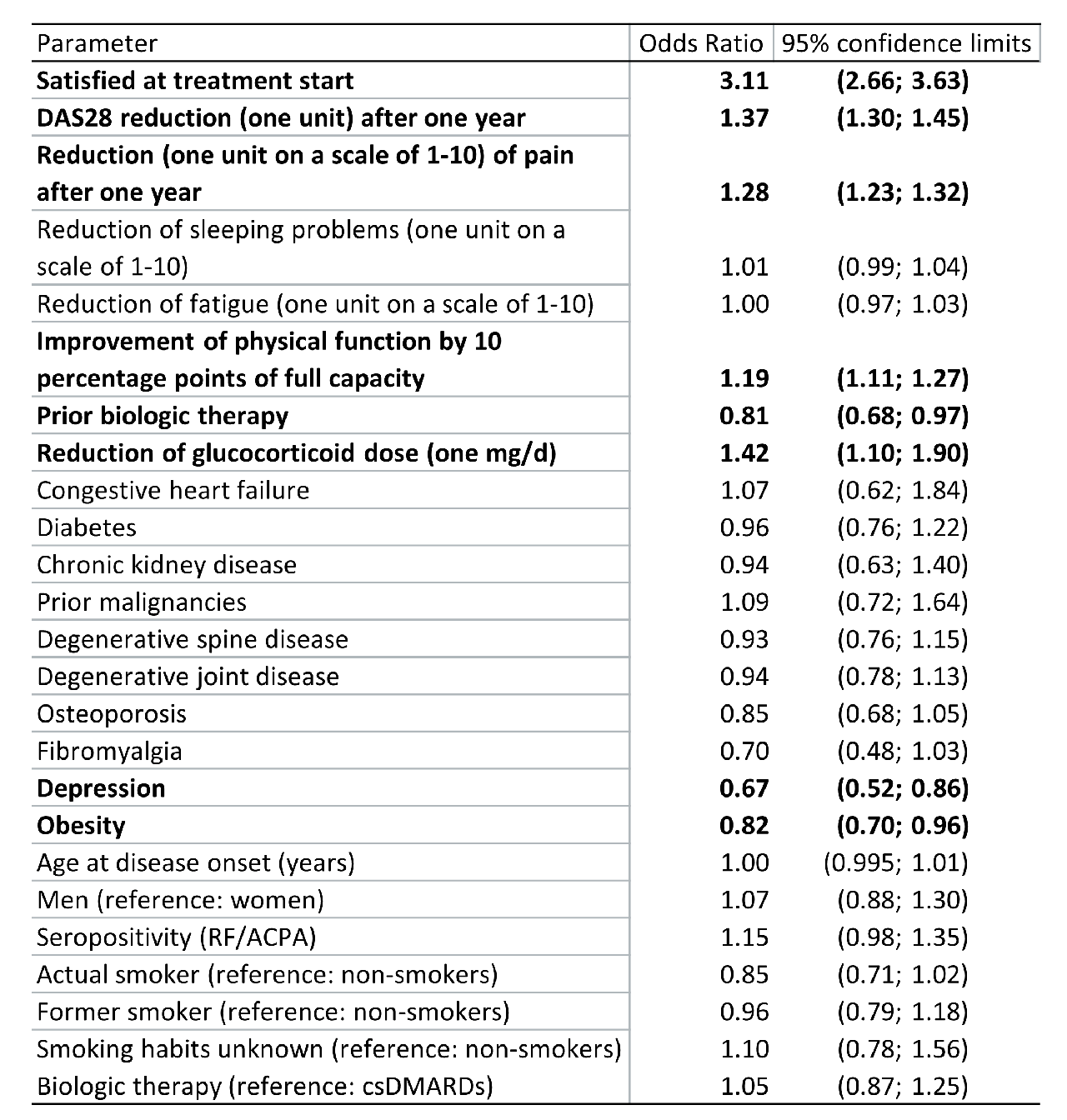
Satisfaction with the applied treatment was measured in four categories from “very satisfied” to “very unsatisfied”. Logistic regression combined with multiple imputation of missing values was performed to calculate odds ratios (ORs) for factors which might have an influence on treatment satisfaction.
Results: At treatment onset, 55% of the 8,677 patients were “very” or “rather” satisfied (in the following: “satisfied”), while the rest was “very” or “rather” unsatisfied (in the following: “unsatisfied”) with their therapy. After one year of treatment, 86% of patients were satisfied with their treatment. Satisfaction at baseline, reduction of DAS28-ESR, pain and log glucocorticoid dose as well as the increase of physical function were positively associated with the achievement of treatment satisfaction after one year. Depression, obesity as well as a prior treatment failure of biologic (b)DMARDs were negatively associated with it (see Table 1). A prevalent fibromyalgia tends to have a negative effect as well. Regarding glucocorticoid therapy, being still treated with either 5 to 15 mg/d (OR: 0.69, 95% CI: 0.55; 0.85) or ≥ 15 mg/d glucocorticoids (OR: 0.27, 95% CI: 0.16; 0.44) was negatively associated with the achievement of therapy satisfaction (data not shown).
Conclusion: Reductions in disease activity, pain and glucocorticoid dosage as well as improvement of physical function present a positive association with the achievement of treatment satisfaction, while depression, obesity, and prior treatment failures with bDMARDs present a negative one. Our results show clearly that efforts to taper glucocorticoid doses are positively associated with the improvement of patients’ satisfaction.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Schaefer M, Kekow J, Rockwitz K, Liebhaber A, Zink A, Strangfeld A. Which Factors Influence Achievement of Treatment Satisfaction in Rheumatoid Arthritis? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/which-factors-influence-achievement-of-treatment-satisfaction-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/which-factors-influence-achievement-of-treatment-satisfaction-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/