Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Synovial biopsies are increasingly performed for research purposes but also in clinical practice. The development of US guided procedure has made this procedure simpler. In addition, both small and large joints as well as tendon sheaths and bursae are accessible. In clinical practice, synovial biopsies are traditionally performed in cases of suspected septic arthritis. The goal of this work was to assess the usefulness of synovial biopsies in a large cohort of synovial biopsies performed in clinical practice.
Methods: This was a retrospective monocentric study. Biopsies were indicated when SF cultures have been unhelpful or not possible (synovitis without effusion), in case of suspicion of slow-growing bacteria or granulomatous disease. For each biopsy, we recorded the characteristics of the patients, indications and final diagnosis. Diagnosis of septic arthritis relied either on positive sample cultures or, when cultures were negative, on suggestive histological and/or clinical findings.
Results: 153 biopsies were performed between 2007 and 2018. 22 patients were finally diagnosed with septic arthritis. There were 11 females, mean age 63 years old (+/- 18). The biopsy was performed in the knee (n=9); wrist (n=3); shoulder, hip, elbow (n=2 each); ankle, sternoclavicular acromioclavicular and flexor of hand (n=1 each). Biopsy did not retrieve synovial tissue in 2 cases. Pathological analysis was characteristic of septic arthritis in 5 cases, compatible in 9 cases, not suggestive in 5 cases. Characteristics of the patients, synovial fluid and biopsy and blood test results are summarized in table 1. Overall, the bacteria were identified by culture or PCR in 16 cases. Mycobacterium sp. was identified in 2 cases with a positive synovial fluid analysis and/or lavage. Slow-growing bacteria were identified in 8 cases: Lyme disease (n=5), Whipple disease (n=2) and coxiella burnetii (n=1). In these cases, PCR was positive in the synovial tissue in 4 cases but negative in 4 cases (diagnosis based on blood serology or PCR of other tissues). Pyogenic bacteria were identified in 7 cases: diagnosis was made only on the culture of the synovial biopsy in 4 cases; on serum saline lavage of the joint in 2 cases (negative synovial tissue culture); on the blood culture in one case.
Conclusion: Synovial biopsies remain useful in case of suspicion of septic arthritis, allowing a pathological, culture and PCR analysis of the synovial tissue. However, our work shows that: 1. Serum joint lavage, blood culture should always been performed during the biopsies as they could lead to the identification of the bacteria; 2. Pathological analysis of the synovial tissue could be not suggestive of septic arthritis in case of slow growing bacteria; 3. None of these analyses are highly sensitive for the diagnosis that remains based on epidemiological, clinical, bacteriological and histological arguments.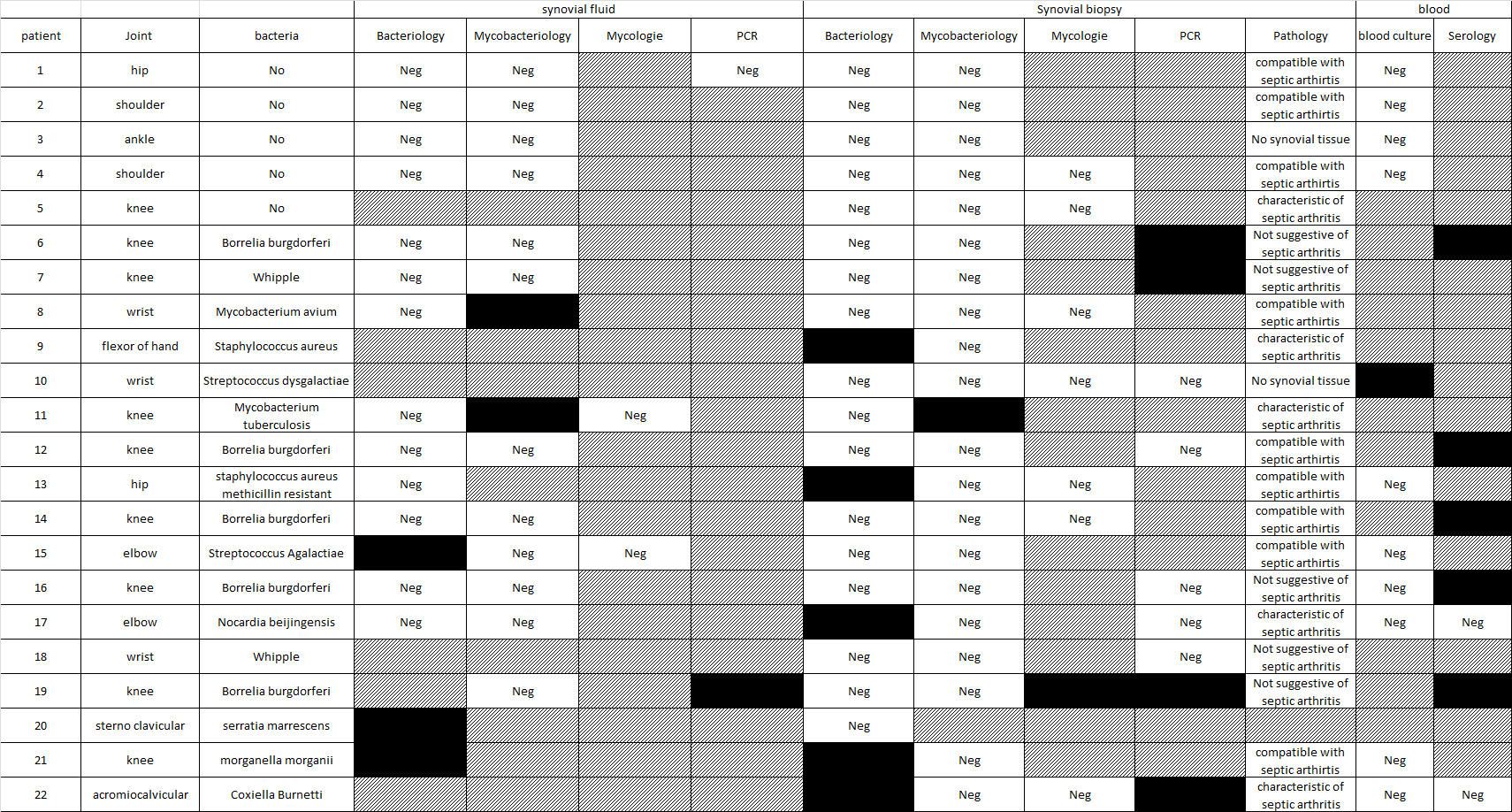
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ouvrard B, Bart G, Darrieutort C, Najm A, Le Goff B. What Is the Value of Synovial Biopsies for the Diagnosis of Septic Arthritis? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/what-is-the-value-of-synovial-biopsies-for-the-diagnosis-of-septic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/what-is-the-value-of-synovial-biopsies-for-the-diagnosis-of-septic-arthritis/
