Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Voclosporin is a novel calcineurin inhibitor recently approved for the treatment of adult patients with active lupus nephritis in combination with background immunosuppressive therapy. Voclosporin has a favorable metabolic profile and a consistent dose-concentration relationship, eliminating the need for therapeutic drug monitoring. Pooled data from the similarly designed Phase 2 AURA-LV and the Phase 3 AURORA 1 trials demonstrated that compared with standard of care agents (mycophenolate mofetil [MMF] and low-dose steroids) alone, the addition of voclosporin resulted in higher complete renal response rates (CRR) at 24 weeks (31.7% vs 20.3%; odds ratio [OR] 2.01; p=0.0008) and one year (43.7% vs 23.3%; OR 2.76; p< 0.0001) of treatment in patients with lupus nephritis. This abstract reports CRR by biopsy class in the same pooled data.
Methods: AURA-LV and AURORA 1 enrolled patients with a diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus according to ACR criteria, biopsy-proven active lupus nephritis (Class III, IV, or V ± III/IV) and proteinuria of ≥1.5 mg/mg (≥2 mg/mg for Class V). Treatment randomization was stratified by biopsy class (Class V only vs Others) and by MMF use at screening. Pooled data included 268 patients in the voclosporin (23.7 mg BID) arm (89 from AURA-LV and 179 from AURORA 1) and 266 patients in the control arm (88 from AURA-LV and 178 from AURORA 1). All patients received MMF (1 g BID) and low-dose steroids (rapidly tapered to 2.5 mg/day at week 16). Though the trials were not powered to detect a significant difference between treatments groups by biopsy class, a post-hoc analysis of CRR by biopsy class subgroups was conducted.
Results: Demographic and clinical characteristics of the pooled population are shown in Table 1. The pooled analysis includes 79 (14.8%) patients with pure Class III, 253 (47.4%) with pure Class IV, 75 (14.0%) with pure Class V, and 127 (23.8%) with mixed Class V + III/IV lupus nephritis. The OR for CRR at one year in the voclosporin arm compared to control arm was 4.26 for pure Class III, 2.59 for pure Class IV, 1.50 for pure Class V, and 2.68 for mixed Class V + III/IV (Figure 1). Overall, 93.7% of patients in the voclosporin arm and 75.2% of patients in the control arm achieved ≥50% reduction from baseline in UPCR; the median time to ≥50% reduction in UPCR was 29 days for voclosporin arm and 58 days for the control arm (HR 1.96; log rank p< 0.0001; Figure 2). At 6 months, 83.2% of patients in the voclosporin arm and 85.0% of patients in the control arm were on ≤2.5 mg/day prednisone. At 12 months, 75.8% and 73.9% of patients in each arm, respectively, were on prednisone ≤2.5 mg/day.
Conclusion: Patients with lupus nephritis treated with voclosporin in addition to MMF and low-dose steroids had improved CRR rates (OR >1) across all biopsy class subgroups compared to the control arm, with the highest OR seen in pure Class III. This analysis further supports the efficacy of voclosporin and the critical need to consider lower doses of steroids in the treatment of lupus nephritis.
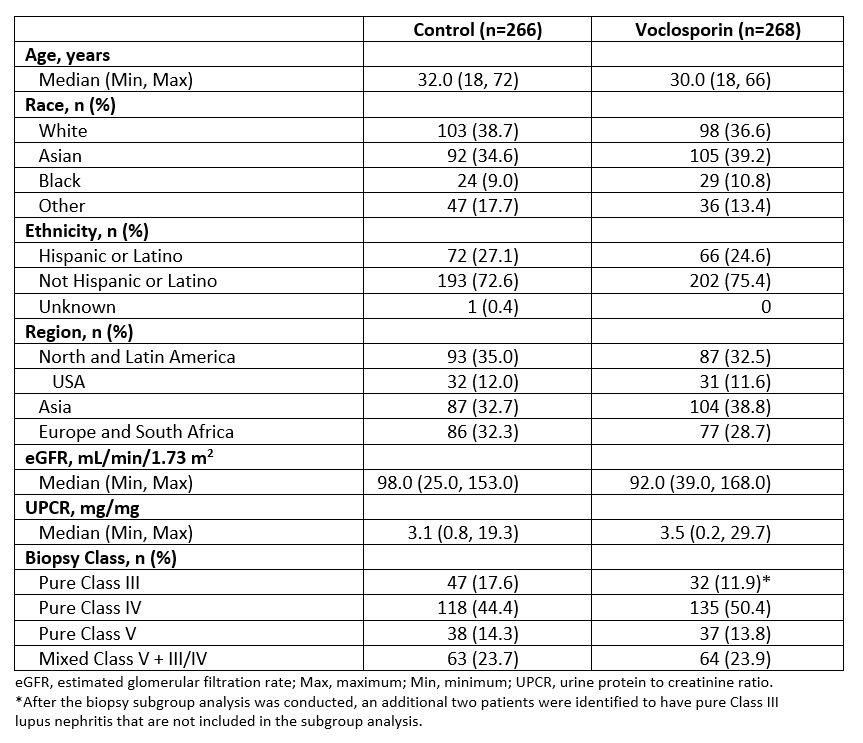 Table 1. Baseline and Demographic Characteristics
Table 1. Baseline and Demographic Characteristics
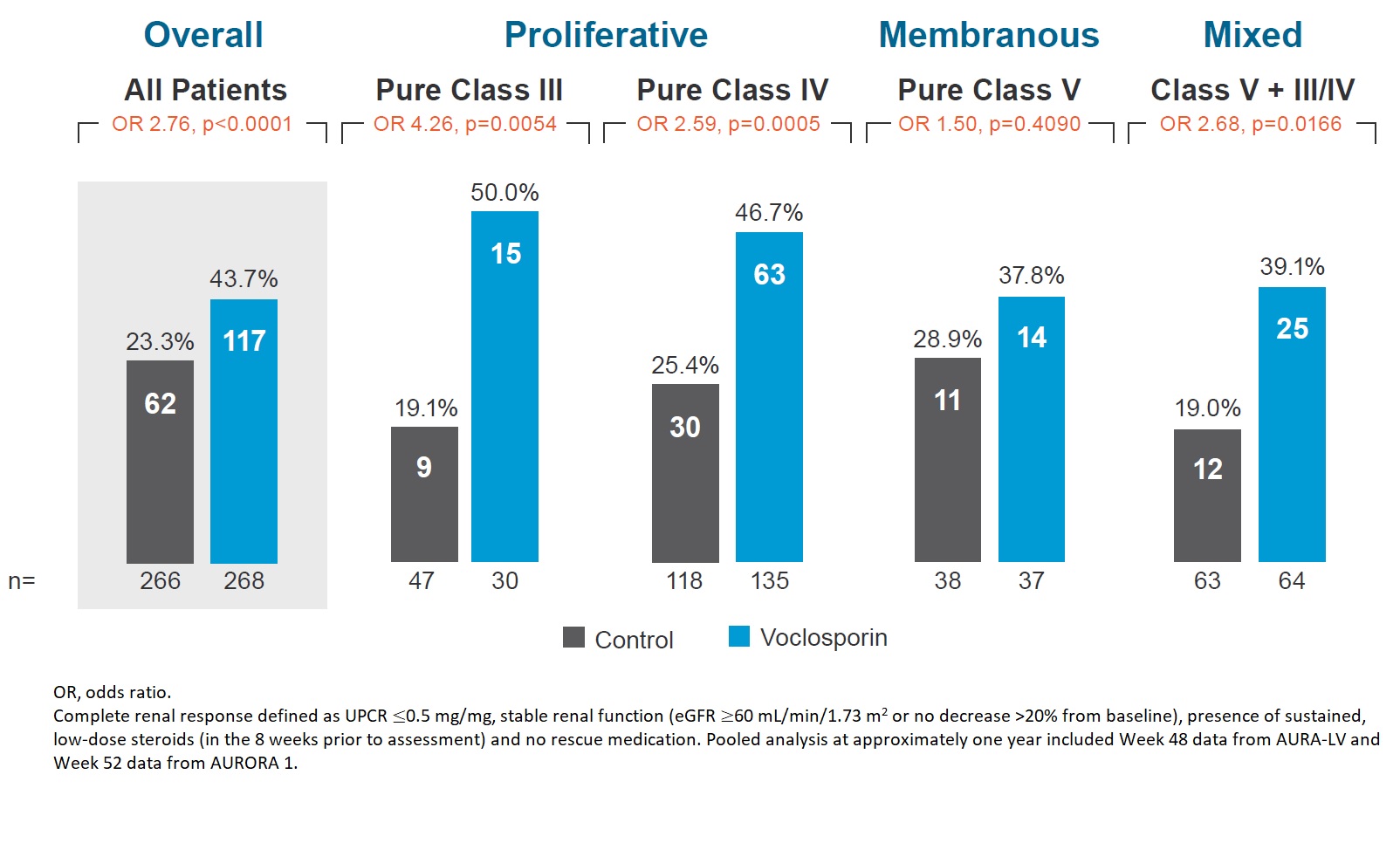 Figure 1. Complete Renal Response by Biopsy Class at One Year
Figure 1. Complete Renal Response by Biopsy Class at One Year
 Figure 2. Time to UPCR Reduction of ≥50%
Figure 2. Time to UPCR Reduction of ≥50%
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Askanase A, Randhawa S, Lisk L, Mina-Osorio P. Voclosporin Is Effective in Achieving Complete Renal Response Across Lupus Nephritis Biopsy Classes: Pooled Data from the AURA-LV and AURORA 1 Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/voclosporin-is-effective-in-achieving-complete-renal-response-across-lupus-nephritis-biopsy-classes-pooled-data-from-the-aura-lv-and-aurora-1-trials/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/voclosporin-is-effective-in-achieving-complete-renal-response-across-lupus-nephritis-biopsy-classes-pooled-data-from-the-aura-lv-and-aurora-1-trials/
