Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2022
Title: Abstracts: SLE – Treatment
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: In the Phase 3 AURORA 1 study, the addition of voclosporin to mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) and low-dose steroids led to significant reductions in proteinuria at one year in patients with lupus nephritis (LN). Here we report on the recently completed AURORA 2 continuation study evaluating voclosporin compared to control in patients treated for an additional two years after AURORA 1.
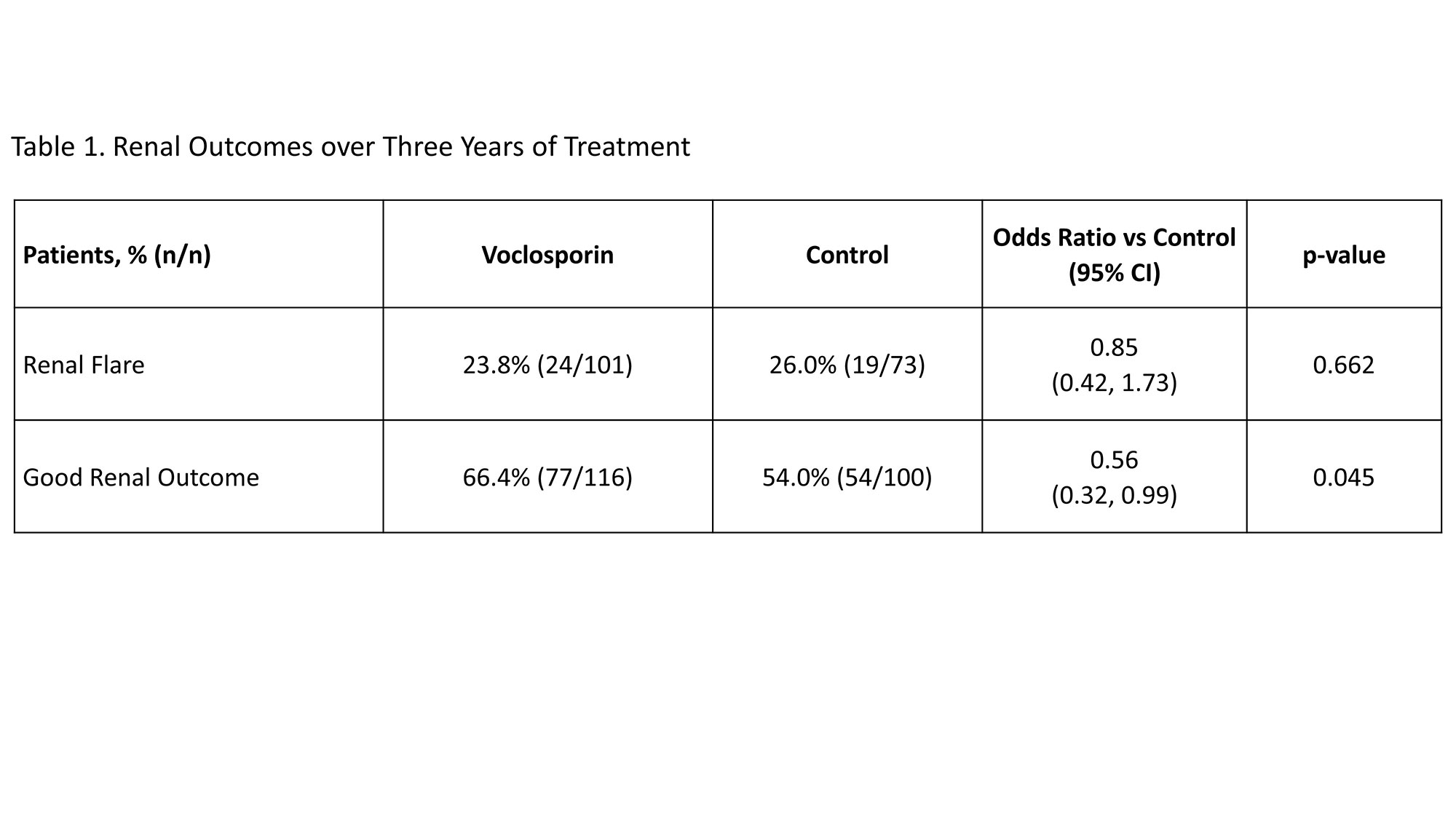
Methods: Patients with LN completing AURORA 1 were eligible to continue on the same double-blinded treatment of voclosporin or placebo in AURORA 2; all patients received MMF and low-dose steroids. Outcomes assessed over the three year treatment period of both studies included adverse events, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), urine protein creatinine ratio (UPCR), good renal outcome and renal flare. Good renal outcome was defined based on achievement of an adequate response (i.e. sustained reduction in UPCR to ≤0.7 mg/mg) and without renal flare (i.e. an increase to UPCR >1 mg/mg from a post-response UPCR of < 0.2 mg/mg or an increase to UPCR >2 mg/mg from a post-response UPCR of 0.2 to 1.0 mg/mg), as adjudicated by a blinded Clinical Endpoints Committee.
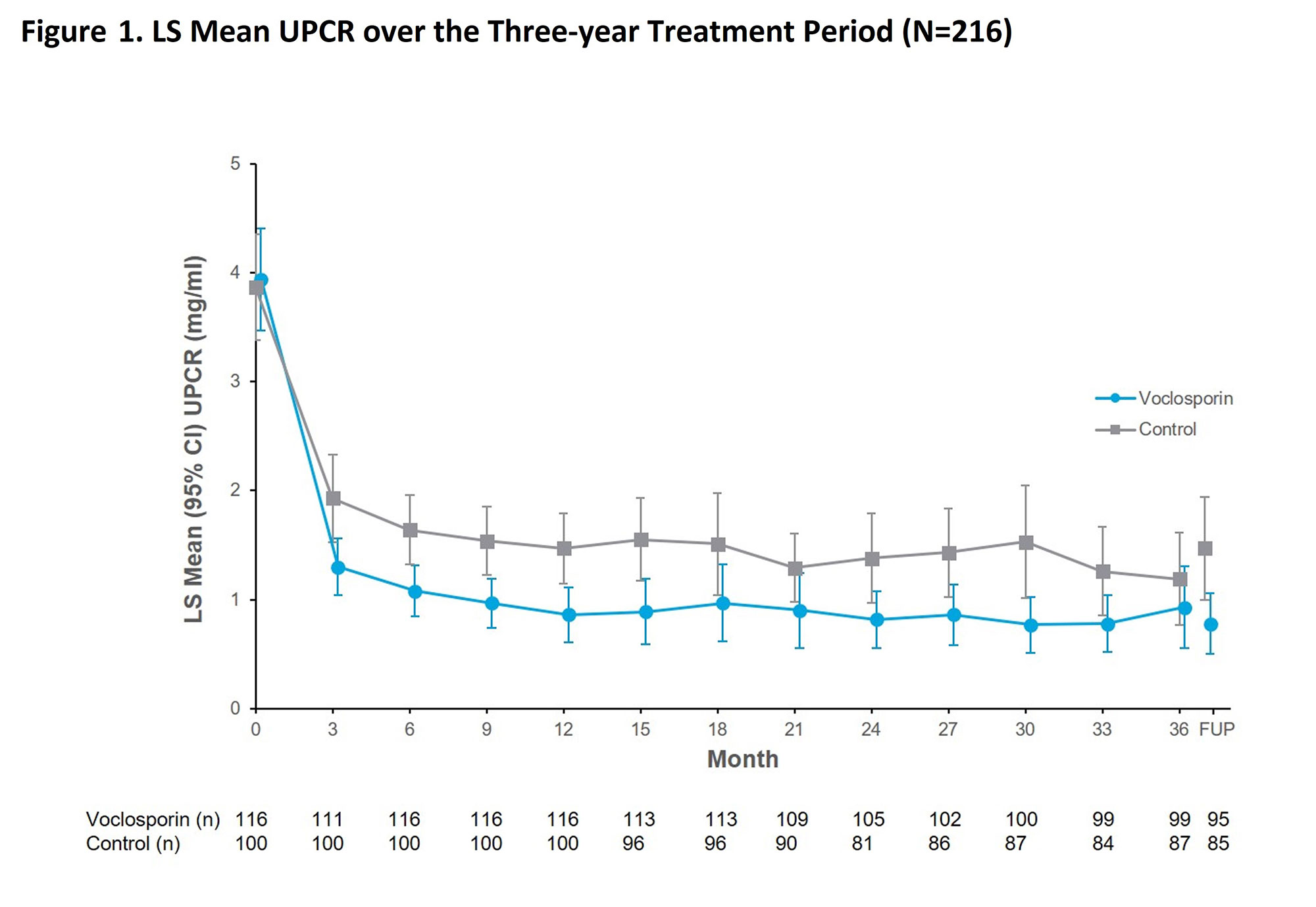
Results: Overall rates of serious adverse events in the voclosporin arm (26.7% of 116 patients) and control arm (28.0% of 100 patients) were similar. There were no deaths in the voclosporin arm during AURORA 2; four deaths occurred in the control arm (pulmonary embolism, n=1; coronavirus infection, n=3). Mean corrected eGFR was within the normal range and stable over the study period including at the follow-up visit occurring 4 weeks after study drug discontinuation. The reductions in UPCR achieved in AURORA 1 were maintained in AURORA 2 (Figure 1) and significantly more patients in the voclosporin arm achieved a good renal outcome (66.4% in voclosporin vs 54.0% in control; p-value=0.045, Table 1). Renal flare occurred in 24 of 101 patients with adequate response in the voclosporin arm and 19 of 73 patients in the control arm (23.8% in voclosporin vs 26.0% in control; p-value=0.662); 69.8% of all patients with renal flares completed study treatment.
Conclusion: Voclosporin was well-tolerated over three years of treatment. The significant reductions in proteinuria initially achieved in AURORA 1 were maintained throughout AURORA 2, and more patients in the voclosporin arm achieved a good renal outcome. These data provide evidence of a long-term treatment benefit of voclosporin in patients with LN.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Arriens C, Parikh S, Hodge L, Mela C, Leher H. Voclosporin for Lupus Nephritis: Assessment of Long-Term Safety and Efficacy Including Renal Outcome over Three Years of Treatment in the Phase 3 AURORA 1 and AURORA 2 Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/voclosporin-for-lupus-nephritis-assessment-of-long-term-safety-and-efficacy-including-renal-outcome-over-three-years-of-treatment-in-the-phase-3-aurora-1-and-aurora-2-studies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/voclosporin-for-lupus-nephritis-assessment-of-long-term-safety-and-efficacy-including-renal-outcome-over-three-years-of-treatment-in-the-phase-3-aurora-1-and-aurora-2-studies/