Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0229–0251) Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Gout, which is a prevalent form of inflammatory arthritis, is generally considered to be more effectively managed through medication. Besides of maintaining medication, they were required to modify their life style habits including eating habits. Because some gout patients failed to control their disease due to improper lifestyle. Improper lifestyle can affect the gout patient’s quality of life.
The Gout Impact Scale (GIS), a part of the Gout Assessment Questionnaire 2.0, is an instrument measuring the gout-specific health-related quality of life (HRQOL). Recently, GIS was translated in to Korean, K-GIS was validated. There have been recommendations for lifestyle changes as well as medication to control gout. So far, there were no research revealing the correlation life style habits and GIS. Therefore, we aimed to evaluate the relationship of GIS and gout patient’s life style habit in this study.
Methods: Patients with gout aged ≥18 years who fulfil the 2015 classification criteria for gout with necessity of ULT are enrolled. The case report form (CRF) lists demographic and clinical data, comorbidities, lifestyle habits, medications, quality of life (on the gout impact scale), the score on Gout Impact Scale (GIS), laboratory results, and radiological findings.
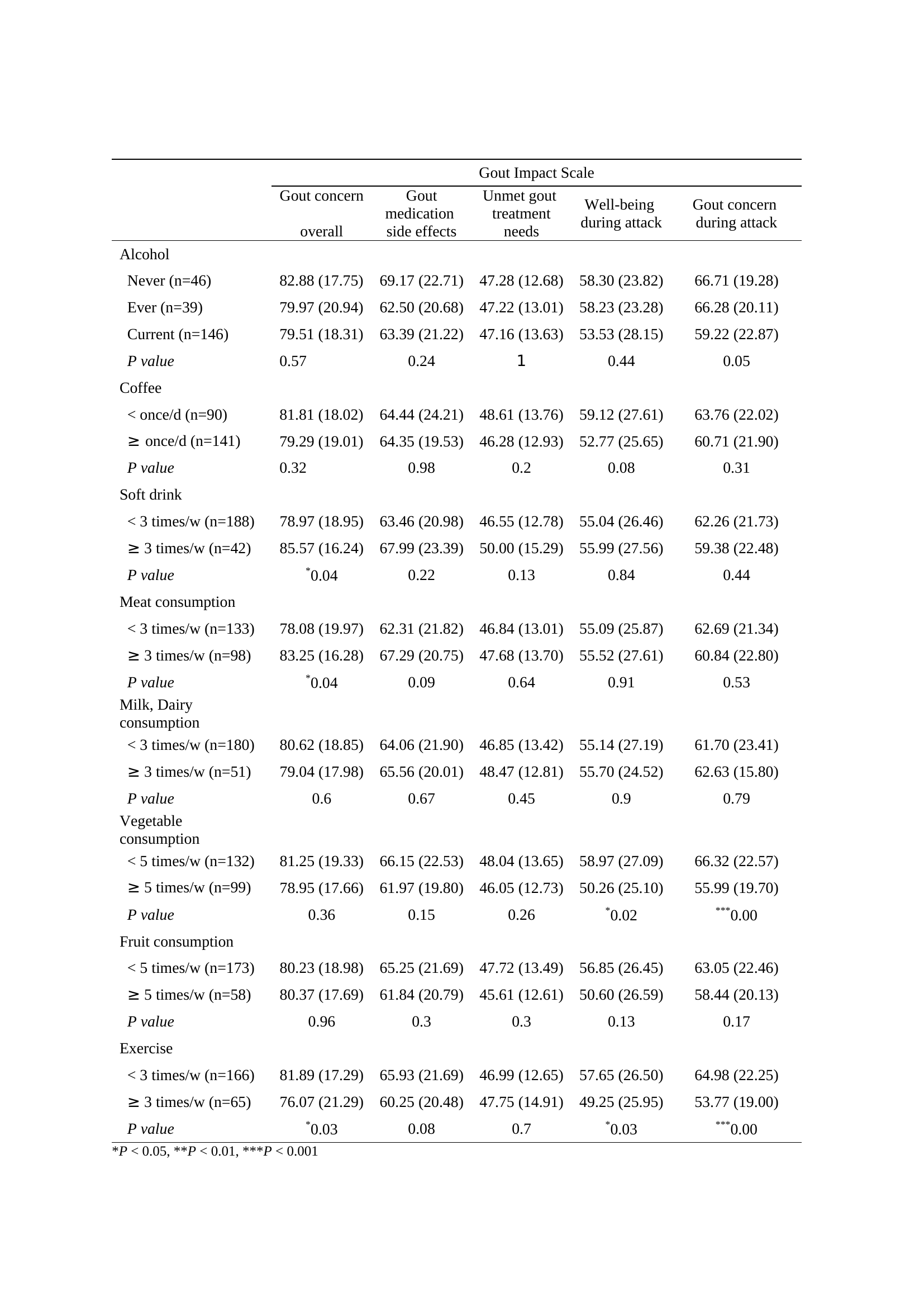
Results: The study included 232 patients, and the baseline characteristics of the patients were described in the Table 1. The mean scores for each GIS subscale (mean ± SD ) were as follows: 80.27 ± 18.63 for gout concern overall; 64.39 ± 21.47 for gout medication side effects; 47.20 ± 13.28 for unmet gout treatment needs; 55.27 ± 26.56 for well-being during attack; 61.63 ± 22.28 for gout concern during attack.
There was a statistically significant difference of gout concern overall subscale in the number of times of soft drink, meat consumption. Also, the number of times of exercise showed difference significantly. The number of times of milk, dairy consumption, vegetables, fruits, alcohol and coffee consumption showed no significant difference. In well-being during gout attack subscale in GIS, number of vegetables consumption and exercise did show difference. Regarding well-being during gout attack, soft drink, meat, milk, dairy, fruits, alcohol and coffee consumption did not show significant results between groups according to the number of times.
In gout concern during attack subscale in GIS, the score was significantly different in vegetable consumption and exercise. (Table 2).
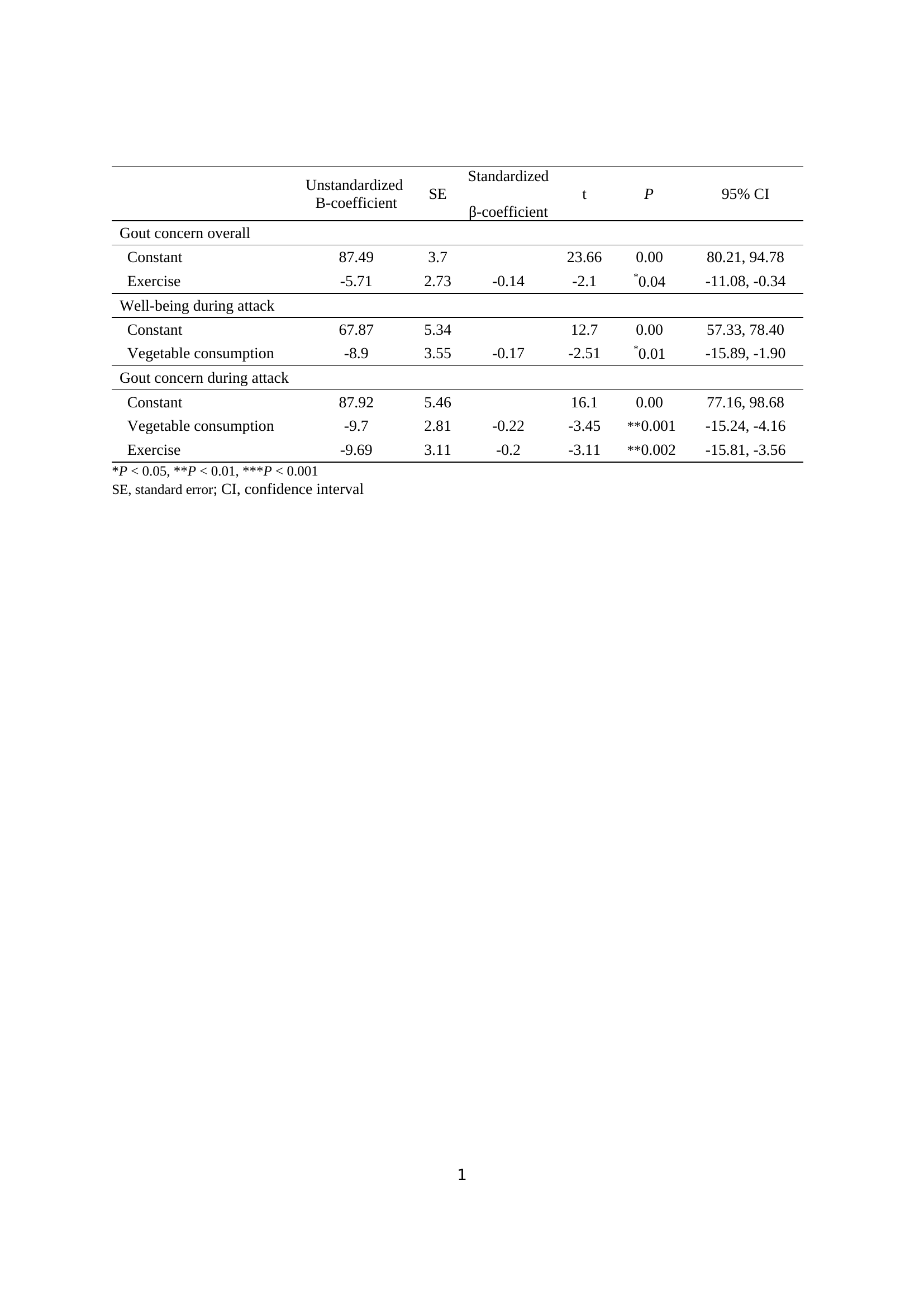
In gout concern overall subscale in GIS, the number of times of regular exercise showed a negative linear correlation (B= -5.71, P= 0.04). In well-being during attack subscale in GIS, the number of times of vegetable consumption showed a negative linear correlation (B= -8.90, P=0.01). In gout concern during attack subscale in GIS, the number of times of vegetable consumption and regular exercise showed a negative linear correlation (B= -9.70, -9.69, respectively) (P < 0.01) (Table 3).
Conclusion: It has been confirmed that the GIS score is related to specific life style, vegetable consumption, exercise regularly. Based on these results, gout patients can be encouraged to have specific life style habits.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
DO H, Moon K. Vegetable Consumption and Regular Exercise Are Associated with Better Quality of Life in Gout [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/vegetable-consumption-and-regular-exercise-are-associated-with-better-quality-of-life-in-gout/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/vegetable-consumption-and-regular-exercise-are-associated-with-better-quality-of-life-in-gout/