Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Interleukin-6 (IL-6) cytokine signaling is key
in Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) pathophysiology. Blocking IL-6 receptor
(IL6R) has proven to be a highly effective treatment to prevent joint damage.
This study was performed to investigate the association between the genetic
variation atIL6R gene and the severity of joint damage in RA.
Methods: IL6R gene
tagging SNPs (n=5, Figure 1) were genotyped in a discovery group of 527 RA
patients from 5 different university hospitals from Spain. For each marker, a multivariate
linear regression analysis was performed to test for association with joint
damage and also to adjust several covariates including years disease evolution,
autoantibody status and gender. Haplotypes combining the SNPs were also
estimated and tested for association with the level of joint destruction. Using
an independent cohort of 705 RA patients from 6 university hospitals we
performed a validation study of the SNPs associated in the discovery phase.
Results: In the discovery group we found a highly significant
association between IL6R SNP rs4845618 and the level of joint
destruction in RA (P=0.0058, Table 1), and a moderate association with
SNP rs4453032 (P=0.02, Table 1). The resulting haplotype from both SNPs
was more significantly associated with joint damage (P=0.0037). Using
the validation cohort, we replicated the association between the two IL-6R SNPs
with the degree of joint destruction in RA (P=0.007 and P=0.04,
meta-analysis P=0.00011 and P=0.0021, respectively,
Table 1), and the haplotype association ( P=0.0058,
meta-analysis P=6.64 e-5).
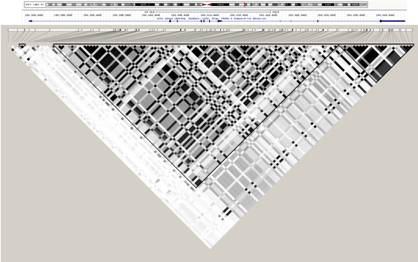
Figure 1. LD pattern at IL6R locus. The two main haplotype blocks covering most common genetic variation
at IL6R gene (in blue) are indicated by solid line triangles.
Table 1. Association of IL6R markers
with the severity of joint damage in RA. Significance
values for IL6R SNPs in the discovery, replication cohorts as well
meta-analysis of the two cohorts.
|
SNP |
Basepair |
MAF |
P-Discovery |
P-Replication |
Meta-analysis P |
|
rs4845618 |
154400015 |
0.44 |
0.0052 |
0.007 |
0.00011 |
|
rs4453032 |
154414086 |
0.4 |
0.51 |
– |
– |
|
rs4845374 |
154426947 |
0.17 |
0.02 |
0.04 |
0.0021 |
|
rs6698040 |
154432948 |
0.21 |
0.11 |
– |
– |
|
rs4379670 |
154439865 |
0.16 |
0.25 |
– |
– |
Conclusion: We show for the first time that genetic variation
at IL6R gene is associated to joint damage in RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
López-Lasanta M, Julià A, Maymo J, Fernandez Gutierrez B, Ureña I, Blanco FJ, Cañete JD, Alperi-López M, Olivé A, Corominas H, Tornero J, Erra A, Almirall M, Palau N, Ortiz Garcia AM, Avila G, Rodriguez-Rodriguez L, Alonso A, Tortosa R, González-Alvaro I, Marsal S. Variation at Interleukin-6 Receptor Gene Is Associated to Joint Damage in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/variation-at-interleukin-6-receptor-gene-is-associated-to-joint-damage-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/variation-at-interleukin-6-receptor-gene-is-associated-to-joint-damage-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/