Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Cognitive impairment (CI) is highly prevalent in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). Screening for CI in SLE may be delayed, if relying on the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) neuropsychological battery (NB), which is time- and resource- intensive. The Automated Neuropsychological Assessment Metrics (ANAM) is a quick and low-cost computer-based screening tool for CI. The overarching aim of this study was to assess the performance of the ANAM as a screening tool for CI in SLE patients employing the ACR NB as the gold standard. The specific objective were to: (a) determine the ability of the ANAM to differentiate between SLE patients with and without CI, (b) assess the ability of selected ANAM subtests to accurately identify CI, and (c) derive an ANAM composite index and cut-off to facilitate its use.
Methods: : Between 2016 and 2019, 211 consecutive adult SLE patients were administered the ACR NB and the ANAM on the same day. Using age- and gender-stratified normative data, patients were classified on the ACR NB as having CI if a z-score of ≤-1.5 was observed in ≥ 2 domains; or non-CI if no domain had a z-score of ≤-1.5. First, discriminative validity of the ANAM was assessed by its ability to differentiate between CI and non-CI patients compared to the ACR NB. All 15 ANAM subtests and their scores (percentage of correct responses [PCT], mean reaction time [MR], throughput [TP], and coefficient of variation [CV]) were studied. Second, we developed 6 ANAM models and the most discriminatory subtests and scores within each model were selected using logistic regression analyses. The area under the receiver operating characteristics curve (AUC) was calculated to establish ANAM models construct validity against the ACR NB. Third, an ANAM composite index and cut-off were derived for the best selected model using the sum of the subtests’ scores multiplied by their parameter estimate from the logistic regression. The sensitivity (Se), specificity (Sp), positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (PPV) of the ANAM composite index and cut-off, to differentiate CI from non-CI were evaluated.
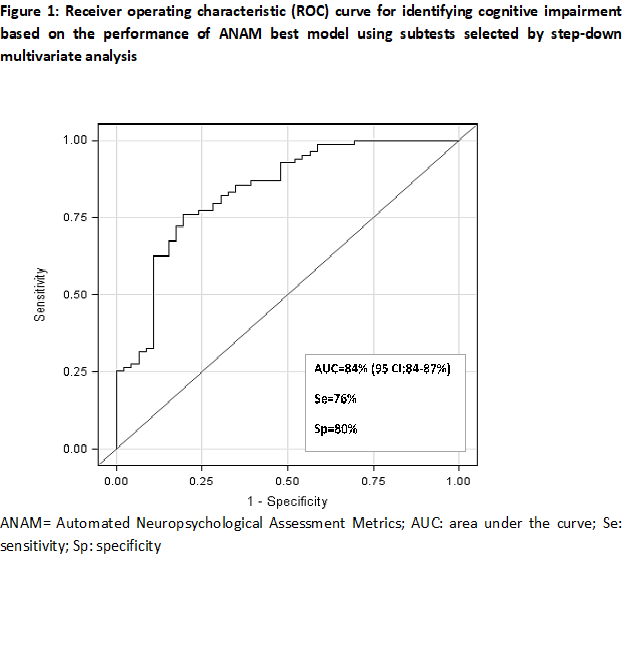
Results: Patients with non-CI performed better on the majority of ANAM subtests in PCT, MR and TP scores compared to those with CI, providing support for ANAM discriminative validity. CI was accurately identified by the best ANAM model (Table 1) with an excellent AUC of 84% [95% confidence interval: 0.84, 0.87] (Figure 1), providing support for the construct validity of the ANAM model using 8 selected ANAM subtests and corresponding scores. The derived composite index (equation provided in Table 1) demonstrated good performance with AUC of 79%. The proposed cut-off yielded Se, Sp, PPV and NPV of 80%, 70%, 83% and 65%, respectively. Figure 2 demonstrates the performance of the composite index over different cut-off values.
Conclusion: This study provides support for the validity of the ANAM along with 8 selected subtests for the screening of CI in adult SLE in the selected model. We derived an ANAM composite index and a cut-off to serve as a summary measure of cognitive performance of SLE patients. This will enhance the applicability and interpretation of the ANAM in clinical practice.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tayer-Shifman O, Green R, Beaton D, Ruttan L, Wither J, Tartaglia M, Kakvan M, Lombardi S, Anderson N, Su J, Bonilla D, Zandy M, Choi M, Fritzler M, Touma Z. Validity Evidence Supports the Use of Automated Neuropsychological Assessment Metrics (ANAM) as a Screening Tool for Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/validity-evidence-supports-the-use-of-automated-neuropsychological-assessment-metrics-anam-as-a-screening-tool-for-cognitive-impairment-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/validity-evidence-supports-the-use-of-automated-neuropsychological-assessment-metrics-anam-as-a-screening-tool-for-cognitive-impairment-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/