Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: A multidisciplinary proposal of screening criteria for interstitial lung disease (ILD) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) was published in 2023 [Narváez J et al. Reumatol Clin (Engl Ed). 2023;19(2):74-81]. This document is just an expert consensus, and its utility has not been contrasted in validation studies yet. The objective of this study is to analyze sensitivity and specificity of the screening criteria in a cohort of early RA patients.
Methods: This is a cross-sectional study in a cohort of early RA patients (1987 ARA or 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria for RA and a time from symptoms onset ≤ 12 months) diagnosed between 2003 and 2023. The ILD screening criteria have been retrospectively revised upon RA diagnosis. An ILD screening through medical history, auscultation, chest X-ray (CXR), and pulmonary function tests (PFT) with spirometry and DLCO was done in all patients on diagnosis. A high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) was carried out if respiratory symptoms, Velcro crackles, or alterations in CXR/PFT were noticed.
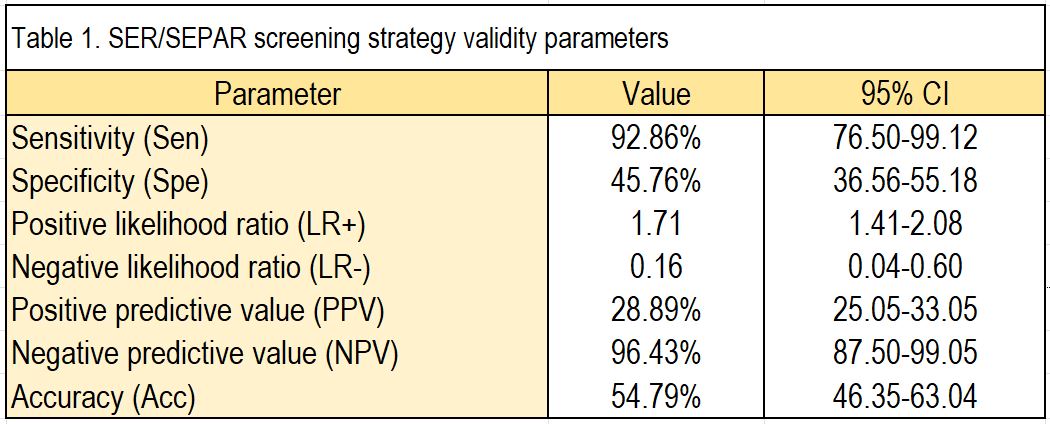
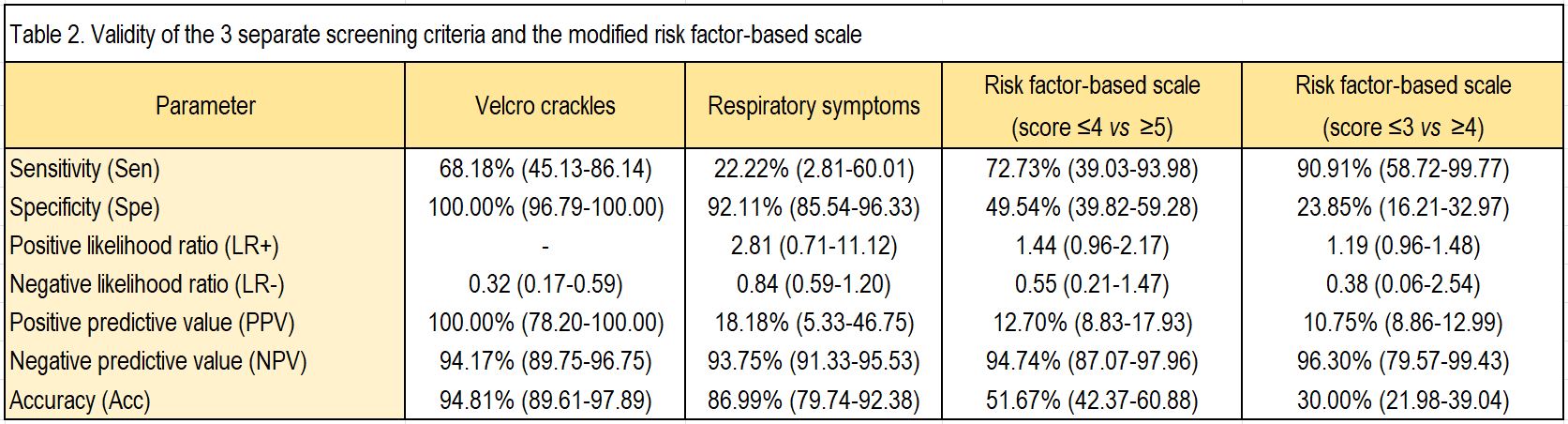
Results: Of the 146 included patients, 28 (19.1%) were diagnosed with ILD by thoracic HRCT. Ninety patients (61.6%) satisfied the screening criteria upon RA diagnosis, which includes presence of Velcro crackles, cough or dyspnea for more than 3 months, or a score ≥5 on the risk factor-based scale. Twenty-eight-point-eight percent (26/90) of these patients had clinical or subclinical ILD. Of the 56 (38.4%) patients that did not satisfy the screening criteria at the time of RA debut, only 1.3% (2/56) had ILD. The sensitivity of the criteria in our cohort was 92.86% (95% CI 76.50-99.12), while the specificity was 45.76% (95% CI 36.56-55.18) [see Table 1]. ILD preceded the onset of joint symptoms in 12 patients (extraarticular-onset rheumatoid disease). Excluding these cases, where the screening would have not been necessary, the sensitivity would be 87.50% (95% CI 61.65-98.45), while the specificity would remain at 45.76%. The validity parameters for each criterion separately are detailed in Table 2. The presence of respiratory symptoms, as defined in the study, had a sensitivity of 22.22% and a specificity of 92.11%. The sensitivity and the specificity of Velcro crackles were 68.18% and 100%, respectively. Lastly, a score ≥5 on the risk factor-based scale had a sensitivity of 72.73% and a specificity of 49.54%. If the threshold is reduced to a score ≥4, the sensitivity increases to 90.91%, but at the expense of a specificity decrease to 23.85%.
Conclusion: According to these preliminary results, the SER/SEPAR criteria for ILD screening have a sensitivity >90% in patients with early RA, which supports their use in daily clinical practice. Considering that a screening strategy aims to enable an early diagnosis of this complication, it is important to apply a high sensitivity test in the first place to detect the greatest number of cases possible.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Aguilar Coll M, Narvaez-García J, Roig Kim M, Maymó P, Palacios J, Nolla J. Validation Study in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients of the Spanish Society of Rheumatology (SER)/Spanish Society of Pulmonology and Thoracic Surgery (SEPAR) Screening Criteria for Interstitial Lung Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/validation-study-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-of-the-spanish-society-of-rheumatology-ser-spanish-society-of-pulmonology-and-thoracic-surgery-separ-screening-criteria-for-interstitial-lun/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/validation-study-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-of-the-spanish-society-of-rheumatology-ser-spanish-society-of-pulmonology-and-thoracic-surgery-separ-screening-criteria-for-interstitial-lun/