Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Abstracts: SpA Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes I
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-2:30PM
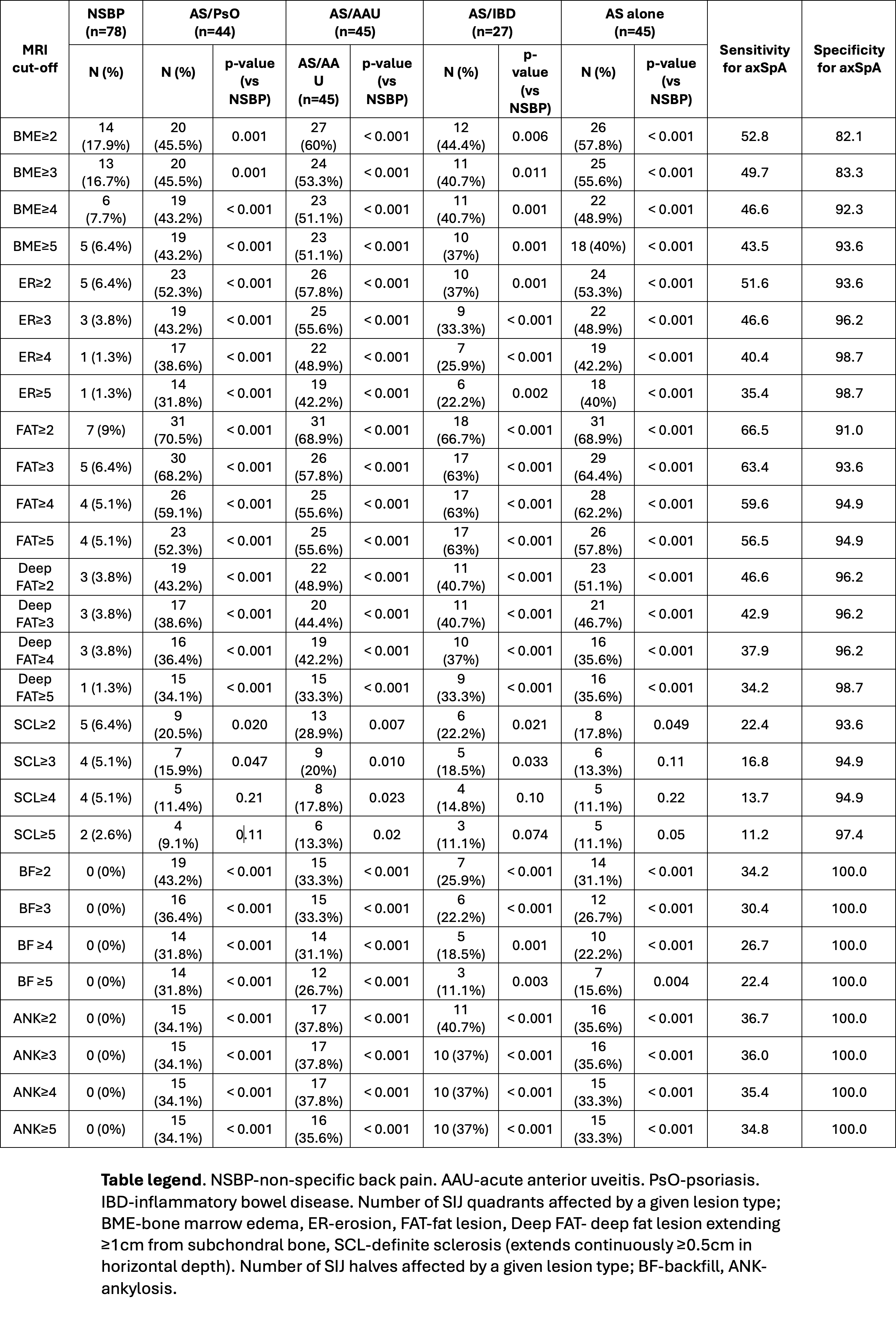
Background/Purpose: Recent analysis of MRI scans from the 2009 ASAS classification cohort has led to a new proposal for the application of more stringent MRI inflammatory and structural lesion cut-offs for defining a positive MRI aimed at higher specificity. The cut-offs are based on numbers of sacroiliac joint quadrants with the affected lesion, being ≥3 for erosion (ER), ≥4 for bone marrow edema (BME), ≥5 for fat lesion (FAT), and ≥2 for deep fat lesion extending ≥1cm from subchondral bone1. We aimed to validate the performance of these cut-offs in patients with axSpA according to different clinical phenotypes encompassing patients with concomitant psoriasis (PsO), acute anterior uveitis (AAU), and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Our comparator was age- and gender-matched mechanical back pain controls diagnosed with non-axSpA.
Methods: Patients diagnosed with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) and fulfilling the modified New York criteria (mNY) were included from a prospective, observational cohort (ALBERTA FORCAST). All axSpA cases with AAU, PsO, or IBD, diagnosed by an ophthalmologist, dermatologist, or gastroenterologist, or axSpA alone with no extra-articular features, and with available MRI SIJ scans (semicoronal T1W, STIR), were matched for age and gender with scans from non-axSpA controls. MRI active and structural lesions per ASAS definitions2 were evaluated by 3 readers blinded to clinical details and recorded in the ASAS MRImagine-consensus based eCRF that comprised global assessment (MRI indicative of axSpA, active or structural lesion typical of axSpA present/absent) and detailed scoring of lesions per SIJ quadrant or halves (SPARCC method). We also assessed the utility of definite sclerosis (SCL), defined as dark signal on MRI that extends continuously ≥0.5cm in horizontal depth. Cut-offs for backfill (BF), and ankylosis (ANK) were assessed according to number of SIJ halves. Sensitivity and specificity of MRI cut-offs from ≥2 to ≥5 SIJ quadrants (for BME, ER, FAT, SCL) or halves (BF, ANK) with diagnosis of axSpA as gold standard, were analyzed.
Results: Scans were available from 44, 45, 27, 45, axSpA patients with PsO, AAU, IBD, or axSpA alone and 78 matched non-axSpA controls. For BME, a substantial increase in specificity was evident with a cut-off ≥4 at 92.3% with limited impact on sensitivity for diagnosis of axSpA among all subgroups when compared to a cut-off ≥3 (Table). For ER, specificity was 96.2% at a cut-off ≥3 with limited impact on sensitivity when compared to a cut-off ≥2. For FAT, specificity was 94.9% at a cut-off ≥5 with limited impact on sensitivity when compared to a cut-off ≥4, while a deep fat lesion already had high specificity of 96.2% even at a cut-off ≥2. BF and ANK had 100% specificity at cut-offs of ≥2 while SCL had high specificity, but sensitivity was low even at the cut-off ≥2.
Conclusion: The data-driven MRI lesion cut-offs demonstrated high performance characteristics, supporting the validity of the preliminary ASAS Data-Driven MRI lesion cut-offs.
< ![if !supportLists] >1. < ![endif] >Maksymowych et al. Rheumatol 2021;60:4778–4789
< ![if !supportLists] >2. < ![endif] >Maksymowych et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2019;78:1550-1558
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pedersen S, Weber U, Bayindir Tsechelidis O, Lambert R, Paschke J, Wichuk S, Maksymowych W. Validation of ASAS Preliminary Data-Driven MRI Lesion Cut-offs for a Positive MRI of the Sacroiliac Joints in Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis and Subgroups with Psoriasis, Iritis, and Colitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/validation-of-asas-preliminary-data-driven-mri-lesion-cut-offs-for-a-positive-mri-of-the-sacroiliac-joints-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-and-subgroups-with-psoriasis-iritis-and-colitis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/validation-of-asas-preliminary-data-driven-mri-lesion-cut-offs-for-a-positive-mri-of-the-sacroiliac-joints-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-and-subgroups-with-psoriasis-iritis-and-colitis/