Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 7, 2020
Title: Epidemiology & Public Health Poster II: OA, Osteoporosis, & Other Rheumatic Disease
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Infliximab Biosimilar, the first biosimilar to infliximab, was approved for multiple indications in the U.S. in 2016. Since the utilization of biosimilar in the U.S. has not been studied, it is unclear if patients on Infliximab Biosimilar are adherent to their treatment. Therefore, we evaluated the characteristics of Infliximab Biosimilar initiators and their adherence using national commercial administrative data.
Methods: We identified Infliximab Biosimilar initiators based on procedure and pharmacy codes in 2016-2017 IBM Marketscan data. Using all available data, we classified Infliximab Biosimilar initiators as naïve Infliximab Biosimilar users (never used infliximab), infliximab early switchers with < 2yr of infliximab use, and late switchers with long-term ( >2yr) use of infliximab. Eligible patients were ≥18 years of age and continuously enrolled with medical and pharmacy coverage in 2014-2017. The date of the first prescription for infliximab biosimilar was considered as “Index date”. Baseline was defined as 365 days prior to the index date. Follow up period started from the index date and ended at the earliest date of death, loss of coverage, and 12/31/2018.We evaluated baseline characteristics in all patients and calculated the proportion of days covered (PDC) at the 12 months of follow up among patients who had >=12m of coverage during follow-up. The PDC adherence level was further categorized as < 50%, 50 to 80%, and > 80%.
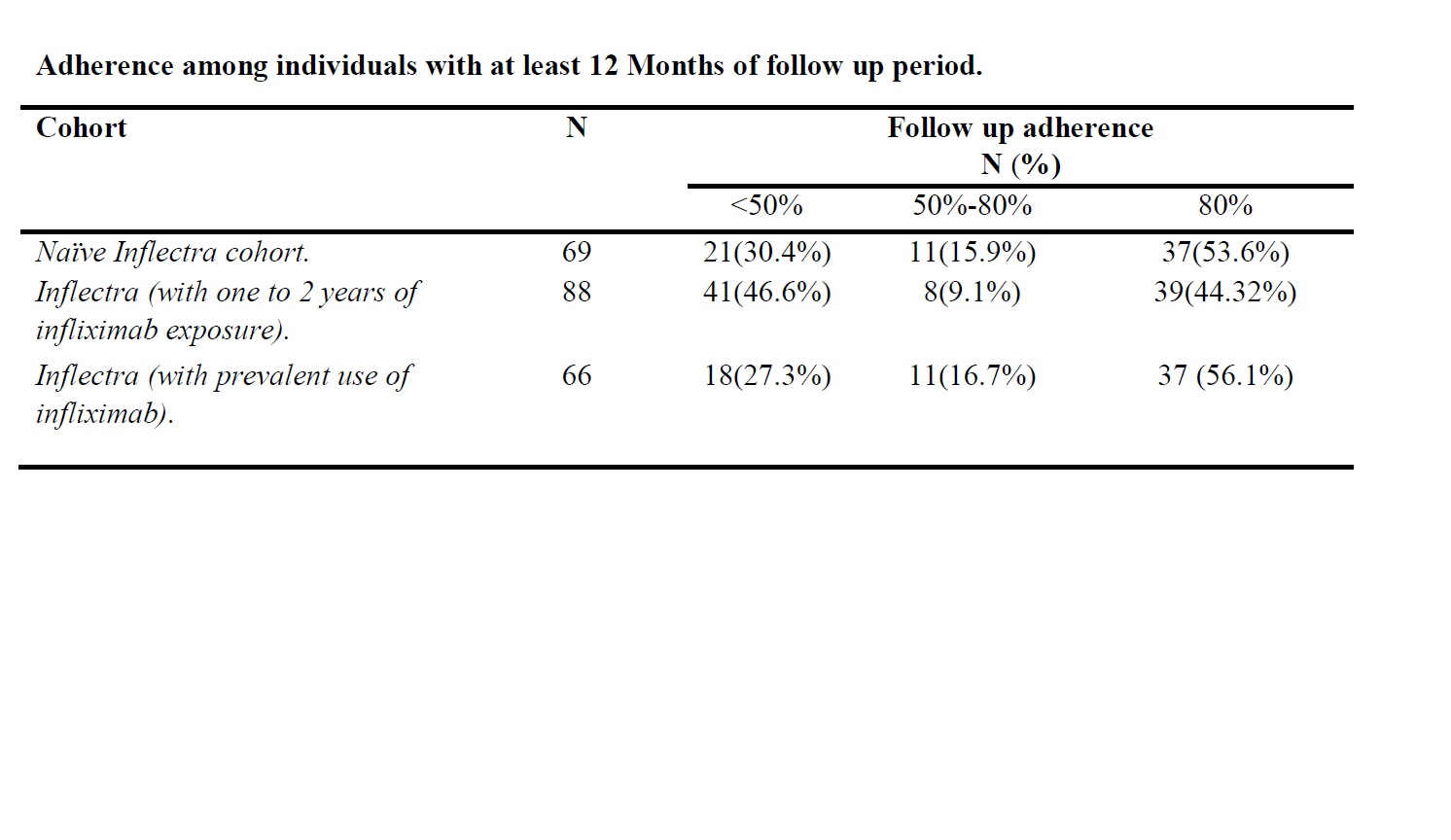
Results: We identified 98 Naïve Infliximab Biosimilar users, 114 early switchers, and 113 late switchers. Compared to (early or late) switchers, naive users were younger and more likely to be female. The highest proportion of autoimmune disease was inflammatory bowel disease (40.9-45.4%), followed by rheumatoid arthritis (15.4-29.6%) and psoriasis (9.7-13.9%). Among patients who had >=12m of follow-up, 53.6% naive users, 44.3% early switchers, and 56.1% late switchers continued to be adherent ( >80%) at 12 months (Table).
Conclusion: Approximately half of the Infliximab Biosimilar initiators were highly adherent at 12 months. Further studies are needed to evaluate the long-term adherence among Infliximab Biosimilar users.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sarvesh S, Alanaeme J, Curtis J, Yun H. Utilization and Adherence Among Infliximab Biosimilar Initiators in a U.S. National Commercial Insurance Database [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/utilization-and-adherence-among-infliximab-biosimilar-initiators-in-a-u-s-national-commercial-insurance-database/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/utilization-and-adherence-among-infliximab-biosimilar-initiators-in-a-u-s-national-commercial-insurance-database/