Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: Pediatric Rheumatology – Clinical Poster II: Systemic JIA, Autoinflammatory, & Scleroderma
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Mental health problems are common and often untreated in youth with rheumatologic disease, yet their relationship with disease features is poorly understood. We engaged patients and parents on the research team to identify cross-cutting disease factors impacting mental health in this population.
Methods: An anonymous cross-sectional online survey examined mental health experiences of patients with juvenile arthritis, juvenile dermatomyositis, or systemic lupus erythematous. Youth ages 14-24 years and parents of youth 8-24 years were eligible. The survey was developed with patient and parent advisors, the Childhood Arthritis & Rheumatology Research Alliance (CARRA), and the Patients, Advocates, and Rheumatology Teams Network for Research and Service (PARTNERS). Participants were recruited through the Arthritis Foundation, Lupus Foundation of America, and Cure JM Foundation. Primary outcome was the presence of any clinician or self-diagnosed mental health problem. Exposures of interest included several cross-cutting disease factors: disease duration, active disease status, current steroid medication, history of disease flare following remission, and appearance-altering comorbidities (psoriasis, stretch marks, alopecia, skin ulceration, visible scarring). We used logistic regression models to examine the association between any clinician or self-diagnosed mental health problems and disease factors for the combined youth/parent sample, and for youth and parents separately. Secondarily, we examined results by mental health problem (depression, anxiety, self-harm/suicidal ideation). Alpha values < .05 were considered significant.
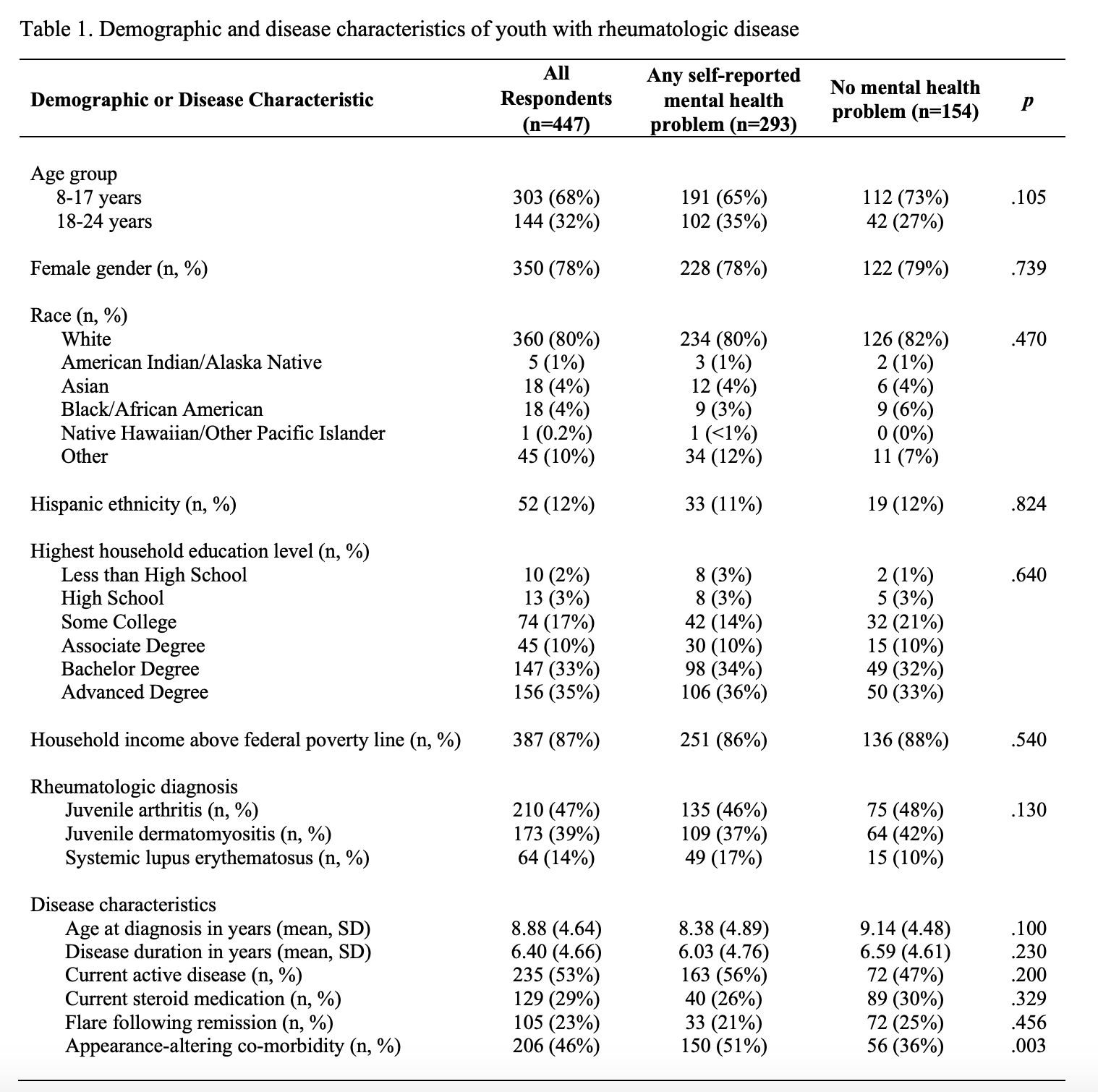
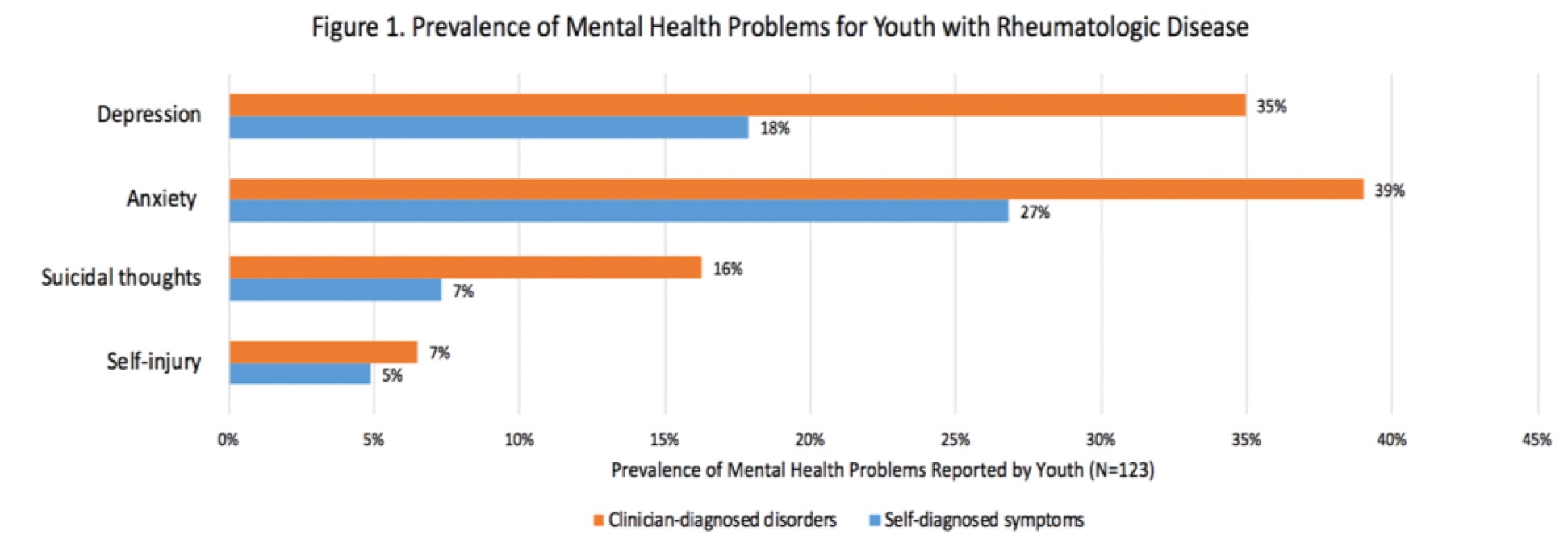
Results: See Table 1 for sample characteristics. 447 respondents included 123 youth and 324 parents; they were not required to be dyads. Combining youth and parent responses, 210 had juvenile arthritis, 173 had juvenile dermatomyositis, and 64 had systemic lupus erythematosus. Those with and without mental health problems were comparable on many demographic and disease factors, although patients with appearance altering comorbidities were more likely to report mental health problems. Rates of clinician and self-diagnosed depression, anxiety, suicidal thoughts, and self-harm are shown in Figure 1.
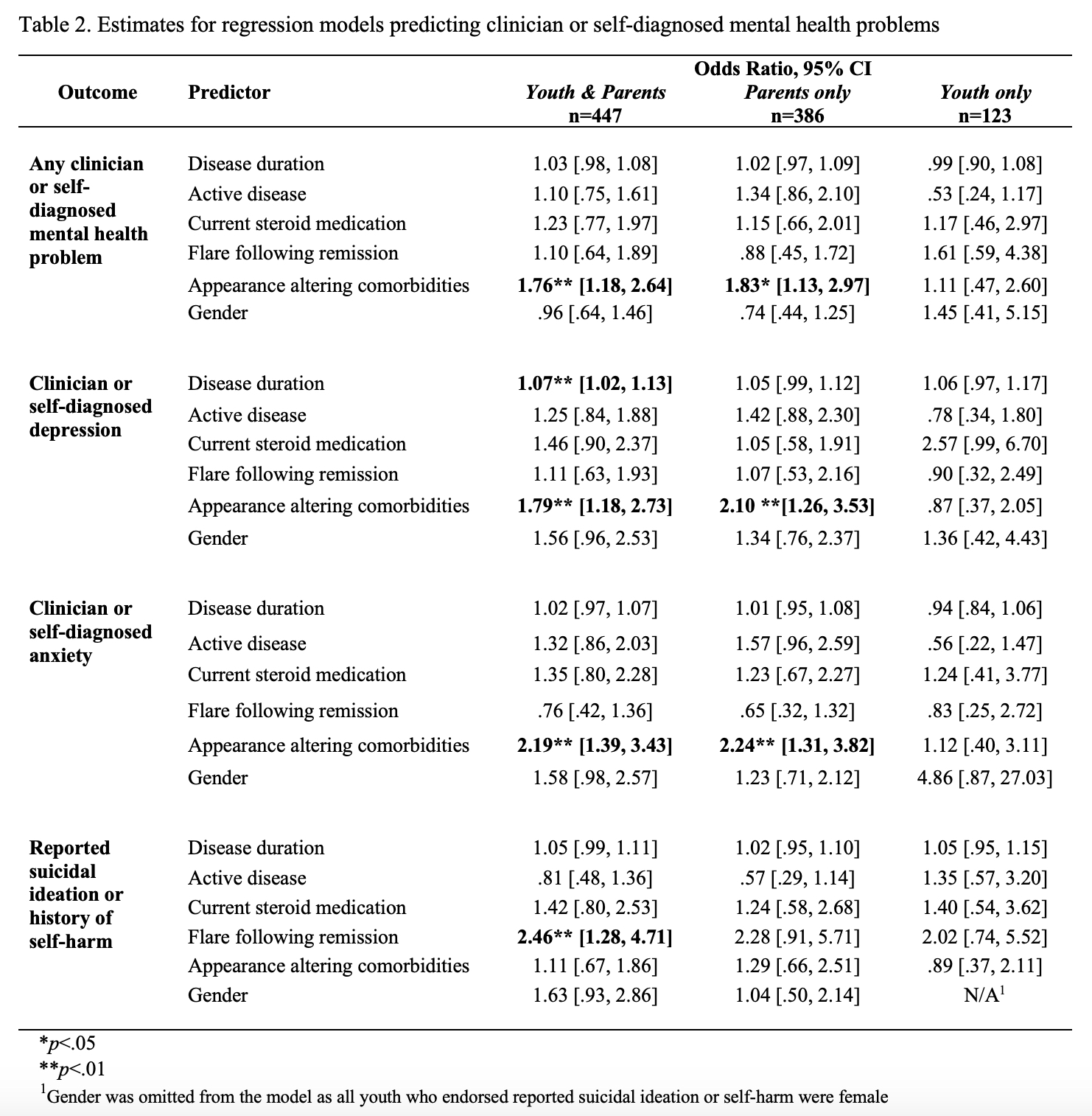
Adjusted logistic regression models (Table 2) indicate that having appearance altering comorbidities predicted the presence of a mental health problem in the combined youth/parent sample and in the parent-only sample. In the combined sample, appearance altering comorbidities also predicted depression and anxiety problems, whereas history of flare following remission predicted reported suicidal ideation or self-harm. Within the youth responses, reported depression trended to be more likely among those taking steroids (p=.053).
Conclusion: Certain cross-cutting rheumatologic disease factors such as appearance-altering comorbidities are predictive of mental health problems such as depression or anxiety. These findings are helpful for identifying targets for mental health screening in youth with rheumatologic disease, and should be addressed in screening recommendations.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Danguecan A, Fawole O, Reed M, Harris J, Hersh A, Rodriguez M, Onel K, Lawson E, Rubinstein T, Ardalan K, Morgan E, Paul A, Barlin J, Daly R, Dave M, Malloy S, Hume S, Schrandt S, Marrow L, Chapson A, Napoli D, Napoli M, Moyer M, Delgaizo V, von Scheven E, Knight A. Using a Patient-Engaged Approach to Identify Cross-Cutting Disease Factors Impacting Mental Health in Youth with Rheumatologic Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/using-a-patient-engaged-approach-to-identify-cross-cutting-disease-factors-impacting-mental-health-in-youth-with-rheumatologic-disease-2/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/using-a-patient-engaged-approach-to-identify-cross-cutting-disease-factors-impacting-mental-health-in-youth-with-rheumatologic-disease-2/