Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Ultrasound (US) is recommended as the first imaging modality to assess patients presenting with predominantly cranial symptoms of giant cell arteritis (GCA). However, its value in assessing extra-cranial involvement remains unclear, being the 8F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET/CT the ancillary study recommended. We aim to compare US versus FDG PET/CT to detect cranial and extra-cranial artery involvement in patients with suspected large vessel vasculitis (LVV).
Methods: Retrospective observational study including patients referred to a GCA fast track pathway (FTP) over a 2-years period. All patients underwent US exam of temporal (TA) and large vessel (LV) (carotid, subclavian and axillary) arteries within 24 hours of referral per protocol. Positive US findings were defined as a halo and/or compression sign in TA and a halo and/or intima media thickness >1mm in LV arteries. FDG PET/CT was performed per clinician criteria and was defined as positive if an artery FDG uptake was higher than liver uptake. The qualitative FDG uptake in the aorta, its aortic branches (carotid, axillary and subclavian), iliac and cranial arteries was also registered. All US exams were made before the FDG PET/CT evaluation. The external criterion for US and FDG PET/CT comparison was LVV clinical confirmation after 6 months follow-up.
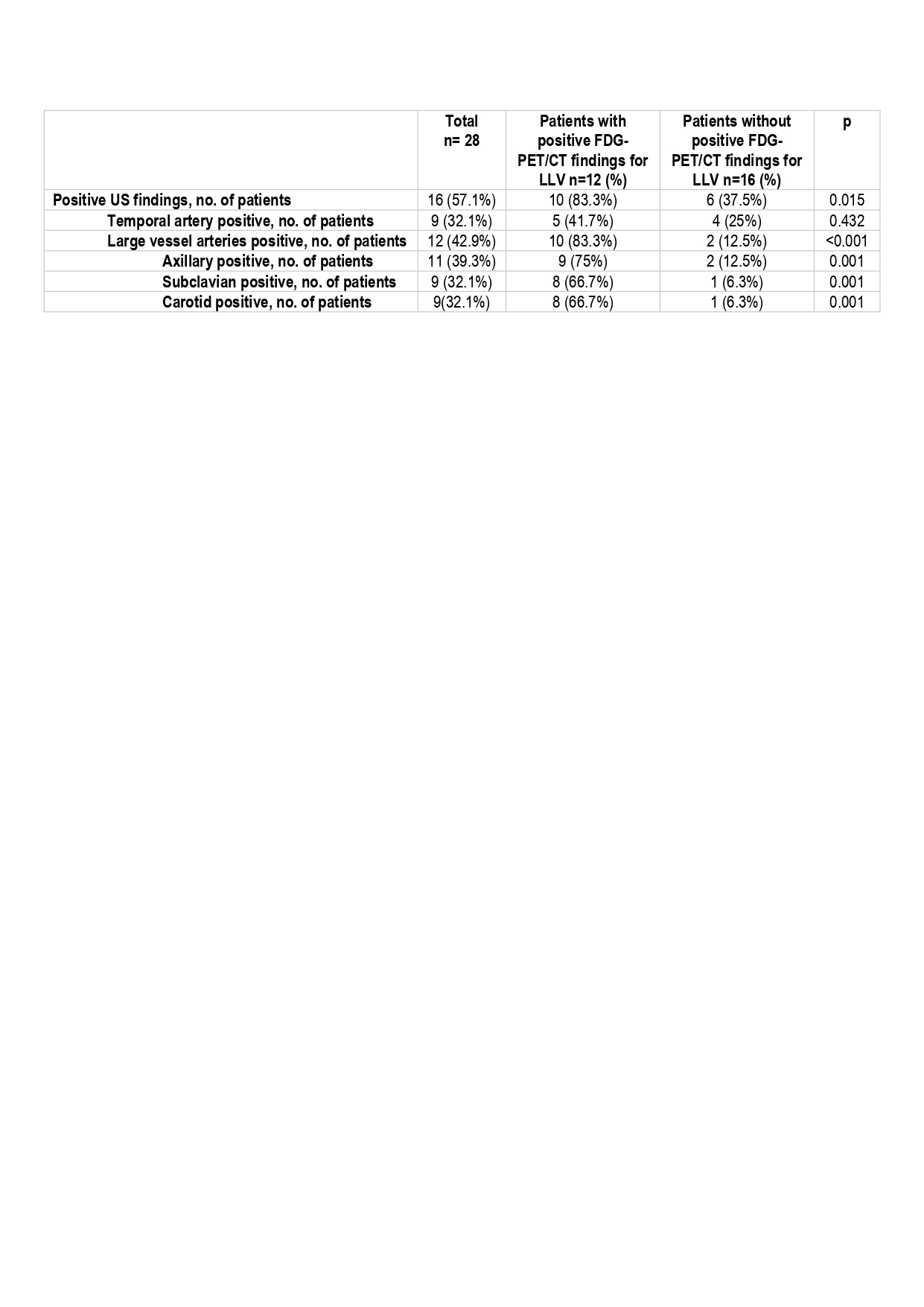
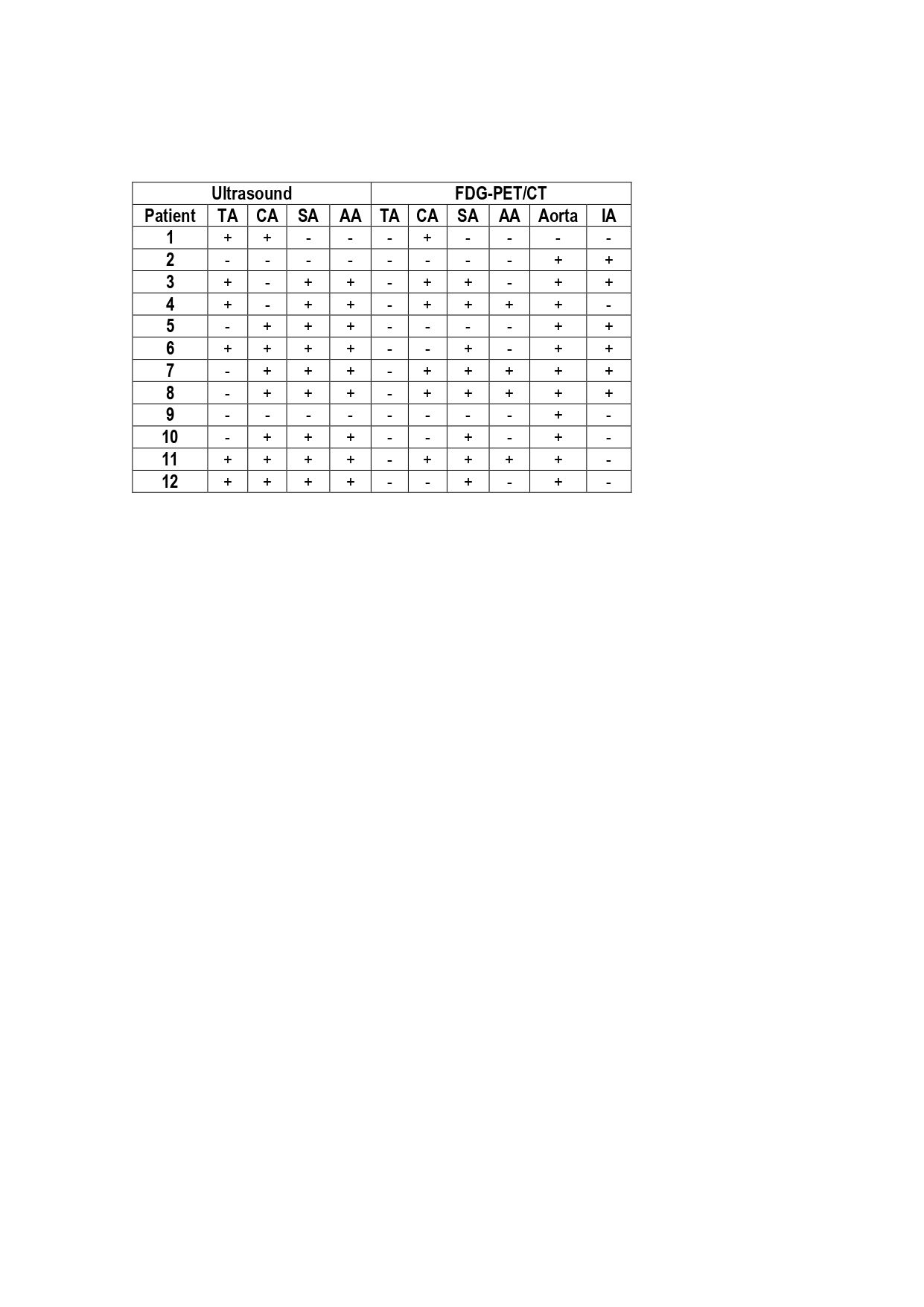
Results: A total of 113 patients were included, 74.3% female with mean age 74 (11) years. After 6 months of follow-up, 37 (32.7%) patients had LVV clinical confirmation (34 GCA and 3 Takayasu). Only 3 (3.9%) patients without LVV versus 32 (86.5%) with LVV had positive US findings (Table 1). Among patients with LVV, 24 (64.9%) had TA involvement and 16 (43.2%) had extra-cranial LVV according to US examination (37.8% axillary, 29.7% subclavian and 32.4% carotid artery involvement). We found a mixed pattern with involvement of both TA and LV arteries in 8 (21.6%) patients. Overall, sensitivity and specificity of US for LVV was 86.5% and 96.1%, respectively, and for exclusively LV involvement was 94.1% and 80.2 %, respectively. A total of 28 patients underwent a FDG-PET/CT, of whom 12 (42.9%) showed positive findings. Taking FDG-PET/CT as the reference, US showed positive extracranial findings in 10 (83.3%) of those 12 patients and was able to detect 2 (12.5%) additional cases of large vessel involvement with negative FDG-PET/CT examination (Table 2). On the other hand, FDG-PET/CT showed LV artery involvement in 2 patients with negative US findings (1 patient with isolated aortitis and 1 patient with aorta and iliac artery involvement) (Table 3). FDG-PET/CT showed cranial arteries uptake in none of patients.
Conclusion: US is comparable to FDG-PET/CT for LVV diagnosis. Although presence of US extra-cranial artery inflammation is consistent with FDG-PET/CT examination, a negative US scan does not rule out extracranial involvement. FDG-PET/CT is of limited value for assessing cranial arteries. Thus, US may be used as the first line investigation not only in suspected cranial, but also extracranial LVV.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Molina J, Castrejón I, Rivera J, Martínez Barrio J, Nieto J, López K, Montero F, Trives Folguera L, González C, Alvaro-Gracia J. Usefulness of Ultrasound and (FDG) PET/CT to Detect Cranial and Extracranial Artery Involvement in Patients with Suspected Large Vessel Vasculitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/usefulness-of-ultrasound-and-fdg-pet-ct-to-detect-cranial-and-extracranial-artery-involvement-in-patients-with-suspected-large-vessel-vasculitis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/usefulness-of-ultrasound-and-fdg-pet-ct-to-detect-cranial-and-extracranial-artery-involvement-in-patients-with-suspected-large-vessel-vasculitis/