Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: A systematic review of survey literature from 2014-2018 found that clinicians in the US and Europe are cautious about biosimilar use (JMCP; 2019;25:102). We sought to evaluate current perceptions of biosimilar products among US rheumatologists who prescribe tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α inhibitors now that 8 TNFα inhibitor biosimilars and 1 rituximab biosimilar are FDA approved (thus far, only 1 is marketed in the US).
Methods: A 19-question self-administered online survey was administered by WebMD, LLC from May 7-28, 2019. Rheumatologists (n=9050) who were members of medscape.com and its partner panels were invited to participate via email. The target sample size is 320 board-certified US rheumatologists (self-report); the survey is ongoing and here we present interim results.
Results: Data have been collected from 291 US rheumatologists, 84% are ACR fellows. Nearly all respondents were familiar with the US FDA’s definition of a biosimilar product (very/extremely familiar, 82%; moderately familiar, 16%). While 97% of rheumatologists were aware that an infliximab biosimilar was FDA approved, fewer realized that adalimumab, etanercept, and rituximab biosimilars were FDA approved (57%, 62%, and 40%, respectively). When asked to rank what factors are considered when selecting a biosimilar product vs its corresponding reference product (1, most important to 7, least important), responses were varied: 78% selected effectiveness as most important (ranked either 1 or 2), whereas 51% selected physicochemical/functional characteristics as least important (ranked 6 or 7). Most respondents (84%) were aware that an approved biosimilar was not automatically deemed interchangeable by the FDA; 85% felt it important/very important for interchangeable approval to be on the label. Overall, 80% were familiar with the term “totality of evidence.” When provided with different patient scenarios, rheumatologists were more likely to initiate biosimilar treatment for a biologic treatment-naïve patient with RA (72%) than they were to switch to the biosimilar for a patient with RA doing well on the reference product (33%); see table. About half (54%) of respondents were familiar with the term “non-medical switching” (a misnomer for a biosimilar); among those responding yes, about half (51%; 80/158) had patients for whom this switch had been suggested. The main reasons for non-medical switching included pharmacy benefit insurance/formulary coverage (80%), hospital system formulary (68%) and requirement for a stepped therapy (63%).
Conclusion: This survey suggests that US rheumatologists have an increased understanding and acceptance of biosimilar products, particularly for the initiation of treatment in biologic-naïve individuals. Physicians are hesitant to switch from a reference product to a biosimilar for a patient doing well on the reference product. Additional education on biosimilars is required to help inform treatment decisions by rheumatologists.
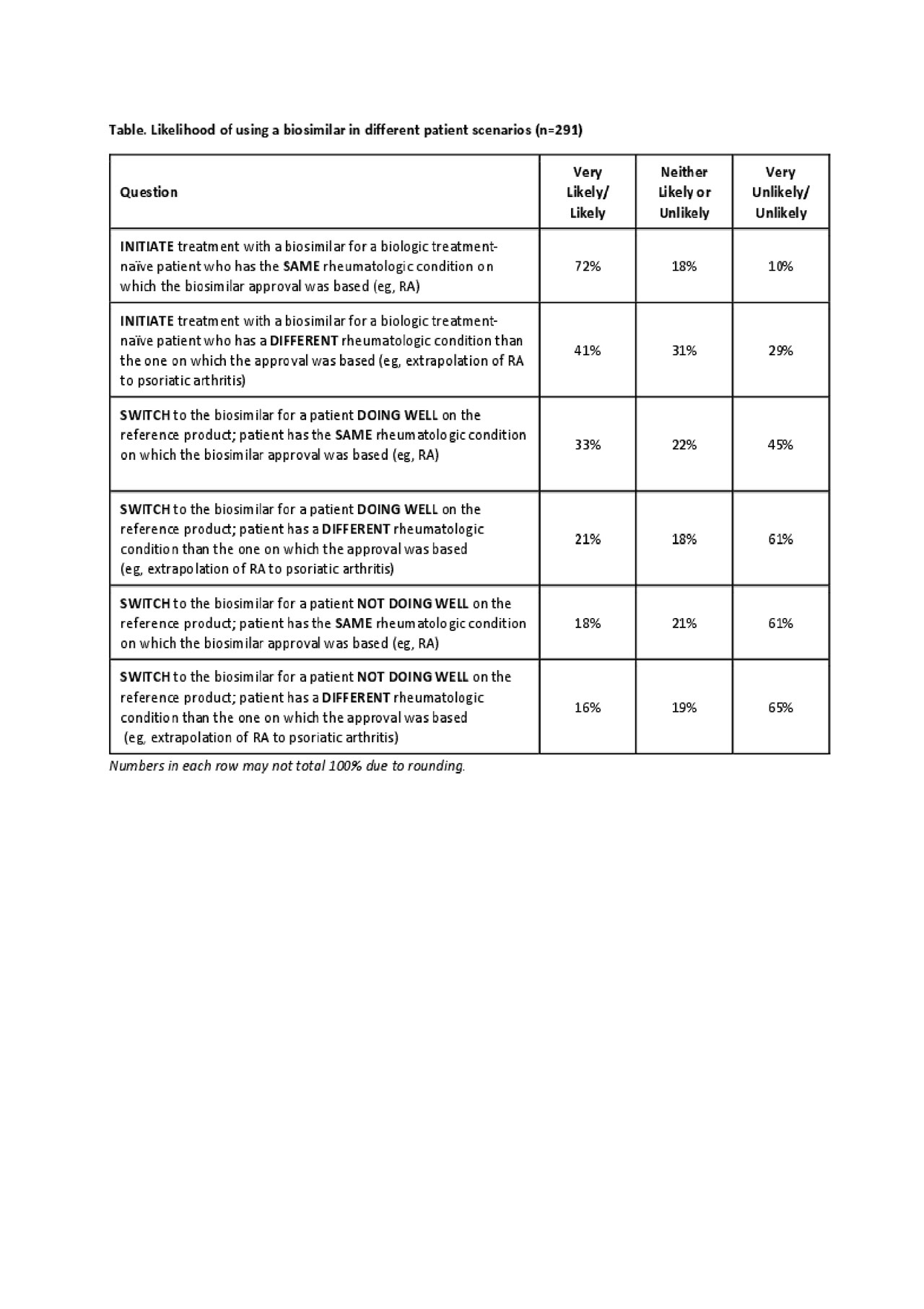
Biosimilar Knowledge Among US Rheumatologists_3June_Table Only
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gibofsky A, McCabe D, Badawi S. US Rheumatologists’ Beliefs and Knowledge About Biosimilars – an Ongoing Survey [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/us-rheumatologists-beliefs-and-knowledge-about-biosimilars-an-ongoing-survey/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/us-rheumatologists-beliefs-and-knowledge-about-biosimilars-an-ongoing-survey/
