Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 10, 2015
Title: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus - Clinical Aspects and Treatment Poster Session III
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Renal
Disease Subcommittee of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) Ad Hoc
Committee on Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) has recommended the urinary
protein level in a spot (untimed) urine specimen (determined as urinary
protein:urinary creatinine ratio; spot PC ratio) over a 24-hour urine protein
excretion, because it is more easily and reliably obtained. In addition, the committee
stated that renal function refers to the estimated glomerular filtration rate
(GFR) and selected the abbreviated Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD)
study equation. Accordingly, complete renal remission was defined by the ACR subcommittee
as an estimated GFR of >90 ml/minute/1.73 m2 and a urinary PC
ratio of <0.2 and inactive urinary sediment. However, recent work suggests
that the spot PC ratio may be inaccurate in the assessment of the degree of
proteinuria in lupus nephritis (LN) as compared with other forms of chronic
glomerular disease. In addition, there is no consensus as to which estimating
equation is preferred for estimated GFR. In the present study, we aimed to ensure
the reliability of spot PC ratio and estimated GFR as measures of proteinuria
and renal function in patients with LN.
Methods: A total of
46 patients with active lupus nephritis who were admitted to our hospital from
2010 through 2014 were included. All the patients met the revised ACR classification
criteria for SLE. LN was pathologically confirmed in 44 patients and renal
biopsy was not performed in the other 2 patients. Clinical and laboratory data were
retrospectively collected from the medical records and statistically analyzed.
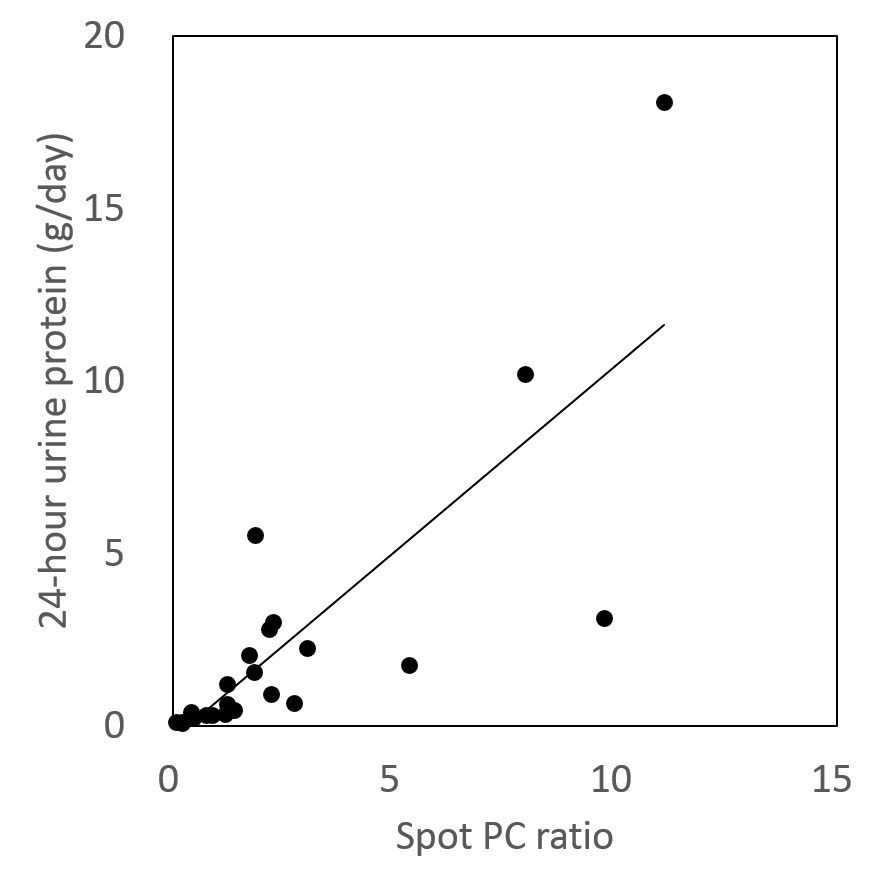
Results: The spot
PC ration and the 24-hour urine protein excretion were highly correlated (n = 23,
Pearson’s r = 0.80). Agreement of the PC spot ratio >0.5 and the
24-hour urine protein excretion >0.5g was good (Cohen’s kappa = 0.60). The
24-hour urinary protein:urinary creatinine ratio is also highly correlated with
the 24-hour urine protein excretion (n = 32, Pearson’s r = 0.87). The estimated
GFR by the abbreviated MDRD study equation and the 24-hour urine creatinine
clearance were moderately correlated (n = 38, Pearson’s r = 0.68).
Conclusion: Our results
supported the reliability of spot PC ratio and estimated GFR by the abbreviated
MDRD study equation as measures of proteinuria and renal function in patients
with LN. Larger and prospective studies are needed to confirm and validate these
findings.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Katsumata Y, Nishina H, Hanaoka M, Kawaguchi Y, Takagi K, Tochimoto A, Ichimura Y, Yamanaka H. Urinary Protein:Urinary Creatinine Ratio in an Untimed Urine Specimen and Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate Are Reliable Measures of Proteinuria and Renal Function in Patients with Lupus Nephritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/urinary-proteinurinary-creatinine-ratio-in-an-untimed-urine-specimen-and-estimated-glomerular-filtration-rate-are-reliable-measures-of-proteinuria-and-renal-function-in-patients-with-lupus-nephritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/urinary-proteinurinary-creatinine-ratio-in-an-untimed-urine-specimen-and-estimated-glomerular-filtration-rate-are-reliable-measures-of-proteinuria-and-renal-function-in-patients-with-lupus-nephritis/