Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Clinical Aspects and Treatment Poster I: Biomarkers and Outcomes
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
–Background/Purpose: Lupus nephritis (LN) represents the main prognostic factor in systemic lupus erythematosus (LES) [1]. The clinical significant classes of LN –due to the need of treatment- are the proliferative (III, IV), membranous (V) and mixed classes (III or IV/V). The aim of the study was to find a urinary metabolomic fingerprint to diagnose classes III, IV and/or V of LN
–Methods: Cross-sectional study. Inclusion criteria: lupus patients with and without clinical significant lupus nephritis (classes III, IV, V and mixed classes). Urine samples were screened for metabolites using gas chromatography mass spectrometry (coupled with electronic nose) and principal component analysis for metabolite selection.
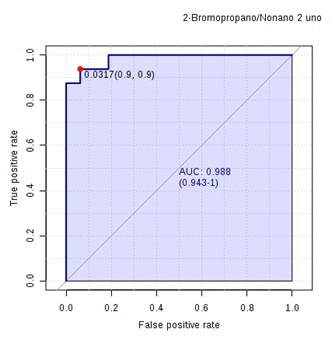
–Results: We included 29 lupus patients, 11 with LN and 18 without LN. Age between groups were 26 years (IQR 14.5) in patients with LN and 33 (IQR 22.3) in patients without LN (p 0.48). The median SLEDAI score in LN patients was of 13 and 3 in those without NL (p <0.0001). Class IV nephritis was present in 45% of LN patients, mixed class in 36%, and class V in 18%. The median proteinuria of patients with NL was 1g/L, (IQR 2.7). We observed differences in metabolic fingerprint in patients with and without LN, with an AUC 90%. Metabolic pathway analysis was conducted, and we found several pathways involved, like methane, glycolysis, pyruvate and glycerophospholipid pathways. The most significant metabolites of the PCA that discriminated LN, were 2-nonanone with a sensitivity of 0.87 and specificity of 0.93. Obtaining the ratio of 2-bromopropane with 2-nonanone, the diagnostic accuracy improved, with a positive likelihood ratio (LR) of 14 and a negative LR of 0.1.
–Conclusion: We identified a urinary metabolomic fingerprint that involved several metabolic pathways; 2-nonanone and the ratio of 2-bromopropane/2-nonanone had the best diagnostic accuracy in our study.
-References: 1. Mok CC, Kwok RCL, Yip PSF. Effect of renal disease on the standardized mortality ratio and life expectancy of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65:2154–60
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Herrera Van Oostdam D, Flores Ramirez R, Rodriguez Aguilar M, Pierdant Pérez M, Abud-Mendoza C, Martínez-Galla D, Martinez-Martinez MU. Urinary Metabolomic Fingerprint As Diagnostic Biomarker for Clinical Significant Lupus Nephritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/urinary-metabolomic-fingerprint-as-diagnostic-biomarker-for-clinical-significant-lupus-nephritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/urinary-metabolomic-fingerprint-as-diagnostic-biomarker-for-clinical-significant-lupus-nephritis/