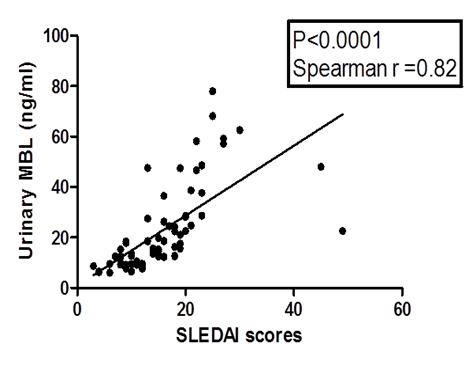Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2015
Title: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus - Clinical Aspects and Treatment Poster Session I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Nephritis is the
most common cause of mortality and morbidity in SLE, develops in 40 to 70% of
cases in 5-10 years with 60% mortality. It is important to detect early involvement
and flare for proper management. Renal biopsy, though gold standard for
diagnosis, is invasive and cannot be serially repeated for monitoring. Mannose
binding lectin (MBL) , member of the collectin type of proteins of PRR family
activates complement cascade or acts as opsonin. Studies have shown that plasma
MBL levels are elevated in SLE patients and significantly correlate with
disease activity of SLE. We hypothesized that urinary MBL would correlate with
disease activity in SLE Nephritis.
Methods: In a cross sectional hospital based observational
study 65 consecutive cases of SLE nephritis fulfilling the ACR criteria were
enrolled. Plasma & urinary MBL levels are measured by ELISA,
according to the manufacturer’s instructions (R&D systems, Minneapolis, MN,
USA). Clinical, serological
and other markers of disease activity (C3, C4 and anti-dsDNA) were measured by
standard laboratory procedures. Disease activity scores like SLEDAI 2K and
renal SLEDAI were calculated. Renal biopsy was done to correlate urinary MBL
levels with histopathological staging. Statistical analysis was done using
Graphpad prism v5.01.
Results: Urinary MBL was high in patients of SLE
Nephritis compared to healthy controls(p=0.01), furthermore patients with nephritis
flare (renal SLEDAI >4) had significantly higher levels of plasma &
urinary MBL compared to non flare patients(p=0.0008,p=0.004).Urinary MBL showed
a strong positive correlation with proteinuria (p<0.0001,r=0.47), SLEDAI
(p<0.0001,r=0.82) and renal SLEDAI (p<0.0001,r=0.59), and an inverse
correlation was observed between urinary MBL and C3(p=0.03,r=-0.21),C4(p=0.04,r=-0.19).
Urinary MBL levels progressively increased with higher histological
staging(ISN/RPS)
Conclusion: This is the first study demonstrating a
role for urinary MBL in predicting SLE nephritis flare.
Significant positive correlation of Urinary MBL with SLEDAI
and renal SLEDAI scores
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pattanaik SS, HM M, Panda AK, Sahoo RR, Tripathy R, Das BK. Urinary MBL : A Promising Biomarker for Predicting Flare in Lupus Nephritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/urinary-mbl-a-promising-biomarker-for-predicting-flare-in-lupus-nephritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/urinary-mbl-a-promising-biomarker-for-predicting-flare-in-lupus-nephritis/