Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Proliferative lupus nephritis (LN) is one of the most common and serious manifestations of SLE and is a major cause of morbidity. A search for the ideal biomarker for LN is still underway, one that can be used for early detection, and correlate with the class & activity of LN. Urine is normally devoid of leucocytes, however, it has been observed that macrophages and T-lymphocytes are routinely present in the urine of LN patients and those with other proliferative renal diseases. This provided the idea for their potential use as biomarkers for proliferative LN. The objective is to study the urinary CD4+, CD8+ T Lymphocytes, and CD14+ monocytes in patients with proliferative lupus nephritis, and explore their use as a biomarker for LN.
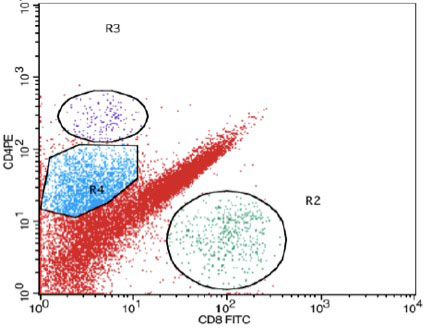
Methods: Our subjects included 30 patients with biopsy-proven proliferative LN (Group A) and 30 SLE patients without clinical or lab evidence of LN as controls (Group B). Laboratory investigations included serum creatinine, urine analysis, protein: creatinine ratio, anti-ds DNA Ab, C3 and C4. For the flow cytometric analysis, 100 ml of freshly voided urine in a sterile container were obtained from patients and controls. All samples were processed within 2-4 hours of collection to ensure viability of the cells. Urine mononuclear cell count was done using a hemocytometer. The urine samples were centrifuged then washed twice by phosphate-buffered saline/bovine serum albumin (PBS/BSA) & re-suspended in about 300 μls PBS. The cells were stained with anti CD8- FITC, anti CD4- PE, anti CD14-PERCP and anti- CD3-APC monoclonal antibodies. The flow cytometric analysis was done using Becton Dickinson, FACS Calibur multi-parameter flow cytometer equipped with BD CellQuest Pro software for data analysis.
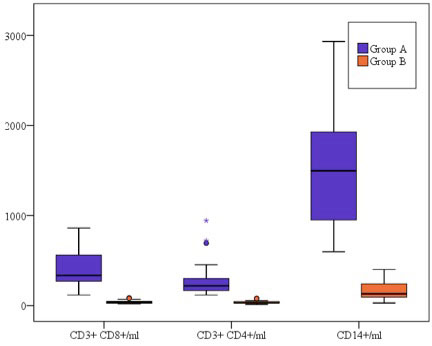
Results: CD14 + cells were the most abundant cells in the urine of LN patients. The mean numbers of urinary CD8+, CD4+ and CD14+ cells/ml were significantly higher in patients with LN (405.6 ± 200.0, 281.1 ± 195.3, and 1554.7 ± 606.8 respectively) than in those without (39.30 ± 17.56, 34.33 ± 16.41, and 161.17 ± 90.91 respectively). AUC for ROC = 1.0 for all 3 markers with CD8+ >85 cells/ml, CD4+ >80 cells/ml, and CD14+ >400cells/ml being observed exclusively in LN.
The cell counts correlated significantly with the protein: creatinine ratio, but not with other markers of disease activity.
The CD4: CD8 ratio was significantly lower in LN patients (0.69 ± 0.21) than in those without (0.91 ± 0.31).
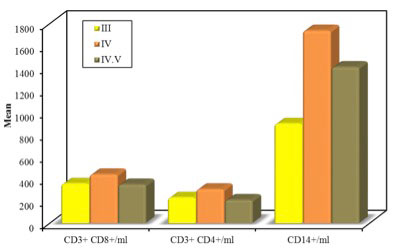
Urinary CD14+ cells seem to occur in much higher counts in Class IV (1736.7 ± 522.0) than Class III LN (898.5 ± 17.68) p=0.084.
Conclusion: Urinary CD8+, CD4+, and CD14+ cells are highly sensitive and specific markers for detecting proliferative LN. A low CD4: CD8 ratio provides a further clue. The cell counts correlate with proteinuria. CD14 cell counts may be a potential biomarker to differentiate between the different classes of proliferative LN.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
El Gerby A, Abdelati A, Donia H, Eshak N. Urinary Cellular Profile as a Biomarker for Proliferative Lupus Nephritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/urinary-cellular-profile-as-a-biomarker-for-proliferative-lupus-nephritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/urinary-cellular-profile-as-a-biomarker-for-proliferative-lupus-nephritis/