Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Serum rheumatoid factor (RF) is a major predictor of the new onset of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In very early arthritis patients, higher titers of both IgA and IgM RF isotypes predicted bone erosions at 2 years (A&R 2010; 62:1739-47). However, no data have been reported on efficacy of IgA or IgM RF isotypes to predict new onset of RA. This cohort study analyzed baseline IgA and IgM RF isotype levels as predictors of new onset of RA, and searched for factors associated with baseline levels of these biomarkers.
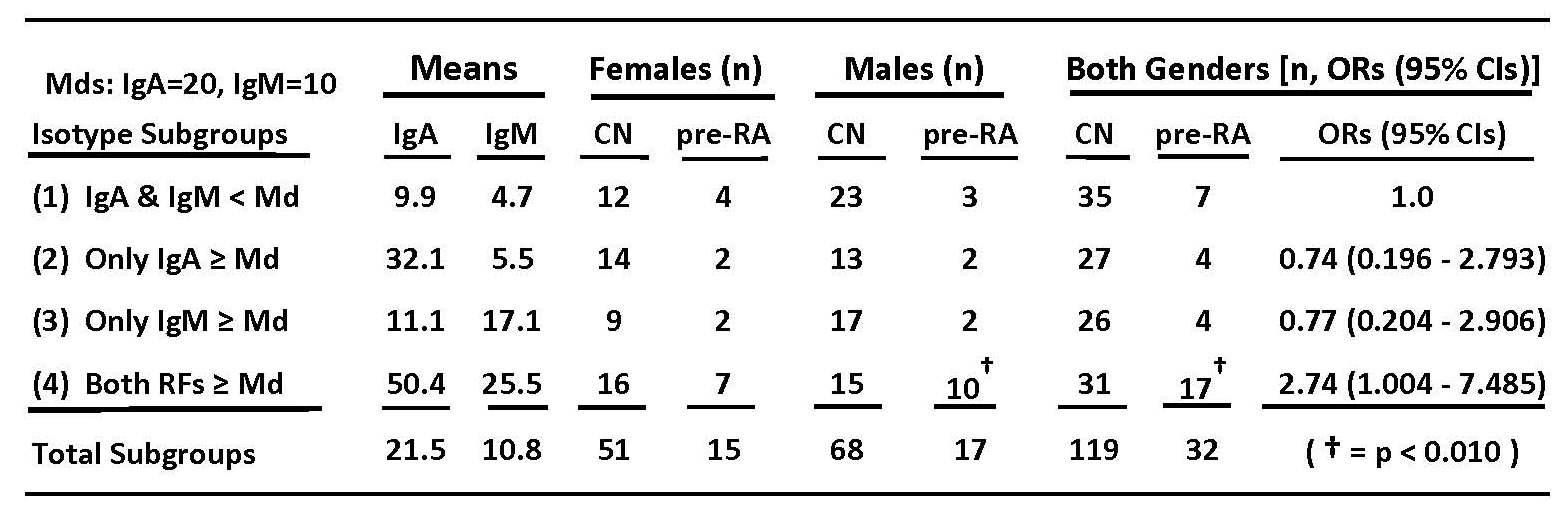
Methods: In 1974, baseline sera were obtained from a community-based cohort (n=21,061 adults) enrolled in the CLUE 1 follow up study. In 1994, baseline pre-RA cases were identified, who subsequently developed ACR-positive RA, 3 to 20 (median 12) years after entry. Four non-RA control (CN) cohort subjects were matched to each case on age, sex, and Caucasian race. The RF isotype assays were performed by ELISA concurrently and without identification, on stored (-70ºC) baseline sera of 32 pre-RA and 119 CN subjects. Median (Md) levels were determined for IgA (20 TU/ml) and IgM (10 IU/ml) RF isotypes from total subject sample values, which were then stratified into 4 gradient subgroups (1 = both < Md, 4 = both ≥ Md). The subgroup with both RF isotypes lower than Md values (1) was used as baseline in odds ratio (OR, 95% CIs) prediction of RA for the other 3 subgroups (Table):
Results: Expected random frequencies were found for the CN in each of the 4 gradient categories, 31 (26%) of 119 in the highest subgroup, whereas pre-RA predominated in that subgroup, 17 (53%) of 32 (p = 0.005). In univariate analyses (Table), category 4 predicted RA onset in total subjects, OR 2.74 (1.004 – 7.485). In males, category 4 also predicted RA onset, 5.05 (1.642 – 15.520), but not in females, 1.91 (0.593 – 6.193). In a logistic regression (LR) model, the higher combined IgA/IgM RF category 4 was included as a dichotomous, independent factor (0 = no, 1 = yes), and predicted (p = 0.006) the dependent RA outcome, OR 3.16 (1.381 – 7.225). The model included other baseline variables: cohort entry age; sex; a 7-category cigarette smoking history score, and years from entry to RA onset. The smoking variable also independently predicted RA outcome, OR 1.28 (1.008 – 1.626). Unlike category 4, neither RF isotype alone in full-range values predicted RA in LR models. In other LR models, using the higher IgA/IgM RF category 4 as the dependent outcome variable, neither the cigarette gradient scores, nor individually-entered serum levels of acute phase proteins (CRP, ASAA, IL-1ra), inflammatory cytokines (IL-1B, IL-6, TNF-α), or selected receptors (sTNF-R1 and sIL-2Rα) were independent predictors.
Conclusion: The combination of upper-half IgA and IgM RF levels was a significant predictor of long-term development of RA in total subjects and males. Factors which influence the combined higher IgA/IgM RF isotype levels, as was found in pre-RA, deserve further study.
Disclosure:
A. T. Masi,
None;
A. A. Rehman,
None;
J. C. Aldag,
None;
H. Wang,
None;
N. J. Goertzen,
None;
M. C. Teodorescu,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/upper-half-serum-iga-20-tuml-and-igm-10-iuml-levels-significantly-predicted-the-long-term-mean-12-yrs-onset-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-when-combined-but-neither-test-individually-in-their/