Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Several unilateral scoring systems have been proposed to increase the feasibility of ultrasound (US) for joint evaluation in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. Both the clinically most affected side and the dominant hand have been proposed as the default monitoring approach during treatment, however, no consensus exists on which side to choose. the aim is to evaluate if the dominant hand or the hand with more clinically swollen joints is per default the more inflammatory active side, as judged by US, to be chosen for unilateral scoring systems in RA patients.
Methods:
We performed an agreement study exploring the impact on US scoring methods in a cross-sectional study of an early RA (ARCTIC trial, n=230) and established RA cohort (ULRABIT trial, n=212) with patients initiating conventional and biological Disease Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs, respectively. Tender and swollen joint count for 28 joints (TJC28 and SJC28) and C-reactive protein (CRP mg/L) were obtained. Using the hands as model, bilateral MCP 1-5, PIP 2+3 and wrists were evaluated by US using a 0–3 scoring system for both grey-scale (GS) and power Doppler (PD) US according to the atlas by Hammer et al. A GS sum score, a PD sum score and a global synovitis score (GLOSS) were calculated for each hand (0-30). According to our prespecified protocol a reasonable equivalence margin in this study (agreement between groups) was defined to correspond to a 95% Confidence Interval around the observed paired mean difference: -2.99 to +2.99; a difference of at least 3 in sum score defined a clinical significant difference defining which hand was more inflammatory active.
Results:
In total, 442 RA patients were included; 71% women, 79% anti-CCP pos, 71% RF pos, median(IQR) age 54(42-62) years, CRP 7(3-16), SJC28 5(3-26) and TJC28 6(2-28). The median(IQR) PD sum score was 3(0-7) for right hand and 2(0-5) for left hand, GS sum score was 5(2-9) for both hands, and GLOSS was 5(2-10) for right hand and 5(2-9) for left hand.
The dominant hand was not more inflammatory active than the non-dominant (mean difference, 95%CI) for PD sum score -0.58(-1.35 to 0.2), GS sum core -0.69(-1.61 to 0.24) and GLOSS -0.79(-1.76 – 0.18). This was in clear contrast to analyses of the hand with more swollen joints which was statistically significantly more inflammatory active (p<0.0001): for PD sum score 1.70(0.94 to 2.47), GS sum score 2.21(1.30 to 3.12) and GLOSS 2.31(1.36 to 3.26) – see table.
Conclusion:
Based on this study, the dominant hand is not significantly more affected than the non-dominant hand regarding inflammatory activity evaluated by US. As the hand with clinically more swollen joints are more inflammatory active by PD sum score, GS sum score and GLOSS, the hand with most swollen joints is suggested to be chosen as basis for unilateral scoring systems.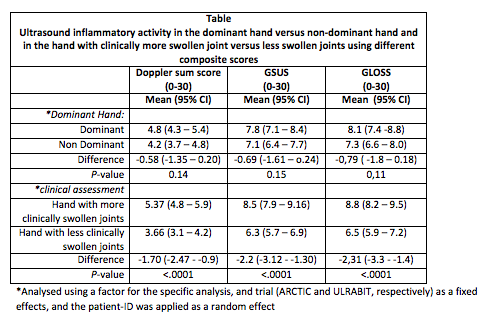
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Terslev L, Christensen R, Aga AB, Sexton J, Haavardsholm EA, Hammer HB. Unilateral Ultrasound Scoring Methods for Synovitis in Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Agreement Study Exploring the Most Inflammatory Active Side [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/unilateral-ultrasound-scoring-methods-for-synovitis-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-an-agreement-study-exploring-the-most-inflammatory-active-side/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/unilateral-ultrasound-scoring-methods-for-synovitis-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-an-agreement-study-exploring-the-most-inflammatory-active-side/
