Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: This study aimed to identify risk factors associated with adverse events (AEs) and infections in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and comorbid interstitial lung disease (ILD) receiving biologics or targeted synthetic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (b/tsDMARDs), using data from the Korean College of Rheumatology Biologics (KOBIO) registry.
Methods: We analyzed data from a cohort of 2,266 adult RA patients who received b/tsDMARDs between December 2012 and December 2021, including 169 patients having comorbid ILD. We identified risk factors for AEs and infections in the whole RA group and RA-ILD group and investigated the impact of infections on mortality in patients with RA and comorbid ILD.
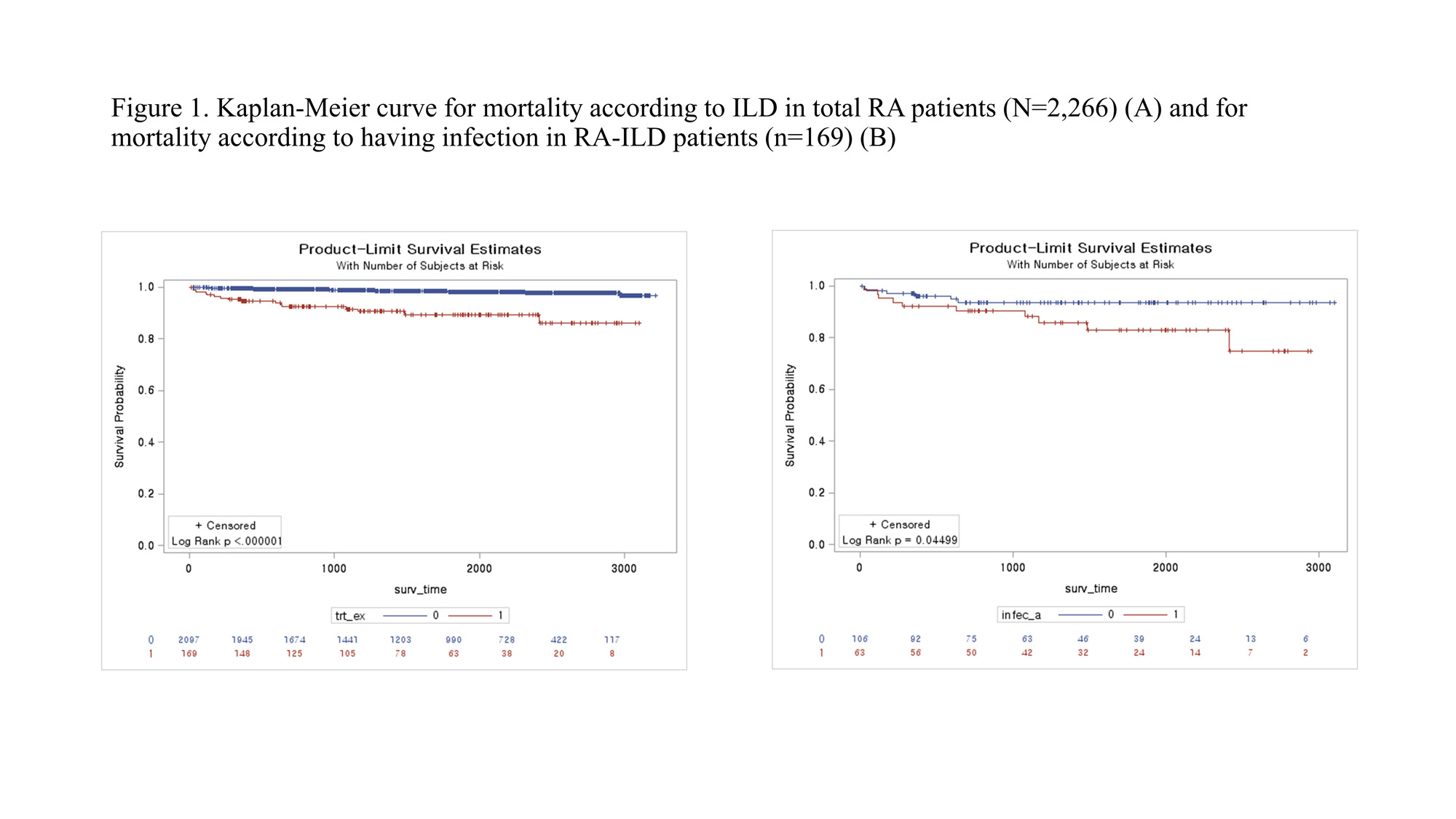
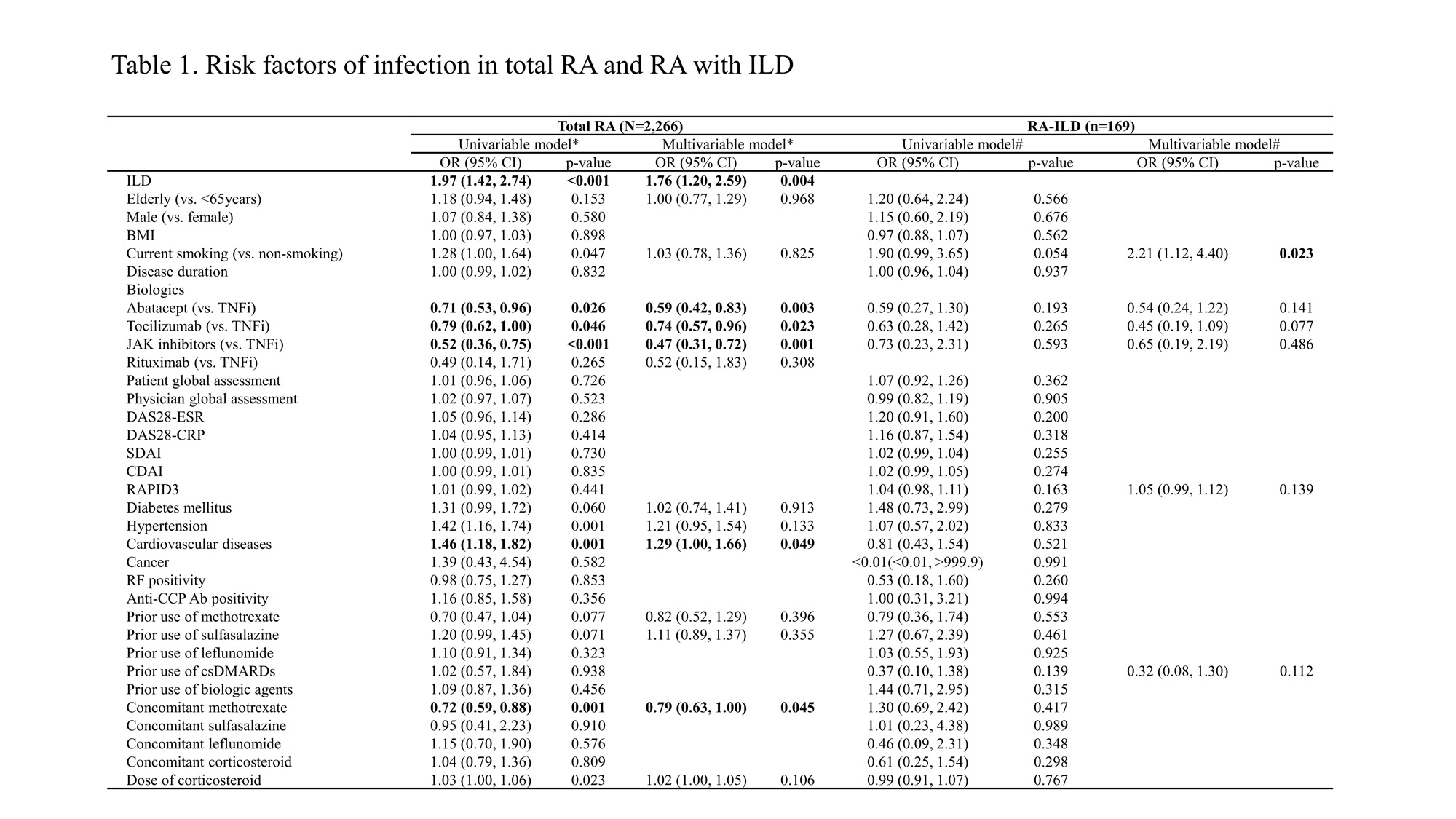
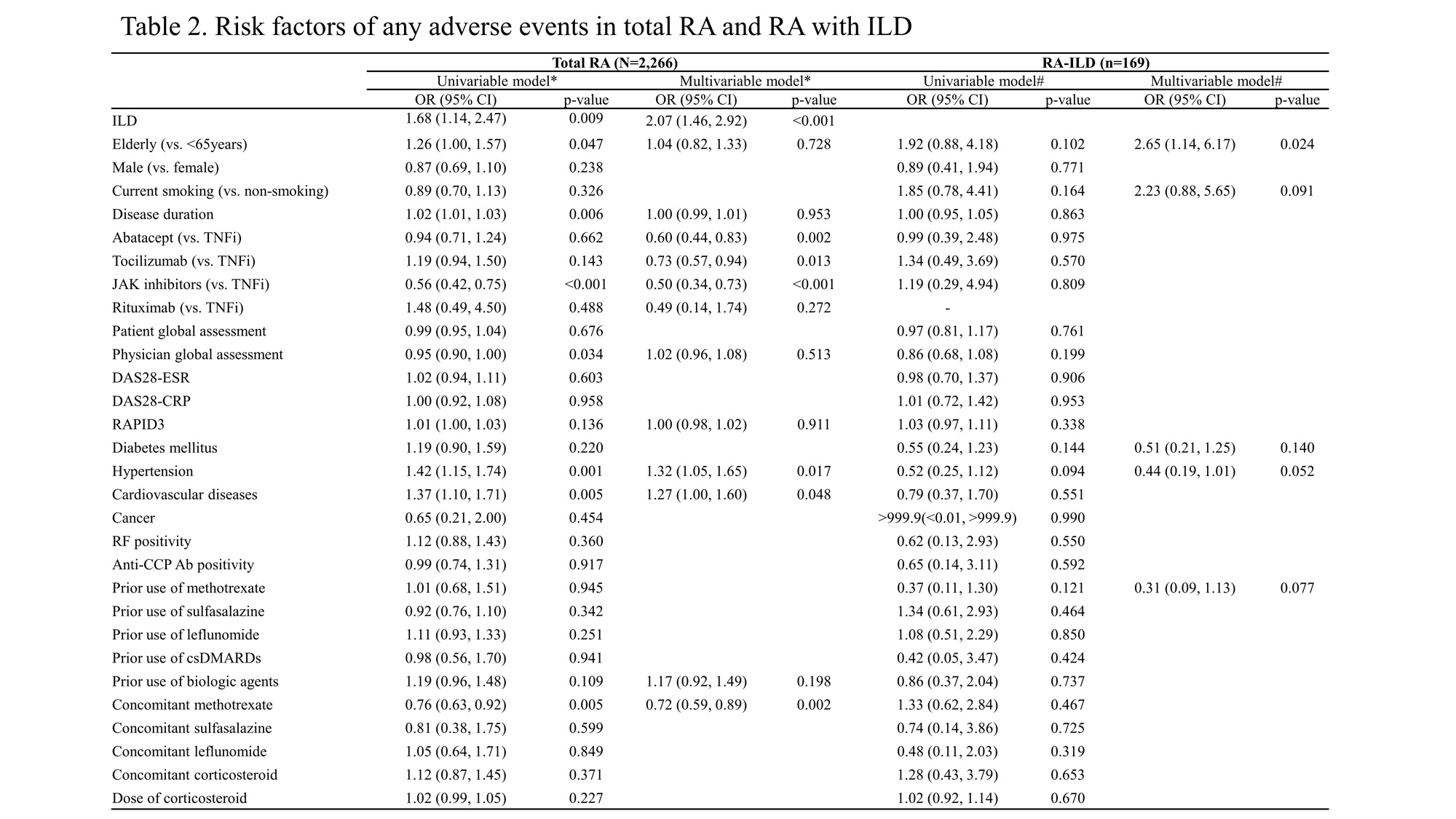
Results: Among all RA patients, 45.7% withdrew b/tsDMARDs, while in the RA-ILD group, a higher proportion of 57.4% withdrew their regimen. The main reason for withdrawing b/tsDMARDs in the RA-ILD group was adverse events (AEs), with infections being the largest proportion among the reported AEs. In the RA without ILD group, the frequency of AEs was significantly lower compared to the RA-ILD group (ILD: 45.4%, non-ILD: 27.8%, p < 0.001), among the AEs, infusion-related reactions were more common than infections. In multivariate analysis of risk factors for AEs and infections in the RA-ILD group, older age was identified as a risk factor for AEs (OR, 2.65, p = 0.024), and only current smoking was identified as a risk factor for infections (OR, 2.214, p = 0.023). In the whole RA, ILD (OR = 1.97, p < 0.001), current smoking (OR = 1.28, p = 0.047), abatacept (OR = 0.71, p = 0.026), tocilizumab (OR = 0.79, p = 0.046), JAK inhibitors (OR = 0.52, p < 0.001), hypertension (OR = 1.42, p = 0.001), cardiovascular diseases (OR = 1.46, p = 0.001), concomitant methotrexate (OR = 0.72, p = 0.001), and dose of corticosteroid (OR = 1.03, p =0.023) were associated with infections.
Conclusion: The patients with RA-ILD had a higher rate of withdrawal of b/tsDMARDs due to AEs and infections compared to patients with RA without ILD. In RA-ILD group, older age was identified as a risk factor for AEs, while current smoking was identified as a risk factor for infections.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kim J, Jung J, Suh C, Kim H. Uncovering Risk Factors for Adverse Events and Infections in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis with Interstitial Lung Disease Under Biologics or Targeted Synthetic DMARDs: Insights from the KOBIO Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/uncovering-risk-factors-for-adverse-events-and-infections-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-rheumatoid-arthritis-with-interstitial-lung-disease-under-biologics-or-targeted-synthetic-dmards-insights-from-th/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/uncovering-risk-factors-for-adverse-events-and-infections-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-rheumatoid-arthritis-with-interstitial-lung-disease-under-biologics-or-targeted-synthetic-dmards-insights-from-th/