Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: RA – Treatments Poster III: RA Treatments & Their Safety (1674–1710)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) activates innate neuroimmune reflexes that have been shown to reduce pro-inflammatory cytokines and clinical disease activity in subjects with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (Koopman PNAS 2016). We previously reported primary clinical outcomes from a first-in-human, double-blind study of a novel, implanted VNS device called a MicroRegulator (MR). That study showed 5/10 subjects with drug-refractory RA met or exceeded the minimal clinically important difference (MCID) in DAS28-CRP; 2 subjects achieved DAS28 remission (DAS28-CRP < 2.6); and pro-inflammatory cytokines were decreased by >30% following 12 weeks of VNS (Genovese et al. Lancet Rheum 2020). We now report 24-week efficacy and safety findings from this study.
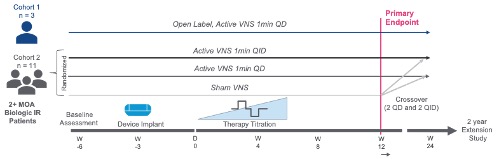
Methods: The primary study was enrolled in 2 stages: Stage 1 (n=3) was open-label, and Stage 2 (n=11) was randomized and sham-controlled (Figure 1). Three weeks after MR implantation, the first 3 subjects were stimulated 1 min QD in Stage 1. Following safety review board approval, the remaining 11 patients were implanted with the MR and randomized to 1 min of sham, QD, or QID VNS in Stage 2. At Week 12, the blind was lifted, sham subjects were re-randomized to either QD or QID active VNS dosing, and all actively treated subjects remained on their dosing through Week 24. Safety and tolerability were assessed, and several secondary efficacy endpoints were evaluated measuring the change in disease activity from the start of VNS to Week 24.
Results: There were no device-related adverse events from Week 12 through Week 24. Improvement in clinical disease activity was sustained through Week 24: 5/9 patients within the original treatment groups met or exceeded EULAR response criteria for DAS28-CRP at Week 24 vs. 5/10 at Week 12 (one Week 12 responder was lost to follow-up). Similarly, 6/9 patients in the original treatment groups met or exceeded the MCID in CDAI at Week 24 vs. 5/10 at Week 12. In the long-term extension, 1/4 sham crossover patients had both EULAR and CDAI response after 12 weeks of VNS (1/2 QD, 0/2 QID). VECTRA composite scores and component analysis revealed an 18-point drop in median multi-analyte disease activity index in the QD group over 24 weeks of VNS with a decrease in serum levels of several analytes in key component categories (IL-6, serum amyloid A, and VCAM-1). Erosion progression by hand MRI was stabilized or decreased in all but 1 of the stimulated patients at Week 24.
Conclusion: Improvements in clinical disease activity, pro-inflammatory cytokine suppression, and joint preservation were maintained through 24 weeks of VNS treatment. Safety outcomes continue to support the risk/benefit profile of VNS as a treatment option for patients with RA with inadequate responses or intolerance to conventional DMARDS and biologic and targeted synthetic drugs.
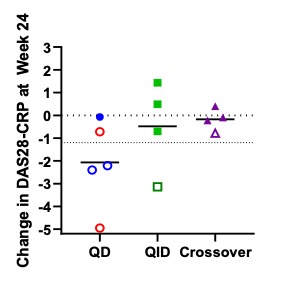 Figure 2: Change in DAS28-CRP at Week 24. Open shapes represent EULAR good and moderate responders. Red shapes represent subjects with a biologic added back as co-therapy with VNS.
Figure 2: Change in DAS28-CRP at Week 24. Open shapes represent EULAR good and moderate responders. Red shapes represent subjects with a biologic added back as co-therapy with VNS.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gaylis N, Genovese M, Sikes D, Kivitz A, Horowitz D, Peterfy C, Levine Y, Chernoff D. Twenty-four-week Follow-up of a Randomized Controlled First-in-Human Trial of the Safety and Efficacy of Neurostimulation with a Miniaturized Vagus Nerve Stimulation Device in Patients with Multidrug-Refractory Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/twenty-four-week-follow-up-of-a-randomized-controlled-first-in-human-trial-of-the-safety-and-efficacy-of-neurostimulation-with-a-miniaturized-vagus-nerve-stimulation-device-in-patients-with-multidrug/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/twenty-four-week-follow-up-of-a-randomized-controlled-first-in-human-trial-of-the-safety-and-efficacy-of-neurostimulation-with-a-miniaturized-vagus-nerve-stimulation-device-in-patients-with-multidrug/