Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The Tool for Administrative Reimbursement Drug Information Sharing (TARDIS) is an electronic platform combining the collection of data from all Belgian patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) on biologic (b) and targeted synthetic (ts) DMARDs, together with the submission of a request for reimbursement of this medication. Therapy choice after failure of 2 classical synthetic (cs) DMARD is left at the discretion of the treating physician in Belgium. Therapy is prolonged after 3 months for tsDMARDS and after 6 months for bDMARDs if treatment is effective. Our aim was to investigate which factors are associated with a successful prolongation of therapy in the TARDIS-RA registry.
Methods: The Tool for Administrative Reimbursement Drug Information Sharing (TARDIS) is an electronic platform combining the collection of data from all Belgian patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) on biologic (b) and targeted synthetic (ts) DMARDs, together with the submission of a request for reimbursement of this medication. Therapy choice after failure of 2 classical synthetic (cs) DMARD is left at the discretion of the treating physician in Belgium. Therapy is prolonged after 3 months for tsDMARDS and after 6 months for bDMARDs if treatment is effective. Our aim was to investigate which factors are associated with a successful prolongation of therapy in the TARDIS-RA registry.
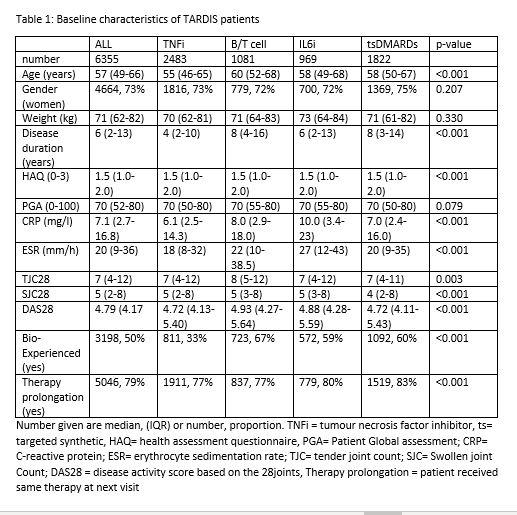
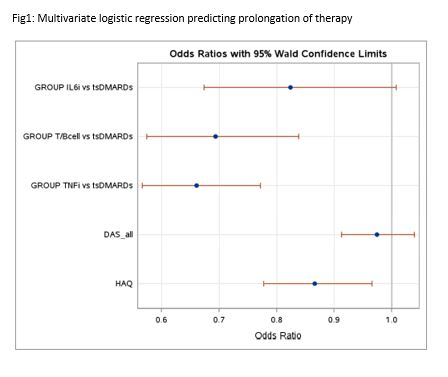
Results: We could include 6355 drug observations in 5471 unique patients. Table 1 describes this population in detail. In univariate logistic regression, prolongation of therapy was associated with lower baseline Patient Global Assessment (p=0.032), lower baseline disease activity score (p=0.036), lower baseline Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) score (p=0.003) and starting at baseline tsDMARD therapy instead of either TNFi (p< 0.001), T/B cell (p< 0.001) or IL6 inhibition therapy (p=0.049) therapy. In multivariate logistic regression, prolongation of therapy remained associated with lower baseline HAQ score (p=0.022) and starting at baseline tsDMARD therapy instead of either TNFi (p< 0.001) or T/B cell (p< 0.001) therapy (Figure 1). Sensitivity analyses in advanced therapy naïve patients confirmed these results, but in advanced therapy experienced patients, baseline HAQ score became statistically insignificant (p=0.780).
Conclusion: TsDMARD therapy and lower baseline HAQ scores seem to be associated with more prolongations of therapy, even after adjusting for other confounding factors. However, the absolute difference between groups is small as all therapies show high rates of therapy prolongation, indicating effective initial therapy choices by Belgian rheumatologists.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
De Cock D, Durez P, Elewaut D, Lauwerys B, Westhovens R, Verschueren P. tsDMARD Therapy Is Associated with More Initial Therapy Prolongations Compared to bDMARDs Both in Bionaive and Bioexperienced Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tsdmard-therapy-is-associated-with-more-initial-therapy-prolongations-compared-to-bdmards-both-in-bionaive-and-bioexperienced-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tsdmard-therapy-is-associated-with-more-initial-therapy-prolongations-compared-to-bdmards-both-in-bionaive-and-bioexperienced-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/