Session Information
Date: Wednesday, November 15, 2023
Title: Abstracts: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes IV: Outcomes & Comorbidity
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Avascular necrosis (AVN) can be a debilitating complication of autoimmune diseases and steroid treatment, with a higher prevalence in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) (0.8-33%) compared to rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (0.4%-12). AVN frequently leads to progressive joint destruction necessitating arthroplasty. Limited research exists on trends following the introduction of newer steroid-sparing agents as well as sociodemographic and clinical factors associated with AVN. We aimed to analyze rates, trends, and characteristics associated with AVN and AVN-related joint arthroplasties among SLE and RA hospitalizations using the largest publicly available all-payer inpatient US database, the National Inpatient Sample (NIS).
Methods: This cross-sectional study used NIS data (2000-2019) to identify hospitalized adults (≥18 years) with diagnoses of SLE and RA, and those with concomitant AVN diagnoses using validated International Classification of Disease (ICD) codes. AVN was further grouped into whether or not they had arthroplasties to examine trends. We compared SLE and RA hospitalizations with and without AVN, and arthroplasties using STATA and the Joinpoint regression program to calculate annual percent change (APC).
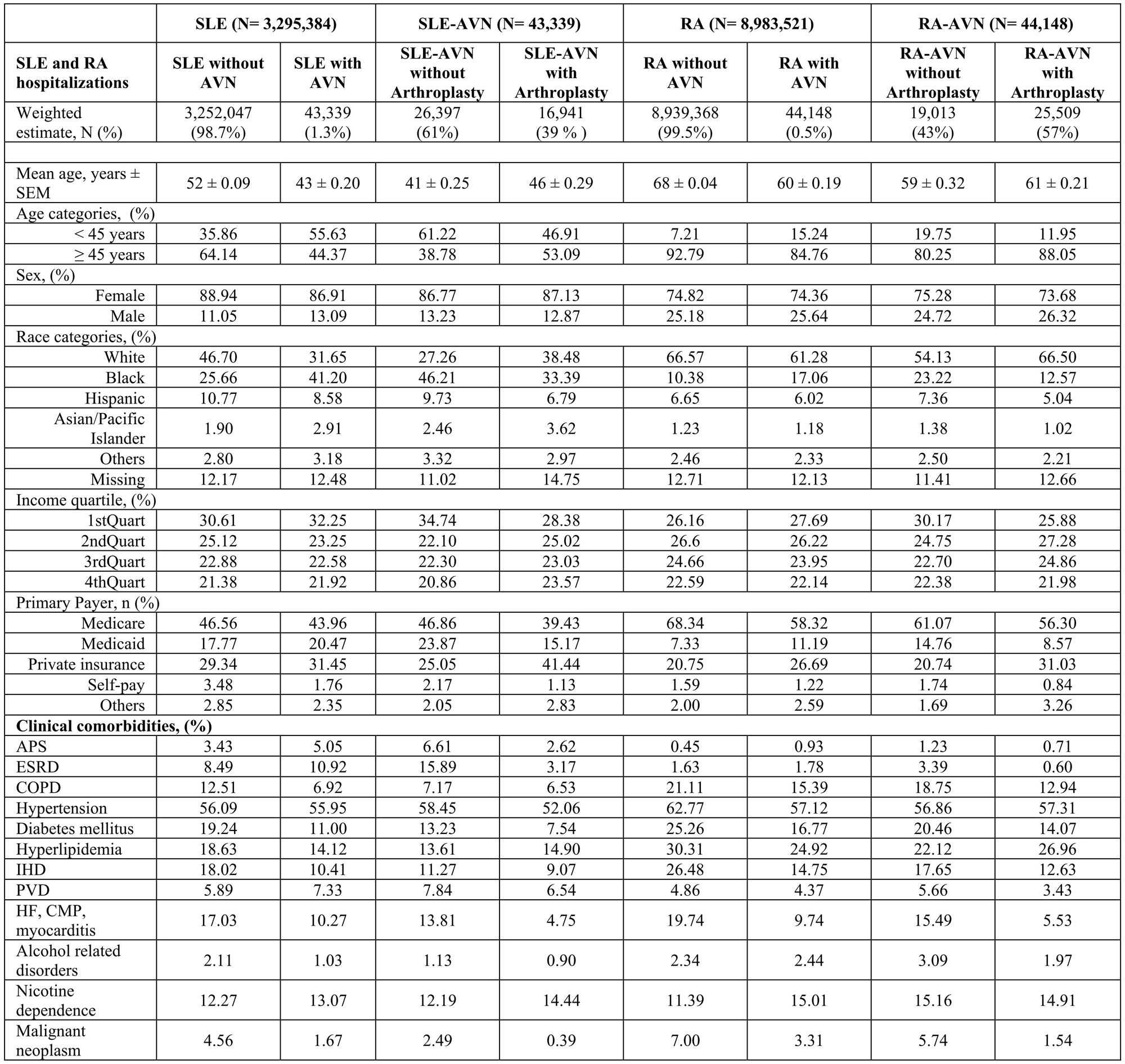
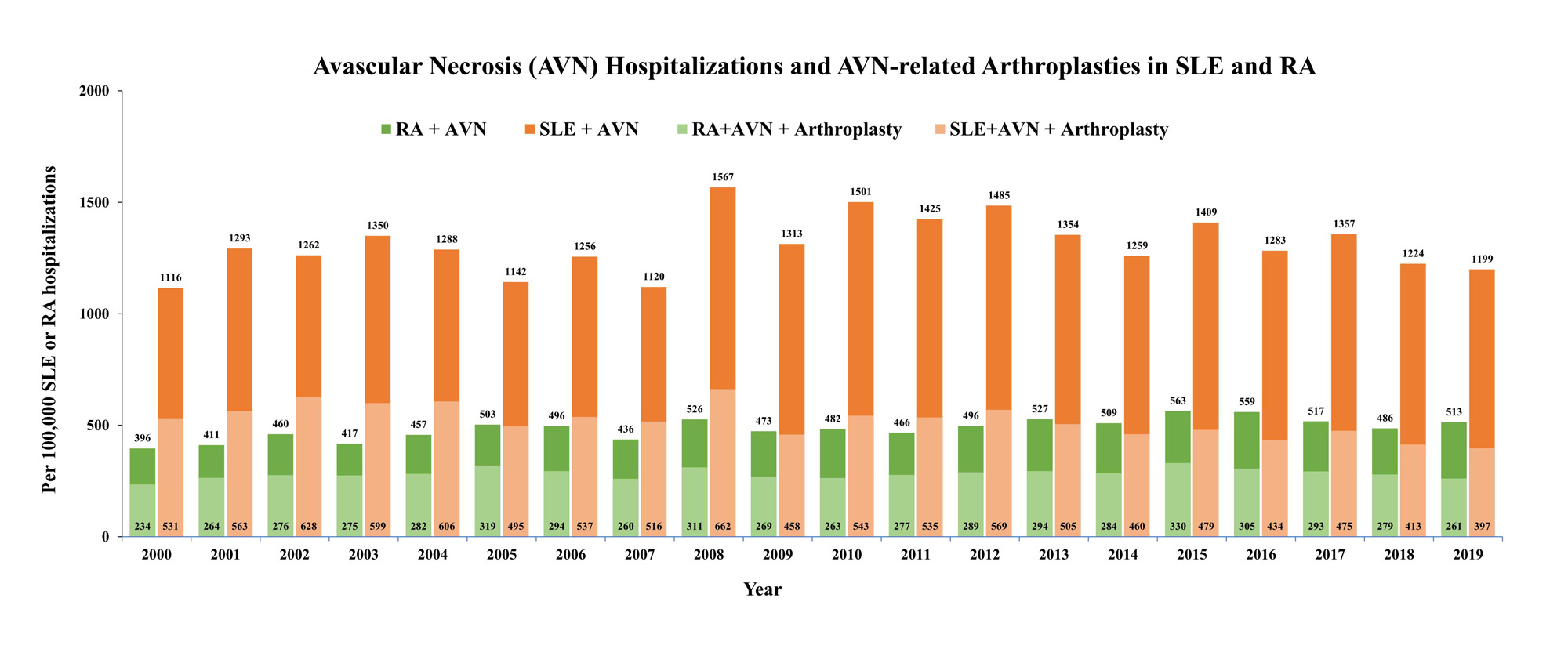
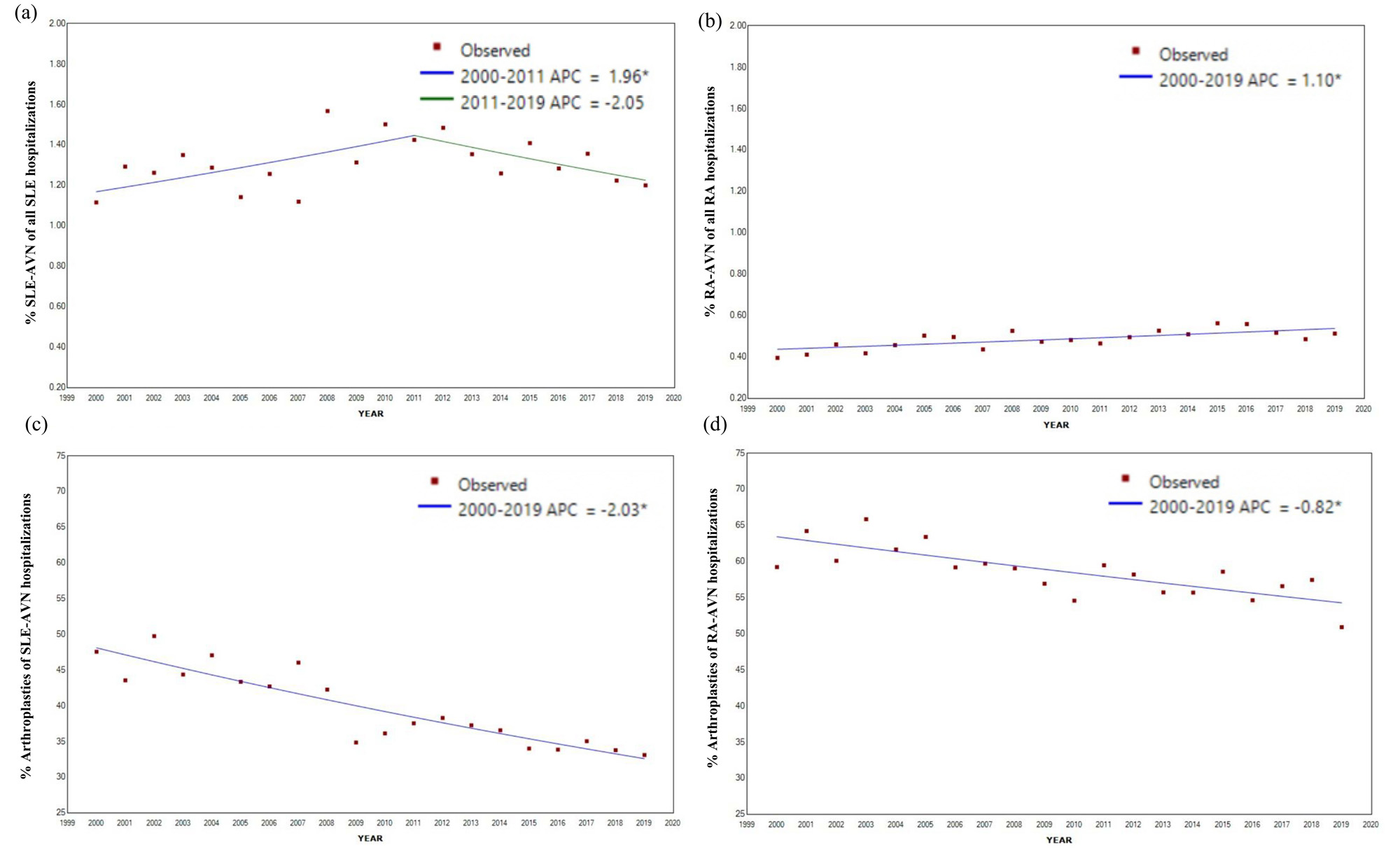
Results: From 2000-2019, there were 3,295,384 SLE and 8,983,521 RA hospitalizations, among which 43,339 (1.3%) and 44,148 (0.5%) had concomitant AVN (herein referred to as SLE-AVN and RA-AVN, respectively; Table 1). Of the SLE-AVN and RA-AVN, 16,941 (39%) and 25,509 (57%) underwent arthroplasties, respectively (Table 1, Figure 1). We observed an uptrend in RA-AVN (APC: 1.10*), with a decrease in the proportions of arthroplasties (APC: -0.82*; Figure 2). In contrast, there was an initial increase followed by a tendency to decline in SLE-AVN (APC 2000-2011: 1.96* APC 2011-2019 -2.05), with a decrease in the proportion of arthroplasties over time (APC -2.03*, Figure 2). Hospitalizations with AVN were younger [SLE (mean age: 43 vs 52 without), RA (mean age: 60 vs 68 without)] and more often Black race [SLE (41% Black with AVN, 26% without), RA (17% with AVN vs 10% without); Table 1]. SLE-AVN patients had higher rates of antiphospholipid syndrome (5% vs 3%) and end-stage renal disease (11% vs 9%); RA-AVN patients had higher nicotine use (15% vs 12%) compared to those without AVN. Among SLE-AVN and RA-AVN, encounters with arthroplasty (Table 1) were less likely to be Black (34% vs 46% in SLE-AVN and 13% vs 23% in RA-AVN) or have Medicaid coverage (15% vs 24% for SLE-AVN, and 9% vs 15% for RA-AVN) or most comorbidities than those without.
Conclusion: We report an initial increasing trend of SLE-AVN followed by a tendency to decline, which may relate to newer steroid-sparing therapies (i.e., Belimumab approval in 2011). There was an overall declining trend of AVN-associated arthroplasties in both SLE and RA. AVN hospitalizations were more likely to be younger and of the Black race. Yet, arthroplasty was less likely in encounters with patients who were Black or had Medicaid coverage. Our data indicate potential healthcare disparities that may influence surgical access. Further research should examine sociodemographic and treatment differences impacting AVN and arthroplasty rates.
*SLE: systemic lupus erythematosus, RA: rheumatoid arthritis, AVN: avascular necrosis, SEM: standard error of mean
APS: Antiphospholipid syndrome ESRD: End-stage renal disease IHD: Ischemic heart disease PVD: Peripheral vascular disease HF: Heart failure, CMP: cardiomyopathy
Differences in variables between groups are significant with p < 0.05 except for:
SLE without AVN vs SLE with AVN: hypertension;
SLE-AVN without and with arthroplasty: sex, COPD, hyperlipidemia, alcohol-related disorders;
RA without AVN vs RA with AVN: sex, ESRD, alcohol-related disorders;
RA-AVN without and with arthroplasty: sex, hypertension, nicotine dependence
Green represents RA, orange represents SLE, arthroplasties are represented by lighter shading.
(a) The percentage of AVN among SLE hospitalizations shows an initial significant uptrend (APC 1.96*) with a peak around 2011
(b) The percentage of AVN among RA hospitalizations shows a modest significant uptrend over time (APC 1.10*), however, rates are lower compared to SLE-AVN.
(c) AVN-related arthroplasties in both SLE-AVN (APC _2.03*) and (d) RA-AVN (APC -0.82*) show a significant decline over time.
The rate of change from 2000 to 2019 was calculated using Joinpoint regression software and expressed as Annual Percent Change (APC). *Indicates significant difference at alpha = 0.05 level.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dhital R, Singh N, Pedersen B, Bartels C. Trends, Sociodemographic and Clinical Factors Associated with Avascular Necrosis and Related Arthroplasties in Hospitalized Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/trends-sociodemographic-and-clinical-factors-associated-with-avascular-necrosis-and-related-arthroplasties-in-hospitalized-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-and-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/trends-sociodemographic-and-clinical-factors-associated-with-avascular-necrosis-and-related-arthroplasties-in-hospitalized-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-and-rheumatoid-arthritis/