Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) exhibits varied epidemiological patterns across states in the United States, influencing disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), incidence rates, prevalence, and mortality. This study aims to analyze the incidence, prevalence, death, and DALY trends in RA from 1991 to 2021 at a state level in the United States.
Methods: The Global Burden of Disease database was used to extract age-standardized incidence, prevalence, death, and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) of Rheumatoid Arthritis from 1991 to 2021 for both males and females across all states of the U.S. We then calculated the percent change in the rates between 1990 and 2021.
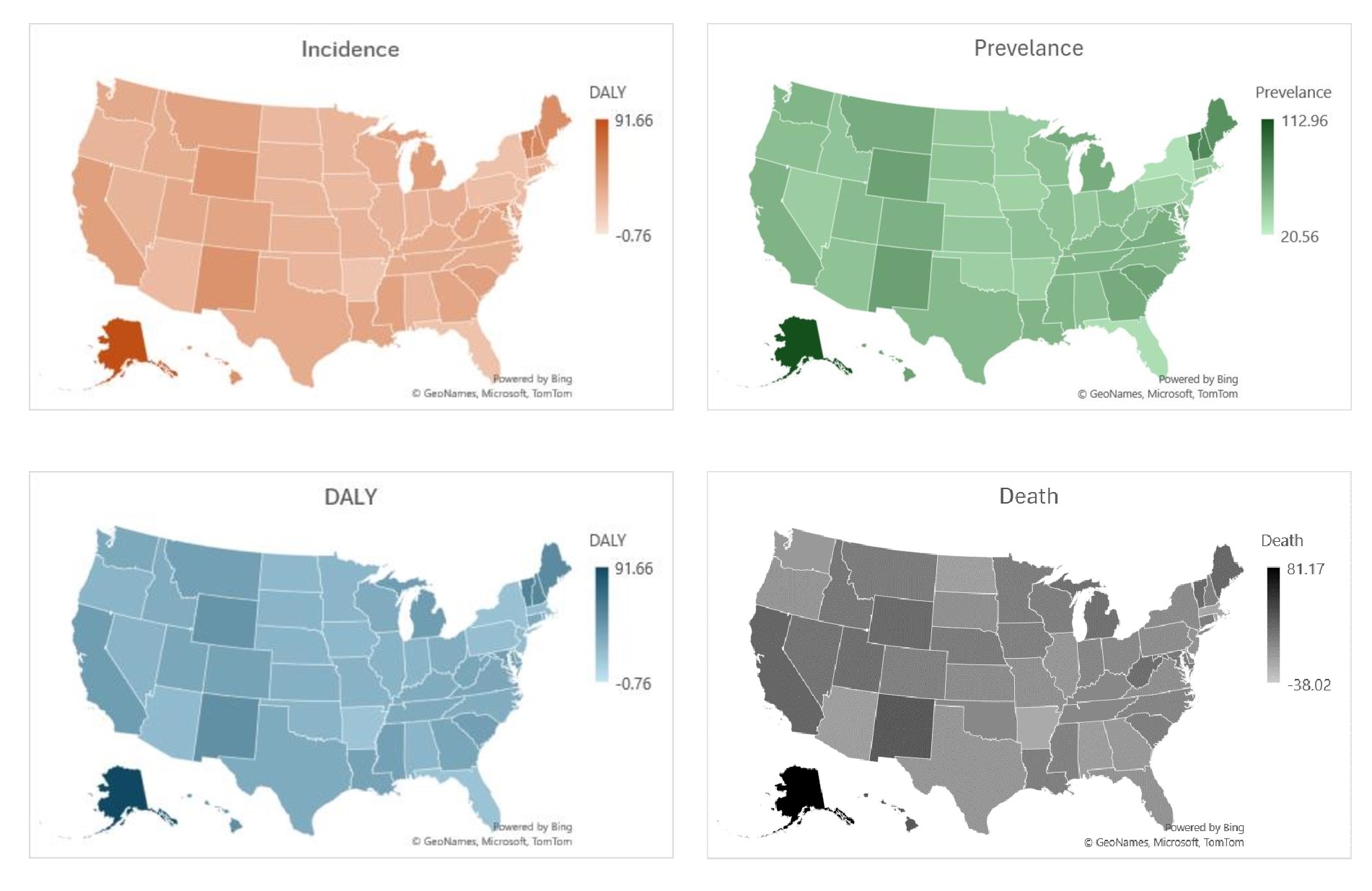
Results: The incidence, prevalence, DALYs, and death related to RA in the United States increased by 42.86%, 48.29%, 31.51%, and 1.36% respectively between 1991 and 2021. Analyzing data from multiple states reveals significant disparities in RA burden (Figure 1). States like Alaska and Maine record higher DALYs, exceeding 90, indicating substantial disability attributed to RA. Conversely, states such as Florida and North Dakota report lower DALYs, suggesting a relatively lower disability impact. Incidence rates highlight Arizona and Hawaii with rates exceeding 50 cases per 100,000 population annually, contrasting with lower incidence in states like Alabama and Arkansas. Prevalence rates demonstrate a similar distribution, with higher rates observed in states such as Vermont and Minnesota. Mortality rates related to RA vary across states, with Alaska and Idaho showing elevated rates, while Delaware and Vermont exhibit lower mortality impacts.
Conclusion: The rising incidence and disparity in rheumatoid arthritis among different states over time may be influenced by several factors, including increased and early recognition and treatment of the disease, genetic and environmental predispositions (such as smoking and pollution), greater use of immunosuppressive medications, variations in healthcare access, socioeconomic status, social habits, and public health policies. These results highlight the need for targeted interventions to mitigate the increasing disease burden of rheumatoid arthritis. Future studies are needed to identify the factors contributing to the disparity.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Vijaya Prakash A, Hosur Ravishankar V, Sudheer A, Piranavan P. Trends in Rheumatoid Arthritis Incidence, Prevalence, DALY and Death Rates (1991-2021) in the United States: A Comprehensive Analysis of State-Level Disparities [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/trends-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-incidence-prevalence-daly-and-death-rates-1991-2021-in-the-united-states-a-comprehensive-analysis-of-state-level-disparities/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/trends-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-incidence-prevalence-daly-and-death-rates-1991-2021-in-the-united-states-a-comprehensive-analysis-of-state-level-disparities/