Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Despite the increasing availability of newer RA therapies, there is a paucity of data comprehensively evaluating long-term trends for individual DMARDs in the US. The objective of this study was to evaluate patterns in DMARD initiations between 2001 and 2021 among US adults with RA.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study was conducted using a US commercial claims database from 2001 to 2021. A cohort of patients with RA (≥18 years) newly initiating a DMARD was identified. For each calendar year, we calculated the proportion of initiations for 22 individual DMARDs, also grouped into categories of: conventional synthetics (csDMARDs), biologics (bDMARD), and targeted synthetics (tsDMARDs). Secondary analyses included an examination of trends in the first-line use of non-csDMARDs and the uptake of biosimilars.
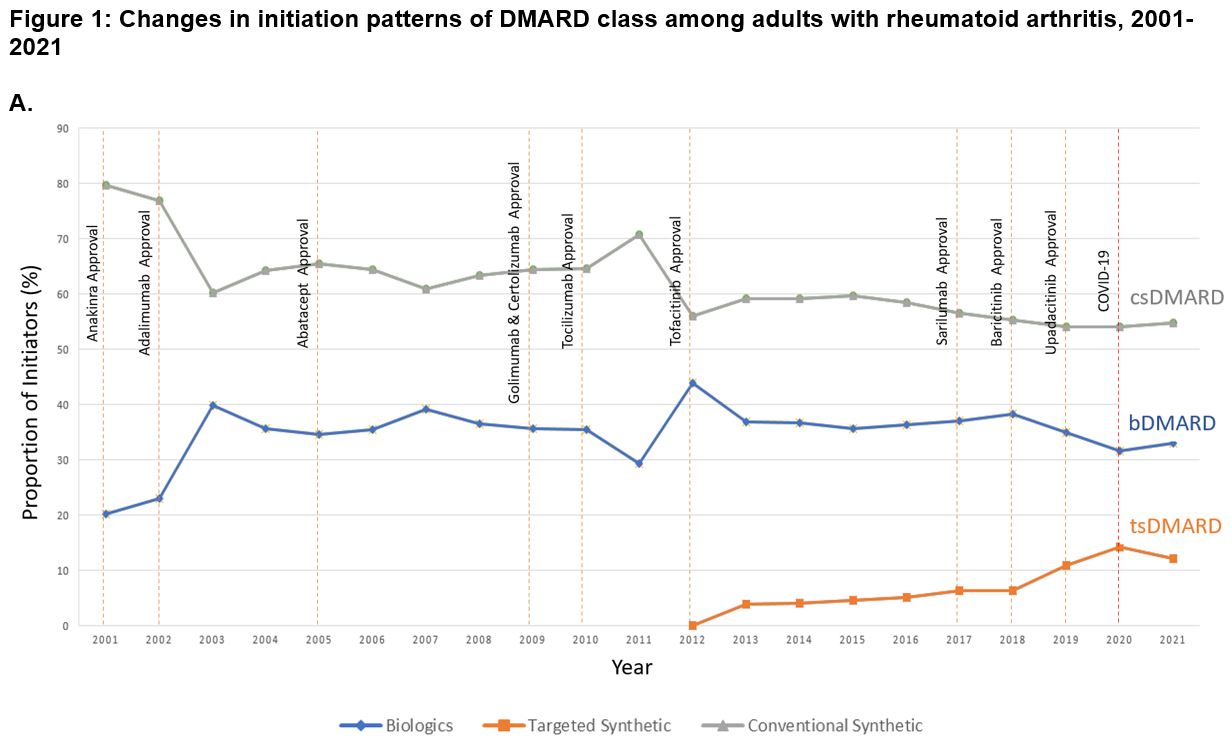
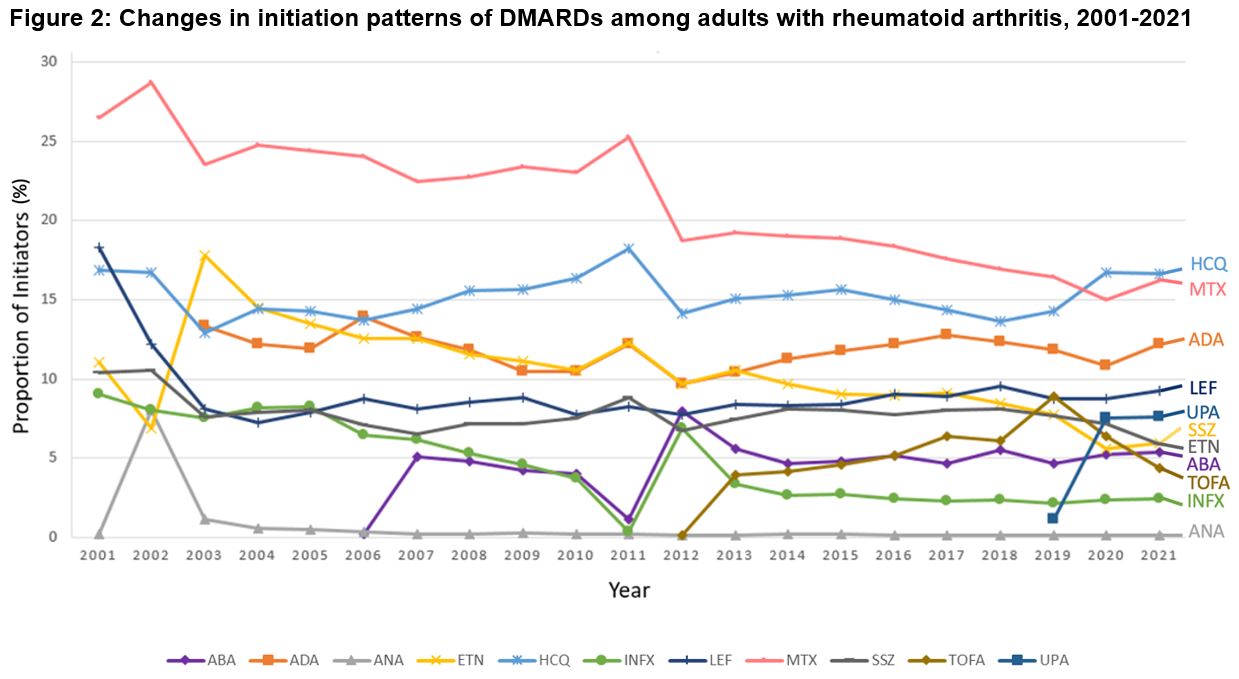
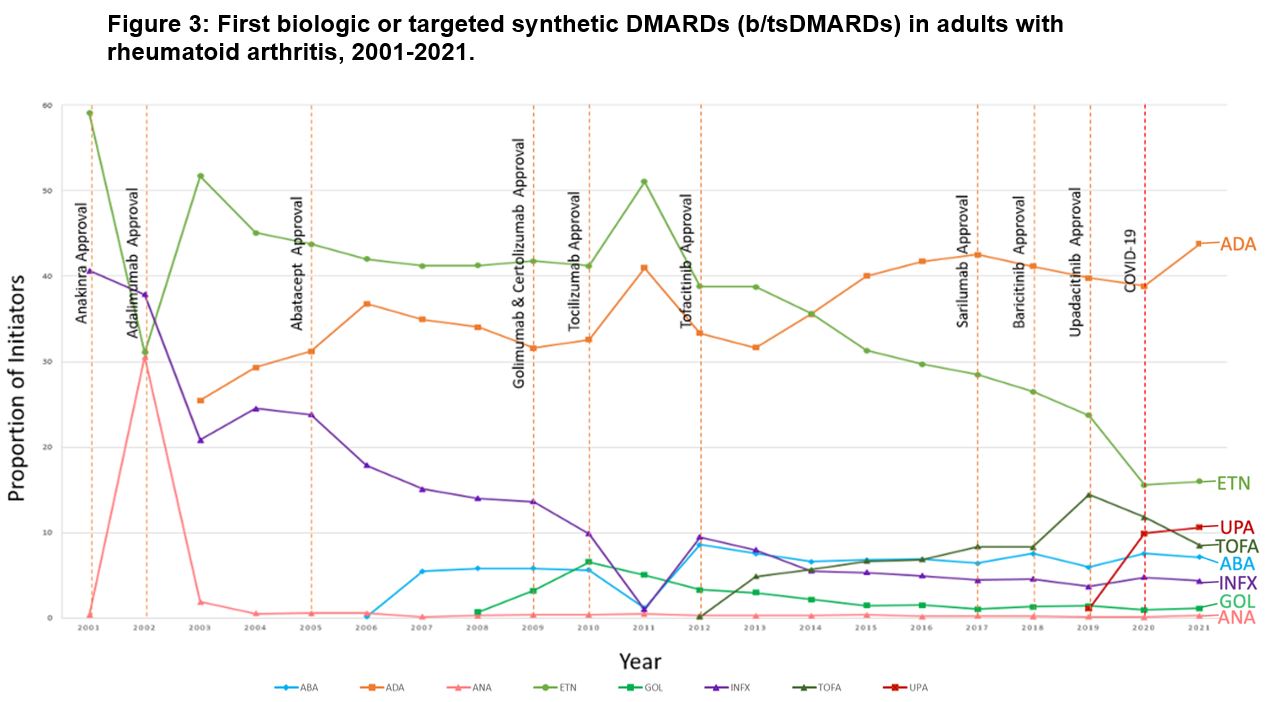
Results: We identified 407,728 DMARD initiation episodes among 229,365 unique patients with RA (median age: 50 [IQR, 44-58 years]; 79.4% female subjects). There were shifts in DMARD utilization, with csDMARD use declining from 79.7% of initiations in 2001 to 54.7% by 2021 (p< 0.001 for trend; Figure 1). Meanwhile, bDMARDs and tsDMARDs initiations increased from 20.3% in 2001 to 33.1% in 2021 (p< 0.001) and from 0.1% in 2014 to 12.2% in 2021 (p< 0.001), respectively. Methotrexate remained the most initiated DMARD over the 21-year study period, albeit declining from 28.7% to 15.0% of initiations over the study period (p< 0.001; Figure 2). Adalimumab was the most frequently initiated bDMARD (13.3% in 2003 and 12.2% in 2021; p=0.05). Among tsDMARDs, tofacitinib use peaked in 2019 (8.9%) and declined to 4.4% in 2021, while upadacitinib use increased from 1.2% to 7.6% during the same period (p< 0.001). For secondary analyses, adalimumab was the predominant first-line b/tsDMARD initiated ( >40%), as seen in Figure 3. Uptake of biosimilars remained low (< 1%) throughout the study period.
Conclusion: Our study provides valuable insights into the evolving landscape of DMARD treatment among US adults with RA. While csDMARDs continue to be a mainstay in treatment regimens, their dominance is gradually diminishing in favor of bDMARDs and, more recently, tsDMARDs. This trend underscores the nuanced preferences and trade-offs made by clinicians and patients, balancing considerations of effectiveness, safety, costs, and convenience. As new DMARDs and biosimilars emerge, future research is needed to examine their impact on real-world treatment patterns.
Abbreviations: DMARD, disease-modifying antirheumatic drug, csDMARD, conventional synthetic DMARD, bDMARD, biologic DMARD, tsDMARD, targeted synthetic DMARD, COVID_19, Coronavirus disease 2019
Abbreviations: DMARD, disease-modifying antirheumatic drug, COVID_19, Coronavirus disease 2019, HCQ, hydroxychloroquine, MTX, methotrexate, ADA, adalimumab, LEF, leflunomide, UPA, upadacitinib, SSZ, sulfasalazine, ETN, etanercept, ABA, abatacept, TOFA, tofacitinib, INFX, infliximab, ANA, anakinra
Abbreviations: DMARD, disease-modifying antirheumatic drug, ADA, adalimumab, ETN, etanercept, UPA, Upadacitinib, TOFA, tofacitinib, ABA, abatacept, INFX, infliximab, GOL, golimumab, ANA, anakinra, COVID_19, Coronavirus disease 2019
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lee L, Sparks J, Yalamanchili P, Horton D, Khan Z, Barone J, Dave C. Trends in Initiation of Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs for Rheumatoid Arthritis Among Commercially-Insured US Adults, 2001-2021 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/trends-in-initiation-of-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-among-commercially-insured-us-adults-2001-2021/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/trends-in-initiation-of-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-among-commercially-insured-us-adults-2001-2021/