Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Limited data are available on whether patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are treated with conventional disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (cDMARDs) according to the current recommendations before they initiate biologic DMARDs (bDMARDs) or JAK inhibitors (JAKis). We examined the treatment patterns among Korean RA patients who received bDMARDs or JAKis in a real world setting, using the 2002-2016 Korean National Health Insurance Service database that covers the entire Korean population.
Methods: We identified RA patients who initiated bDMARDs (TNF inhibitor, abatacept, rituximab and tocilizumab) or JAKis (tofacitinib). Their treatment patterns during 1 year after RA diagnosis (defined as free of any RA diagnosis or any DMARD use for one year before the diagnosis) and prior to the initiation of index drugs (bDMARDs or JAKis) were examined regarding: initial cDMARD used, dose and parenteral use of methotrexate (MTX), use and time to combination therapy of cDMARDs, and steroid use.
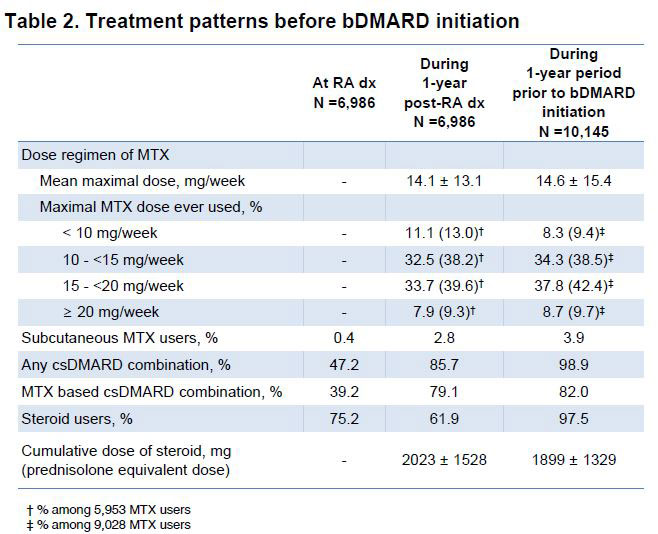
Results: 10,145 RA patients were identified who used index drugs from the database (mean age 57 years, 82% female). Among them, 6,986 patients had identifiable dates for RA diagnosis (mean age 57 years, 79% female). The mean (SD) duration from RA diagnosis to index drug initiation was 1,425 (1,162) days with 1,509 (22%) patients having a duration ≤1 year. At diagnosis, the most common 1st cDMARD used was hydroxychloroquine (63%), followed by MTX (55%) and sulfasalazine (29%) with steroids used in 75%. During the 1 year from the diagnosis, 85% of patients eventually used MTX, 42% ever used MTX ≥ 15mg/week, only 3% used parenteral MTX, and 85% patients used combined cDMARDs with a mean 188 days from the RA diagnosis to combination therapy. Patients whose maximal MTX dose reached 20mg/week were rare (9%) and 62% were still on steroid after 1 year. During the 1 year prior to the index drug use (n = 10,145), the most common cDMARD was MTX used in 89% patients with 46% who ever used ≥ 15mg/week and 4% of parenteral users, followed by hydroxychloroquine (55%), leflunomide (52%), sulfasalazine (38%), and tacrolimus (20%). All patients used combination therapy and 98% steroids.
Conclusion: These data indicate that a substantial proportion of RA patient did not try maximal dose or parenteral use of MTX during the 1 year post-diagnosis as recommended by the current treatment guideline. Instead, they often used cDMARDs combination therapy. During the 1 year before initiating bDMARDs or JAKis, they were treated with intensive cDMARD combination therapy rather than escalating their MTX dose
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kim M, Shin A, Shin S, Ha Y, Lee Y, Lee E, Song Y, Kang E. Treatments Patterns Among Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with a Biologic Disease-modifying Anti-rheumatic Drug: A Nation-wide Study in Korea [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatments-patterns-among-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-with-a-biologic-disease-modifying-anti-rheumatic-drug-a-nation-wide-study-in-korea/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatments-patterns-among-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-with-a-biologic-disease-modifying-anti-rheumatic-drug-a-nation-wide-study-in-korea/