Session Information
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor. Minimum clinically important differences (MCID) for SPondyloArthritis Research Consortium of Canada (SPARCC) MRI SI joint and spine scores (SIJ, spine) are ≥2.5 and ≥5, respectively.1 We assessed whether MCID in SIJ and spine can discriminate between tofacitinib and placebo (PBO) in patients (pts) with AS and whether this is concordant with clinical responses.
Methods: In this 16-week (wk), Phase 2, double-blind, dose-ranging study (NCT01786668),2 207 adult pts meeting modified New York AS criteria were randomized 1:1:1:1 to PBO or tofacitinib 2, 5, or 10 mg twice daily (BID) for 12 wks. Clinical response endpoints included in this post-hoc analysis were: Assessment of AS 20% improvement (ASAS20) and ASAS40 response rates, AS disease activity score major improvement (ASDAS MI), ASDAS <1.3, Bath AS disease activity index (BASDAI), Bath AS functional index (BASFI). Pts (%) achieving MCID in SIJ, spine, both SIJ and spine, in tofacitinib and PBO groups were summarized based on observed data and pooled tofacitinib vs PBO were compared using Fisher’s exact test. Concordance between achieving MCID and Wk 12 clinical responses was assessed. Wk 12 clinical responses were compared between pts achieving/not achieving MCID.
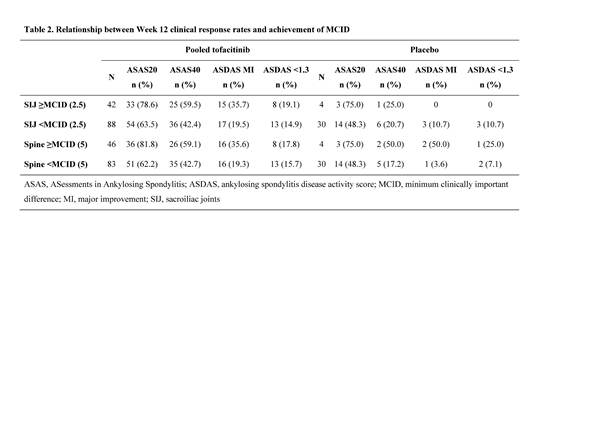
Results: MRI data for 164 pts were evaluated. Baseline demographics were generally balanced between treatment groups and typical of AS populations. All tofacitinib doses improved SIJ and spine scores vs PBO; proportion of pts achieving MCID in SIJ or spine was ~3 times higher in pooled tofacitinib group vs PBO (Table 1; p<0.05 for SIJ, p<0.01 for spine). Achieving MCID in SIJ and spine correlated with clinical response. In pts on tofacitinib, ASAS20, ASAS40, ASDAS MI, and ASDAS <1.3 responses were more likely in pts achieving MCID in SIJ, spine (Table 2), or both SIJ and spine vs not achieving MCID. Compared with not achieving MCID, pts on tofacitinib achieving MCID in SIJ had larger improvements in BASDAI, BASFI, and back pain.
Conclusion: Tofacitinib-treated pts with AS experienced clinically meaningful reductions in axial MRI inflammation. Pts achieving MCID for MRI inflammation had increased clinical response rates. References 1. Maksymowych WP et al. J Rheumatol 2012; 39: 1666-1674. 2. van der Heijde D et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2015; 67: Abstr 5L. 
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Maksymowych W, van der Heijde D, Baraliakos X, Deodhar AA, Brown M, Sherlock S, Li D, Fleishaker D, Hendrikx T. Treatment with Tofacitinib Is Associated with Clinically Meaningful Reductions in Axial MRI Inflammation in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-with-tofacitinib-is-associated-with-clinically-meaningful-reductions-in-axial-mri-inflammation-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-with-tofacitinib-is-associated-with-clinically-meaningful-reductions-in-axial-mri-inflammation-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis/
