Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Systemic Sclerosis, Fibrosing Syndromes and Raynaud's – Clinical Aspects and Therapeutics Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Compared with placebo, treatment with cyclophosphamide (CYC) improved lung function in patients with systemic sclerosis-related interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD) after 1 year in Scleroderma Lung Study (SLS) I.1 However, the effects of CYC waned after monitoring patients for an additional year off therapy.2 In SLS II (comparing CYC and mycophenolate [MMF]), treatment with 1-year of CYC appeared to have a more sustained effect on lung function over 2-years, although SLS II used a different analysis approach than SLS I.3 To further understand the effects of CYC on SSc-ILD outcomes, the present analysis directly compared outcomes between the CYC arms of SLS I and II.
Methods: Participants enrolled in the CYC arms of SLS I (N=79) and II (N=73) were included. SLS I and II randomized participants to oral CYC for 1 year and followed patients for an additional year off therapy (In SLS II, patients received placebo in the second year). Eligibility criteria for SLS I and II were nearly identical. Outcomes included the FVC%-predicted and DLCO%-predicted (measured every 3 months) and quantitative radiographic extent of ILD (QILD) (measured at 1 and 2 years for SLS I and SLS II, respectively). Joint models were created to evaluate the treatment effect on the course of the FVC/DLCO over 2-years while controlling for baseline disease severity.
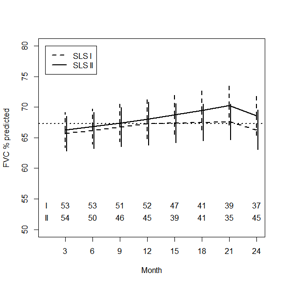
Results: SLS II-CYC participants had similar baseline characteristics compared with SLS I-CYC participants in terms of gender (75% vs. 77% female), disease duration (mean [SD] years: 2.6 [1.8] vs. 3.1 [2.3]), and FVC%-predicted (mean [SD]: 66.9 [9.9] vs. 67.6 [11.4]), respectively. SLS II-CYC patients were slightly older (mean [SD] years: 52.2 [9.6] vs. 48.4 [12.2]; P=0.037) and had a higher DLCO%-predicted (mean [SD]: 54.5 [14.6] vs. 47.2 [13.9]; P=0.0002) than SLS I-CYC participants. After adjusting for baseline QILD and FVC%-predicted, there was no difference in the course of the FVC%-predicted between the CYC arms of SLS I and II (P=0.535), nor the DLCO%-predicted (P=0.172). In both groups, treatment with CYC led to a significant improvement in the FVC%-predicted from 3-12 months, but no significant improvement beyond this point (Figure 1). Treatment with CYC had no effect on the DLCO for either group.
Conclusion: Although there are limitations in comparing participants from two trials, the baseline characteristics of the SLS I and SLS II participants were relatively similar. Treatment with 1 year of oral CYC led to similar improvements in lung function in both SLS I and II, although the effects were not sustained following CYC cessation. There results suggest that increasing the duration of ILD therapy may improve outcomes for SSc-ILD patients.
References:
1. NEJM 2006;354:2655-66.
2. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2007;176:1026-34.
3. Lancet Resp Med 2016;4:708-19.
Figure 1. Course of the FVC%-predicted by CYC treatment
arm based on a joint model analysis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Volkmann ER, Tashkin DP, Sim M, Li N, Khanna D, Roth M, Clements PJ, Hoffmann-Vold AM, Furst DE, Kim G, Goldin J, Elashoff R. Treatment with Cyclophosphamide for Systemic Sclerosis-Interstitial Lung Disease Does Not Lead to a Sustained Improvement in Lung Function in Two Independent Cohorts [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-with-cyclophosphamide-for-systemic-sclerosis-interstitial-lung-disease-does-not-lead-to-a-sustained-improvement-in-lung-function-in-two-independent-cohorts/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-with-cyclophosphamide-for-systemic-sclerosis-interstitial-lung-disease-does-not-lead-to-a-sustained-improvement-in-lung-function-in-two-independent-cohorts/