Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: RA – Treatments Poster II: PROs, Biomarkers, & Systemic Inflammation (1223–1256)
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Fatigue is very common in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and impairs patient quality of life. Baricitinib (BARI) improved fatigue, pain and other patient-reported outcomes (PROs) in patients with active RA and an inadequate response (IR) to conventional synthetic DMARDs (csDMARDs), or to ≥1 tumor necrosis factor inhibitors or other biological DMARDs (bDMARDs).1-3 The aim of the current analysis was to investigate the effects of BARI on fatigue that are influenced by disease activity and those that are independent of disease activity in patients from the RA-BEAM and RA-BEACON trials.
Methods: Data were analyzed from two phase 3 studies, RA-BEAM (NCT01710358, methotrexate (MTX)-IR patients) and RA-BEACON (NCT01721044, bDMARD-IR patients). All trial patients had a diagnosis of adult-onset RA as defined by the ACR/EULAR 2010 Criteria for the Classification of RA.4 Fatigue was assessed by the Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue scale (FACIT-F). In a mediation analysis, the dependent variable was the change from baseline to week 12, 16, 20 or 24 for FACIT-F. The treatment (BARI 4-mg vs. placebo (PBO) or adalimumab (ADA) vs. PBO) was the independent variable. Changes in Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) from baseline to week 12, 16, 20 or 24 were used as the mediator variables. The total treatment effect on fatigue over PBO that can be accounted for by changes in CDAI is the ‘‘indirect’’ or mediation effect; whereas the total treatment effect that cannot be accounted for by the mediation effect is the ‘‘direct’’ effect. The random-intercept cross-lagged panel model (RI-CLPM) was applied for mediation analysis.5
Results: In MTX-IR patients (RA-BEAM trial), disease activity-mediated effect accounted for 50-60% of the fatigue improvement in both BARI 4-mg and ADA over PBO. The total effect, direct effect (i.e., those not associated with disease activity), and mediation effect of treatment on fatigue relief continuously increased in BARI 4-mg group from Week 12 to Week 24 (Table 1). Additionally, the total effect and mediation effect of BARI 4-mg over PBO on FACIT-F were numerically greater than that of ADA over PBO from Week 12 to 24. The direct fatigue relief effect of BARI 4-mg over placebo was significant starting Week 16, but that of ADA was not. In bDMARD-IR patients (RA-BEACON trial), about 20-30% of the effects of BARI 4-mg on FACIT-F were independent of disease activity.
Conclusion: Irrespective of being MTX-IR or bDMARD-IR, BARI 4-mg had a proportion of effects on fatigue that were independent of disease activity in patients with active RA. The direct fatigue relief effect of BARI 4-mg over placebo was significant starting Week 16, whereas that of ADA was not.
References
1Keystone EC, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2017;76:1853–1861.
2 Emery P, et al. RMD Open 2017; 3:e000410
3Smolen et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(4):694-700.
4Aletaha D, et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(9):2569-2581.
5Burns RA, et al. Br J Educ Psychol. 2020;90(1):77-91.
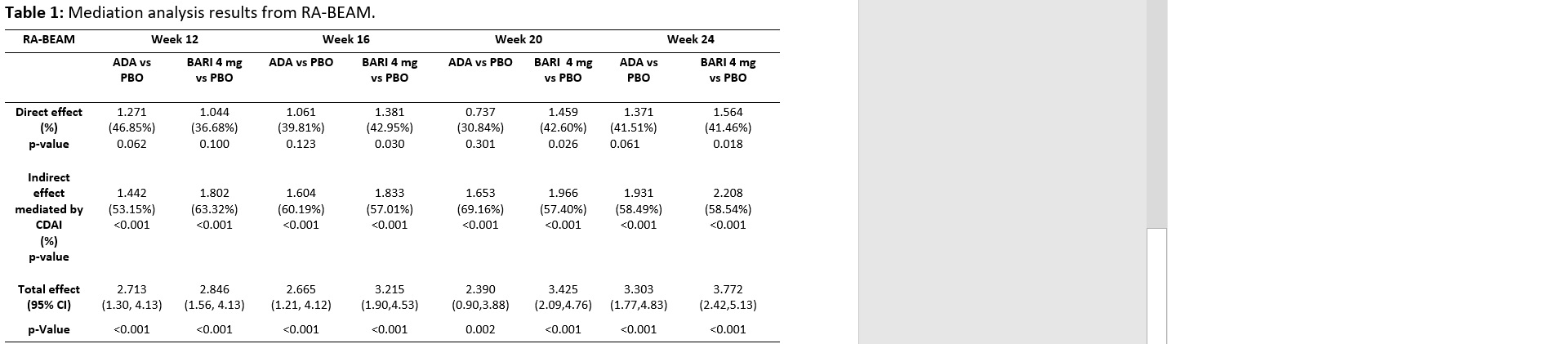 Abbreviations: ADA= Adalimumab, BARI=baricitinib, CDAI= Clinical Disease Activity Index, CIs= confidence intervals. Direct effect=the treatment effect that cannot be accounted by the indirect/mediation effect, indirect effect= The treatment effect on fatigue over PBO that was mediated/influenced by CDAI control. PBO=placebo.
Abbreviations: ADA= Adalimumab, BARI=baricitinib, CDAI= Clinical Disease Activity Index, CIs= confidence intervals. Direct effect=the treatment effect that cannot be accounted by the indirect/mediation effect, indirect effect= The treatment effect on fatigue over PBO that was mediated/influenced by CDAI control. PBO=placebo.
 Abbreviations: CDAI= Clinical Disease Activity Index, CIs=confidence intervals, Direct effect=the treatment effect that cannot be accounted by the indirect/mediation effect, indirect effect= The treatment effect on fatigue over PBO that was mediated/influenced by CDAI control.
Abbreviations: CDAI= Clinical Disease Activity Index, CIs=confidence intervals, Direct effect=the treatment effect that cannot be accounted by the indirect/mediation effect, indirect effect= The treatment effect on fatigue over PBO that was mediated/influenced by CDAI control.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fautrel B, Jia B, Wu J, Ji J, Birt J, Haladyj E, Takeuchi T. Treatment Effect of Baricitinib on Fatigue: Mediation Analysis Results from Two Phase 3 Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-effect-of-baricitinib-on-fatigue-mediation-analysis-results-from-two-phase-3-trials/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-effect-of-baricitinib-on-fatigue-mediation-analysis-results-from-two-phase-3-trials/
