Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 10, 2015
Title: Spondylarthropathies and Psoriatic Arthritis - Clinical Aspects and Treatment Poster III: Therapy
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The treat to target strategy (T2T), aiming at inactive disease
(ID), has become the recommended approach also in the field of axial-SpA
(axSpA) (1). Using the composite disease activity index “Ankylosing
Spondylitis Disease Activity Score” (ASDAS) we assessed the real life
feasibility of the T2T strategy in our cohort of axSpA patients treated with TNFα
inhibitors (TNFi). We analyzed potential differences among the Ankylosing
Spondylitis (AS) and the non-radiographic Ax-SpA (nr-ax-SpA) group and the
influence of the population characteristics and comorbidities in reaching ID.
Methods: The study population was selected from outpatients with axSpA on a
stable TNFi treatment for at least 6 months. Disease activity was
cross-sectionally evaluated in terms of BASDAI and ASDAS-CRP during the latest
follow up visit. ID was defined as ASDAS-CRP< 1.3. Extra-articular
manifestations and comorbidities were assessed. Statistical analysis performed
with STATA.
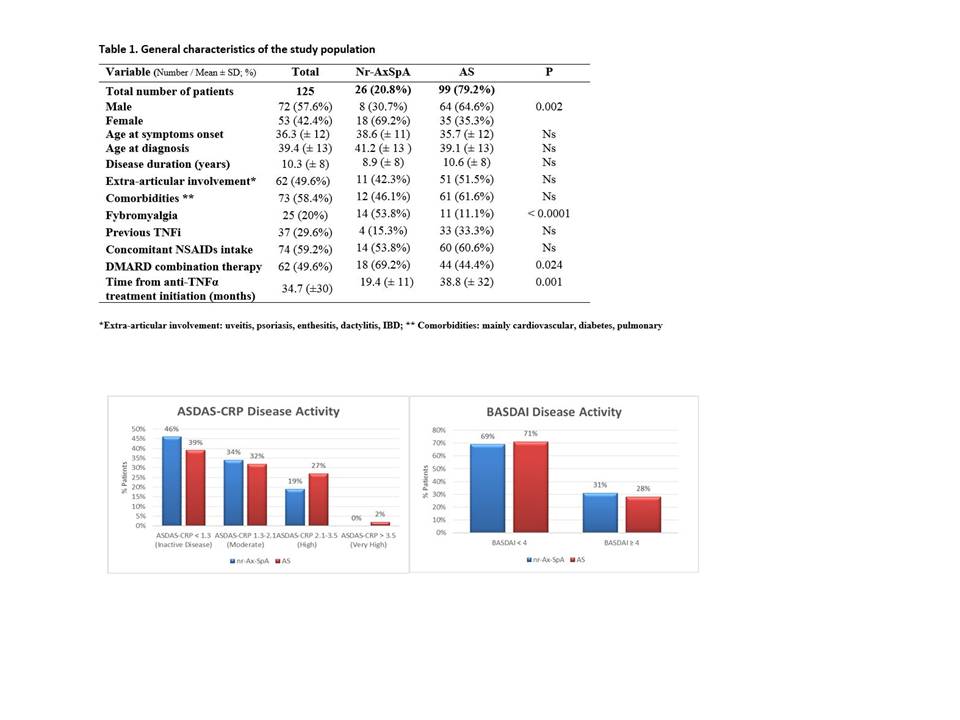
Results: General characteristics of the 125 enrolled patients are presented
in Table 1. Female sex, prevalence of fibromyalgia and frequency of
concomitant DMARDs were significantly more represented in the nr-ax-SpA group. On
the other hand, the time from TNFi initiation was significantly shorter in
nr-ax-SpA. ASDAS-CRP ID was reached by n=51 (40.8%) of our population, while a
good disease control would have been reached by n=89 (71.2%) of patients in
terms of BASDAI. There were no differences in the two groups, with a slightly
higher prevalence of ID in the nr-ax-SpA group not
reaching statistical significance (Figure 1). Multivariate logistic regression
demonstrated a negative correlation of fibromyalgia (OR 0.14; CI95% 0.02-0.77),
higher Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Metrology Index (BASMI) (OR 0.6;
CI95% 0.41-0.89) and number of previous TNFi (OR 0.36; CI95% 0.15-0.89) with
the chances of reaching ID. ID achievement resulted independent from sex, age,
disease duration, DMARDs, NSAIDs and other comorbidities.
Conclusion: The recommended T2T strategy represents a new challenge in the
management of ax-SpA, with recently introduced methods of measuring disease
activity being significantly more stringent. The prevalence of ID was not
influenced by the type of disease (nr-Ax-SpA Vs AS) but was significantly
influenced by the presence of concomitant fibromyalgia, decreased spine
mobility and the previous number of TNFi lines of treatment.
References
1. Smolen JS, et al.
Treating spondyloarthritis, including ankylosing spondylitis and psoriatic
arthritis, to target: recommendations of an international task force. Ann Rheum
Dis 2014; 73:6–16.
Figure 1. Differences
in Disease activity (ASDAS-CRP and BASDAI) among nr-ax-SpA and AS patients.
Disclosures: NONE
Conflict of interest and financial funding:
NONE
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Monti S, Codullo V, Grosso V, Breda S, Montecucco C, Caporali R. Treating Axial Spondyloarthritis to Target: Influence of the Population Characteristics and Comorbidities in Reaching Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) Inactive Disease in a Cohort of Patients Treated with Tnfalpha Inhibitors Agents [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treating-axial-spondyloarthritis-to-target-influence-of-the-population-characteristics-and-comorbidities-in-reaching-ankylosing-spondylitis-disease-activity-score-asdas-inactive-disease-in-a-c/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treating-axial-spondyloarthritis-to-target-influence-of-the-population-characteristics-and-comorbidities-in-reaching-ankylosing-spondylitis-disease-activity-score-asdas-inactive-disease-in-a-c/