Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster I: RA, Spondyloarthritis, & OA
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Treat-to-target is the foundation of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) management. Prioritizing routine measurement of patient-reported disease activity along with conventional physician, laboratory and imaging assessments is vital to achieving this target. However, in the practice setting, alliance with treat-to-target recommendations is often a challenge. A recent report published in Arthritis Care and Research demonstrates that only 35%-55% of patients change their treatment even when experiencing moderate to high disease activity as measured by either the Routine Assessment of Patient Index Data 3 (RAPID3) or Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) RA assessment tools using data from a national registry. Previous research has indicated that nurse-led care management may improve adherence to treat-to-target recommendations. The purpose of this study is to assess the rate of treatment changes among patients with RA who are actively engaged in a care-management program, monitored using the modified Health Assessment Questionnaire (mHAQ), and results shared with the treating physician compared to historically reported national registry based estimates obtained from a recent study.
Methods: This is a single arm retrospective study of patients engaged in care management services between 2016 and 2019. Adult patients (> 18 years), with RA (by International Classification of Diseases , Tenth Revision codes), and engaged with care-management services for at least 12 months from the index date (date of first mHAQ score) were included in this analysis. Treatment changes associated with progressive functional losses were documented and rates of change were assessed. Progressive functional losses were classified as transitioning from normal (mHAQ< 0.3), mild (0.3< mHAQ< 1.3), moderate (1.3< mHAQ< 1.8), and severe (mHAQ >1.8). Baseline regimens were classified based on utilization of cDMARD (MTX, SSZ, LEF, HCQ) and bDMARD (TNF-α inhibitors, Abatacept, Rituximab, Sarilumab, Tocilizumab, Baricitinib, Tofacitinib). Rates of treatment changes were compared to historically reported national registry based estimates obtained from a recent study.
Results: A total of 172 patients were included in the study, the majority were female (76.7%) and the mean age was 52.6 years (SD = 9.5). Baseline treatment regimens included cDMARD (59.3%), bDMARD (7%), combination (8.7%), and treatment naïve (25%). Depression (17.4%) and diabetes (12.8%) were the most commonly reported comorbidities. The rate of therapy change was 68% among those who were actively engaged and warranted a change in therapy based on progressive loss of functional status. Among the treatment naïve, 42% had initiated therapy during the observation period.
Conclusion: Utilization of patient-reported disease severity measures and shared decision making, in a nurse led care-management program appear to improve adherence to treat-to-target recommendations as compared to standard practice without care-management support. A limitation of this study – and potential value for future research – was the lack of a clinician-driven assessment, such as the CDAI, and its correlation to the findings herein based on patient-driven (mHAQ) assessments.
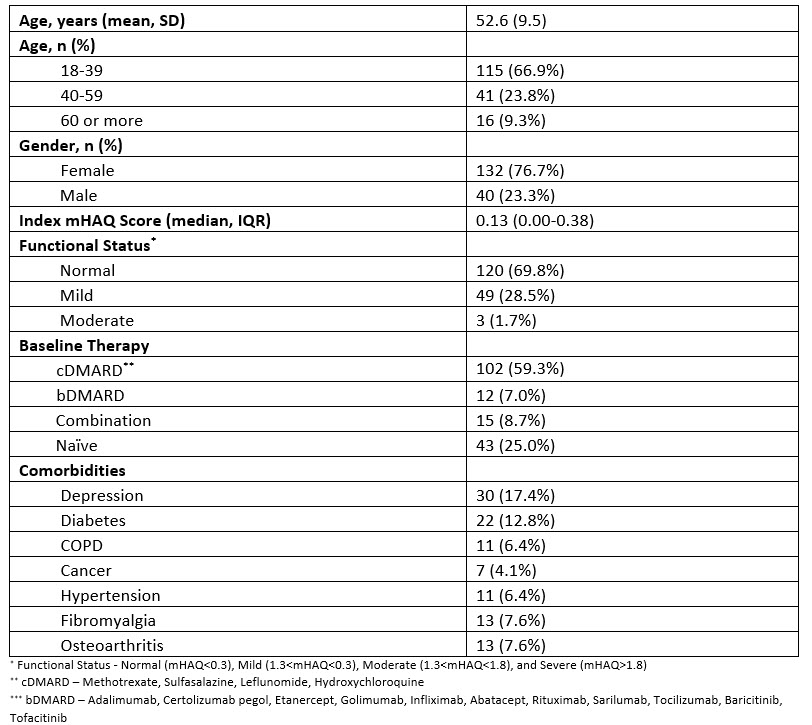 Table 1:Demographic Characteristics (N=172)
Table 1:Demographic Characteristics (N=172)
 Table 2: Rate of Therapy Changes/Initiations
Table 2: Rate of Therapy Changes/Initiations
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Patel P, Krueger A, Lipson A, Hamburger M, Hunter C. Treat-to-Target in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Rates of Treatment Changes in Patients Engaged with Care Management Services Compared to Historically Reported National Registry Based Estimates [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treat-to-target-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-rates-of-treatment-changes-in-patients-engaged-with-care-management-services-compared-to-historically-reported-national-registry-based-estimates/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treat-to-target-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-rates-of-treatment-changes-in-patients-engaged-with-care-management-services-compared-to-historically-reported-national-registry-based-estimates/
