Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2015
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Innate immunity is
implicated in RA pathogenesis and is likely mediated via TLR pathways, with
anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA) serving as key triggers. NI-0101
is the first monoclonal antibody (mAb) that blocks TLR4 signaling independently
of ligand type (i.e., exogenous/endogenous) and concentration. The
objectives of the study were 1)
To investigate NI-0101 ability to block TLR4-mediated inflammatory cytokine
production induced by endogenous TLR4 ligands using RA patient samples; 2) To
evaluate the effect of TLR4 blockade on arthritis progression in RA mouse model;
3) To
determine preliminary tolerability, safety, pharmacokinetic
(PK)/pharmacodynamic (PD) profiles after single administrations of different
NI-0101 doses to Healthy Volunteers (HV).
Methods: Monocytes obtained from HV
or RA patients were stimulated with citrullinated protein immune complexes
(cP-IC) or synovial fluids (SF) of RA patients in the presence and absence of
NI-0101. The correlation of TLR4 blockade with level of endogenous TLR4 ligands
in paired SF and serum was assessed. In parallel, the anti-mouse TLR4 surrogate
mAb, 5E3, was tested in a collagen induced arthritis (CIA) murine model of RA.
Finally, a PK/PD guided single ascending dose Phase 1 study was conducted in 73
HV, in the presence of in vivo and ex vivo challenges with the
TLR4 ligand, lipopolysaccharide (LPS).
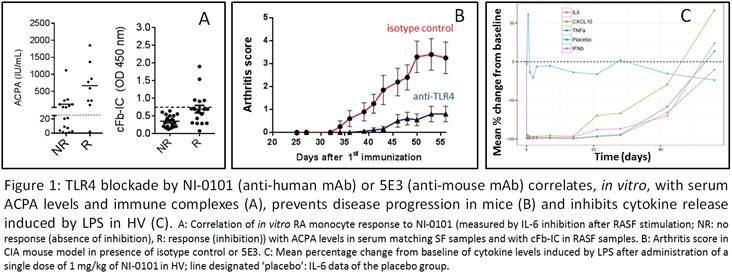
Results: In vitro, NI-0101 efficiently
blocked monocyte TLR4 activation by cP-IC and SF from sub-populations of RA
patients. This inhibition correlated with the presence of anti-citrullinated
protein antibodies and citrullinated fibrinogen immune complexes in the SF and
matching sera (Figure 1A). Administration of 5E3 inhibited arthritis
progression in the CIA mouse model (Figure 1B). NI-0101 was administered up to
a single dose of 15 mg/kg in the Phase 1 study in HV and showed no safety
concerns. The predictable PK profile was biphasic, similar to other therapeutic
IgG targeting cell surface receptors. NI-0101 administration inhibited ex
vivo and in vivo LPS-induced cytokine release (complete inhibition
from a dose of 1 mg/kg) (Figure 1C), as well as prevented CRP increase and
occurrence of flu-like symptoms following LPS administration to HV. NI-0101
PK/PD profiles allowed, through modeling and simulation of multiple
administration of NI-0101, to identify an appropriate dose range to be tested
in Phase 2 trials.
Conclusion: NI-0101 blocks TLR4
activation induced by TLR4 ligands (cP-IC) present in SF and serum in a
subgroup of RA patients and in vivo LPS challenges in HV. NI-0101
safety and PK/PD profiles in HV allow initiation of Phase 2 development. Taken together, these data
strongly support the potential of TLR4 as a valid therapeutic target in RA, and
provide an opportunity to evaluate specific endogenous TLR4 ligands as
biomarkers of NI-0101 treatment response in Phase 2 trials.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Monnet E, Shang L, Lapeyre G, De Graaf K, Hatterer E, Wambiekele G, Ferlin W, Jacqmin P, Gabay C, Sokolove J, Jones S, Choy EH, McInnes IB, Kosco-Vilbois M, De Min C. Translational Data and Phase 1 Study Results of a New Monoclonal Antibody Targeting Toll like Receptor 4 (TLR4) Developed for Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Treatment with a Potential for Personalized Medicine [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/translational-data-and-phase-1-study-results-of-a-new-monoclonal-antibody-targeting-toll-like-receptor-4-tlr4-developed-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-treatment-with-a-potential-for-personalized-medi/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/translational-data-and-phase-1-study-results-of-a-new-monoclonal-antibody-targeting-toll-like-receptor-4-tlr4-developed-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-treatment-with-a-potential-for-personalized-medi/