Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Fli-1 is a member of Ets transcription factor and plays an important role in lupus nephritis development. Reduced Fli-1 expression (heterozygote Fli-1: Fli-1+/-) results in improvement of kidney inflammation and prolongs overall survival in lupus model mouse. Previously, we have reported that Fli-1 directly regulates cytokine/chemokine expression (MCP-1, RANTES, CXCL2, IL-6, and G-CSF) and impacts lupus nephritis development in lupus model mouse. IL-17 is a cytokine with powerful inflammatory properties. Past reports indicate that IL-17 is associated with disease activity in patients with lupus nephritis. The relationship between Fli-1 and IL-17 is unknown. The aim of this study is to elucidate whether reduced Fli-1 expression affects IL-17 production and impacts lupus nephritis development into the kidney.
Methods: Serum IL-17 concentrations of adult (4-months-old or older) Wild-type (WT) and Fli-1+/- MRL/lpr mice were measured by ELISA and compared between the two groups. Kidneys were removed from these mice and evaluated using pathology scoring system (glomerular and interstitial lesions). Immunostaining of IL-17 in the kidney was also performed and compared between the two groups. Expression of mRNA of IL-17, IL-18 and IL-1ƒÀin the kidney tissue were also compared.
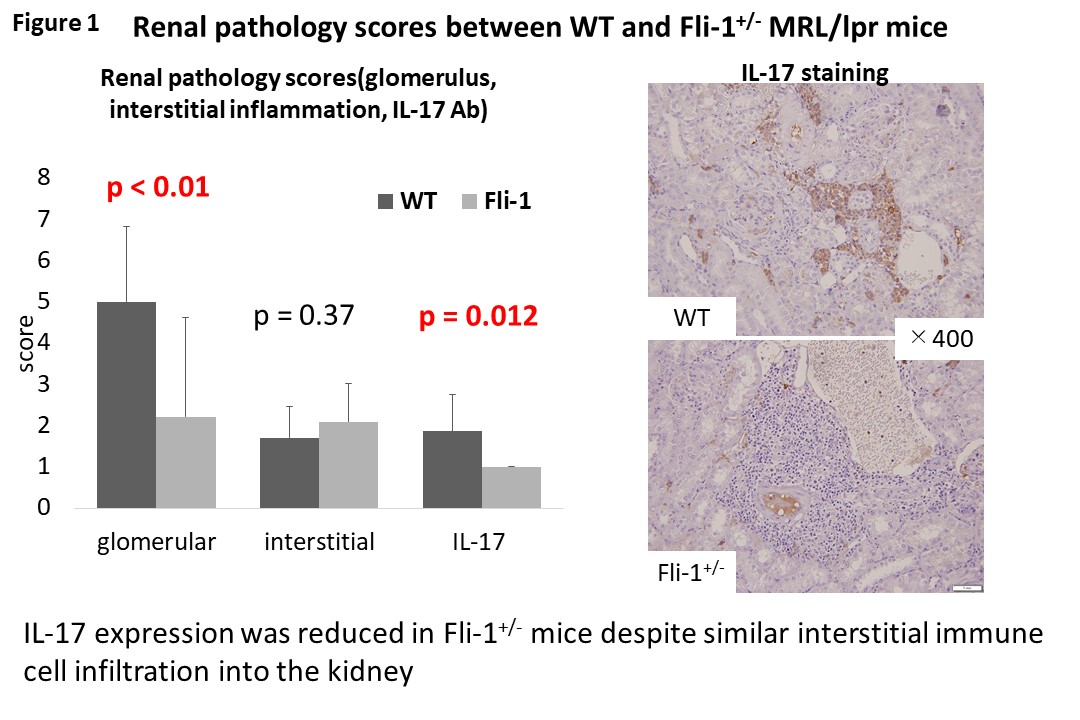
Results: Serum IL-17 concentrations were relatively decreased but not significant in Fli-1+/- MRL/lpr mice (WT: 55.7 vs Fli-1+/-: 3.12 pg/mL, respectively, p=0.35). Relative mRNA expression of IL-17 in the kidney was decreased (19.7%) in Fli-1+/- MRL/lpr mice compared to WT MRL/lpr mice. Relative expression of IL-18 and IL-1ƒÀ mRNA in the kidney were significantly decreased in Fli-1+/- MRL/lpr mice (p=0.02). In histological examination, glomerular inflammation was significantly decreased in Fli-1+/- MRL/lpr mice. However, interstitial inflammation was similar between the two groups. In contrast, immunostaining of IL-17 showed significantly decreased IL-17 positive immune cells in the kidney of Fli-1+/- MRL/lpr mice (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Fli-1 impacts lupus nephritis progression through affecting the reduction of IL-17-positive immune cell infiltration into the kidney. Reduced expression of IL-1ƒÀand IL-18 in the kidney can also affect IL-17 expression in Fli-1+/- MRL/lpr mice.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sato S, Zhang X, Fujita Y, Yashiro M, Asano T, Kobayashi H, Watanabe H, Migita K. Transcription Factor Fli-1 Impacts Renal IL-17 Expression in Adult MRL/Lpr Mouse Despite Similar Interstitial Immune Cell Infiltration into the Kidney [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/transcription-factor-fli-1-impacts-renal-il-17-expression-in-adult-mrl-lpr-mouse-despite-similar-interstitial-immune-cell-infiltration-into-the-kidney/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/transcription-factor-fli-1-impacts-renal-il-17-expression-in-adult-mrl-lpr-mouse-despite-similar-interstitial-immune-cell-infiltration-into-the-kidney/