Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 7, 2017
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Human Etiology and Pathogenesis Poster III
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Genetic variants in AFF3 have been associated with RA, including in our GWAS and ImmunoChip analyses of African-Americans (610 RA; 1543 controls). Likewise, an AFF3 SNP (rs10865035) has been associated with response of RA to TNF inhibitors (TNFi) (Ann Rheum Dis. 2010 69:1029). AFF3 encodes LAF4, a tissue-restricted nuclear transcriptional activator expressed in cells such as monocytes and lymphocytes. Variants most strongly associated with RA are in the 5′ UTR; several are expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs) for AFF3. We examined trans-ethnic associations of AFF3 with RA, prioritized candidate pathogenic variants using established algorithms, and compared this list to variants reported to influence the likelihood of response to TNFi in RA.
Methods: We aggregated our African American RA genetic data with publicly available GWAS data from >100,000 European and Asian RA patients and controls, using METASOFT meta-analysis software to assess overall trans-ethnic association strength (pTE) and concordance of effects in each ethnicity (m-value). m>0.8 indicates high likelihood of existence of effect for a given population. We then used the PAINTOR3 algorithm (which incorporates multiple types of data) on data from all 3 ancestries to prioritize SNPs according to likelihood of being pathogenic. We compared this list to variants implicated in TNFi response.
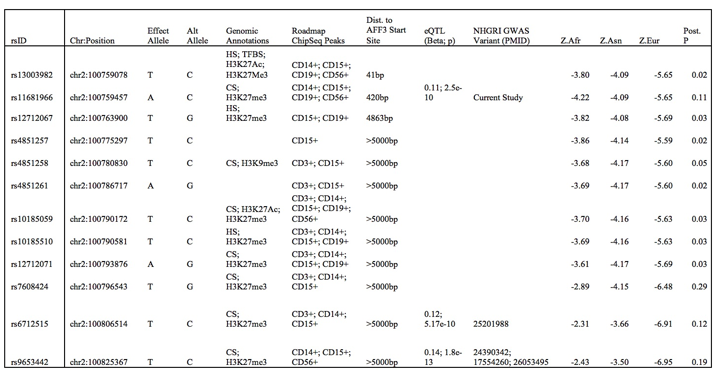
Results: We found strong evidence (m>0.9) of trans-ethnic effect on RA for 91 AFF3 variants, mostly in the 5′ UTR. We confirmed the association of the AFF3 locus and the previously reported index variant (rs9653442) with RA in African-Americans (pAFR = 7.4*10-3, mAFR = 0.975). rs9653442 has a robust trans-ethnic association with RA (mEUR = 1.000; mASIAN = 0.999; mAFR = 0.975; pTE = 1.14*10-15). We identified a set of 12 variants that together are >90% likely to include the pathogenic variant (the 90% ancestry informed credible set, see Table). rs10865035, which was previously associated with TNFi response in RA, was outside our 90% ancestry informed credible set.
Conclusion: We defined a set of 12 leading candidate pathogenic AFF3 variants, which may act to increase AFF3 expression in T cells or monocytes and influence RA susceptibility. Our study did not identify a likely pathogenic role for rs10865035 in RA susceptibility, but further studies are needed to establish whether rs10865035 underlies differences in TNFi response in RA. Our findings will guide selection of SNPs for future functional studies of susceptibility to RA.
Table – The 90% ancestry informed credible set for pathogenic AFF3 variants in RA and their characteristics. eQTL data are from the NESDA NTR Conditional eQTL Catalog (peripheral blood was used). Z.Afr, Z.Asn, Z.Eur are Z-statistics for each variant from each GWAS. Abbreviations: Alt – Alternate. CS – Chromatin State. HS – DNAse hypersensitive region. TFBS – transcription factor binding site.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Laufer VA, Danila MI, Reynolds RJ, Kottyan LC, Kaufman K, Harley JB, Langefeld CD, Arnett D, Bridges SL Jr.. Towards Precision Medicine in Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Trans-Ethnic Analysis and Prioritization of SNPs in the AFF3 Locus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/towards-precision-medicine-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-trans-ethnic-analysis-and-prioritization-of-snps-in-the-aff3-locus/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/towards-precision-medicine-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-trans-ethnic-analysis-and-prioritization-of-snps-in-the-aff3-locus/