Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
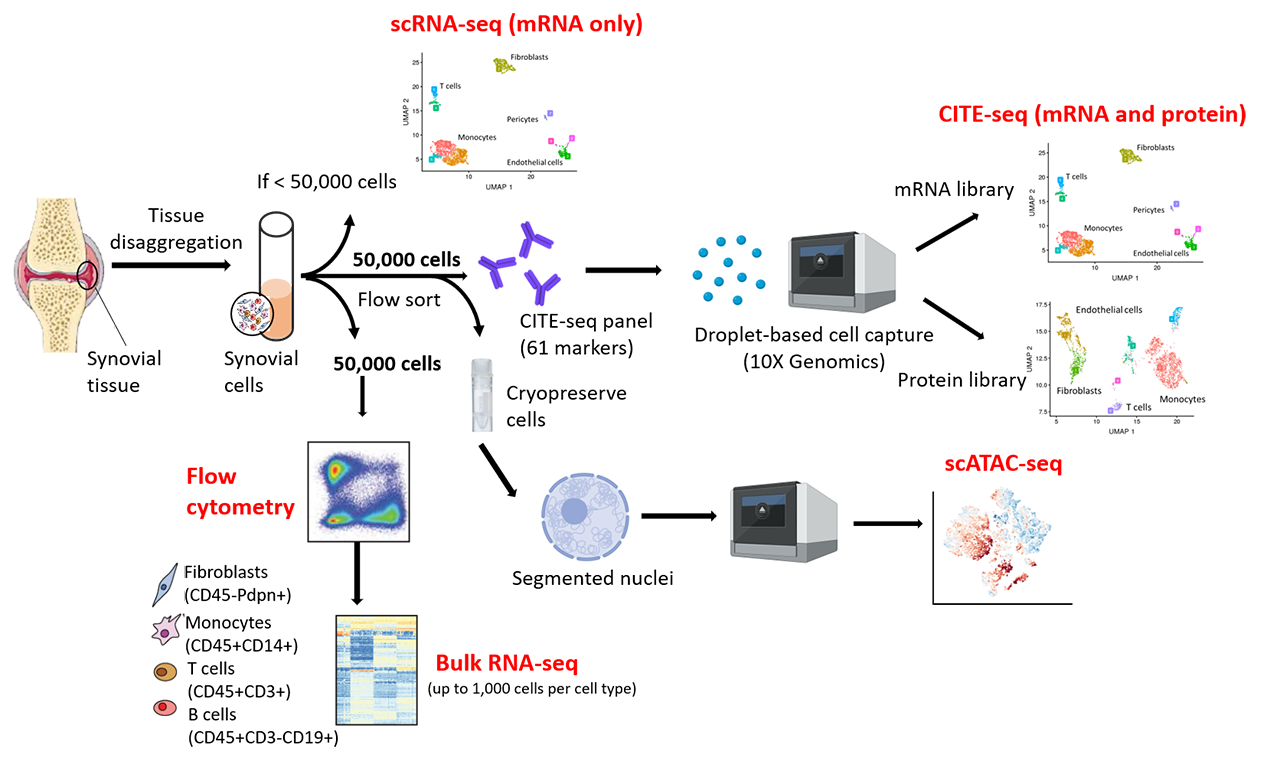
Background/Purpose: The goal of the Accelerating Medicines Partnership (AMP) program is to study synovial tissue from individuals with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) using high-dimensional analyses. During phase 1 of the program, we performed cytometric and transcriptomic analyses of synovial tissues and identified subsets of stromal and immune cells that were enriched in inflamed synovium. For phase 2, we have developed a pipeline to generate parallel single cell transcriptomic, proteomic, and epigenetic datasets of RA synovial cells (Fig.1).
Methods: Synovial tissues were obtained from individuals meeting the 2010 ACR criteria for RA and undergoing elective surgical procedures or synovial biopsies. We developed a histologic grading system to guide selection of biopsies with sufficient cell number and quality to apply multiple analytic technologies. Synovial tissues were cryopreserved after acquisition and then thawed and disaggregated. Viable synovial cells from each sample were sorted for subsequent analysis by scRNAseq, CITE-seq (combined scRNAseq and surface proteomics), and scATAC-seq using droplet-based technology (10X Genomics).
Results: 1. Histologic grading informs tissue cellularity. High quality synovial tissues (Grade A) predicted high cell yield ( >50,000 cells) and whereas low quality (Grade D) predicted low cell yield (< 1,000 cells).
2. CITE-seq on synovial cells. Optimized cell handling enabled CITE-seq analysis on tissues with as low as 50,000 viable cells. After eliminating low-complexity cells (~5% of cells), we consistently recovered >10,000 high quality cells ( >2,000 genes/cell) from each tissue. We tested 83 oligo-conjugated antibodies targeting immune and stromal cell surface markers and identified 61 antibodies with high signal specificity (high K-L divergence within gene-defined clusters) and signal intensity (median non-zero expression). Specificity of proteomic signals were markedly improved through serial titration. Importantly, independently clustering based on either transcriptomic or proteomic data revealed concordant signal that identified 19 distinct immune and stromal cell clusters.
3. Single cell ATAC-seq on synovial cells. We optimized nuclei recovery from synovial cells to enable scATAC-seq analysis from 30,000 viable cells. We demonstrated feasibility of performing scATAC-seq on re-cryopreserved synovial cells to facilitate batched processing. After removing low-read-depth barcodes, we obtained robust scATAC-seq data ( >9,000 mapped fragments/nucleus) with high concordance between scATAC-seq with scRNA-seq. We further demonstrated consistent identification of diverse synovial cell types in both once- and twice-cryopreserved synovial cells.
4. Flow Cytometry and bulk RNAseq. A 14-color flow cytometry panel was used to quantify disease-associated cell populations in conjunction with sorting major synovial cell types for low-input RNAseq.
Conclusion: We demonstrate feasibility of implementing multiple single cell profiling techniques in synovial tissue. The collection of multiple modalities of single cell analysis will add new dimensions to our understanding of the cellular pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wei K, Jonsson A, Zhang F, Nathan A, Mears J, Watts G, Zhu Z, Korsunsky i, Donlin L, Rao D, Filer A, (AMP) A, Boyce B, Gravallese E, Holers V, Moreland L, Gregersen P, Bykerk V, Anolik J, Raychaudhuri S, Brenner M. Towards a Single Cell Portrait of Rheumatoid Arthritis – Development of a Single Cell Multiomics Pipeline for Phase 2 of the Accelerating Medicine Partnership (AMP) – RA Network [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/towards-a-single-cell-portrait-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-development-of-a-single-cell-multiomics-pipeline-for-phase-2-of-the-accelerating-medicine-partnership-amp-ra-network/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/towards-a-single-cell-portrait-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-development-of-a-single-cell-multiomics-pipeline-for-phase-2-of-the-accelerating-medicine-partnership-amp-ra-network/