Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Treatments Poster II: PROs, Safety and Comorbidity
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
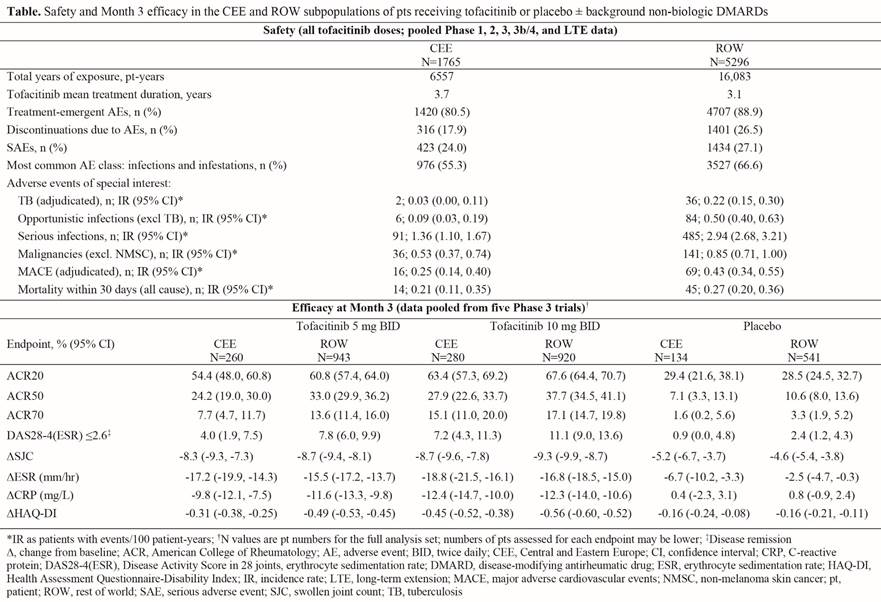
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of RA. This post hoc analysis assessed tofacitinib safety and efficacy in the Central and Eastern European (CEE) subpopulation of the tofacitinib clinical program vs the rest of the world (ROW; not including CEE countries).
Methods: Data for safety analyses were pooled from two Phase (P)1, ten P2, six P3, one P3b/4, and two long-term extension (LTE; ORAL Sequel LTE main study database locked at time of analysis: March 2, 2017) studies in patients with RA. Safety comparisons evaluated were adverse events (AEs), serious AEs (SAEs), and AEs of special interest for combined tofacitinib doses. Pooled data from five pivotal P3 studies (DMARD-IR pts) were assessed for efficacy of tofacitinib 5 and 10 mg twice daily and placebo at Month 3; endpoints are listed in the table. CEE countries in the efficacy analyses from five P3 studies included: Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Czech Republic, Poland, Russian Federation, Slovakia, and Ukraine; safety analyses based on the 21 above studies included these countries plus Hungary, Romania, and Turkey.
Results: 1765 patients (pts) from CEE and 5296 from ROW were included in the safety analyses. Demographics and baseline characteristics were generally similar between CEE and ROW aside from race (99.9% vs 53.1% white), prior TNF inhibitor use (2.2% vs 20.8%) and non-TNF inhibitor biologic DMARD use (1.0% vs 6.4%); mean duration of RA was 7.6 years (range 0–65) in CEE and 8.2 years (range 0–55) in ROW. Safety results based on 21 studies and efficacy results based on five P3 studies are summarized in the table. Efficacy outcomes improved with tofacitinib vs placebo in CEE and ROW pts at Month 3. Improvements in composite measures (ie, ACR response rates and Disease Activity Score in 28 joints using erythrocyte sedimentation rate [DAS28‑4(ESR)] ≤2.6) and Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index (HAQ‑DI) were numerically greater for ROW vs CEE pts; changes in objective measures (ie, swollen joint count and inflammatory markers) were more similar.
Conclusion: Tofacitinib showed substantial improvements in efficacy vs placebo in CEE and ROW. Results were generally consistent between CEE and ROW subpopulations. Following tofacitinib treatment, incidence rates of serious and opportunistic infections were lower for CEE vs ROW, which may reflect the marginally lower RA duration beforehand; the lower prior biologic DMARD use in CEE may also have impacted efficacy and safety. Major limitations include the post hoc nature of this analysis and the small CEE population vs ROW, therefore results should be interpreted with caution. Previous analyses have revealed consistent safety and efficacy with tofacitinib in US and Western European subpopulations vs ROW.1,2
References:
1. Wollenhaupt J et al. Deutschen Gesellschaft für Rheumatologie – 44 kongress 2016; Abstract 16080.
2. Cohen SB et al. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2016; 34: 32-6.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Vencovsky J, Badurski J, Forejtová Š, Lukáčová O, Stanislavchuk M, Yaneva-Bichovska D, Shi H, Vasilescu R, Lukic T, Kabina M. Tofacitinib Safety and Efficacy in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis in a Central/Eastern European Subpopulation [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tofacitinib-safety-and-efficacy-in-the-treatment-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-a-central-eastern-european-subpopulation/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tofacitinib-safety-and-efficacy-in-the-treatment-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-a-central-eastern-european-subpopulation/