Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 15, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy - Poster III
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Disease activity is the main risk factor for developing lymphoma in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, the impact of immunosuppressive drugs remains an unsolved question. On one hand they might decrease the risk of lymphoma by controlling activity of the disease. On the other hand, they might alter anti-tumor immunosurveillance as observed in post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders. Tofacitinib is an oral Janus Kinase (Jak) 3 and 1 inhibitor that has shown positive results in RA patients. Tofacitinib may impair NK-cell function due to its inhibitory action on IL2 and IL15 signaling. Given the fact that NK cells have been recently shown to participate to anti–lymphoma immunosurveillance, we aimed to assess if tofacitinib might impact NK cells function and anti-lymphoma activity.
Methods:
We have studied the consequences of in vitro exposure of NK to tofacitinib (10, 50 and 100 nM) or to DMSO (vehicle) during 6 days in presence of IL-2 (200 UI/ml): phenotype has been studied and then cytotoxicity against 2 non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma cell lines [Farage (EBV+) and SU-DHL4 (EBV-)] was assessed.
Results are shown as mean + standard of the mean (SEM). The Mann Whitney test was used to compare samples stimulated with tofactinib and DMSO (controls).
Results:
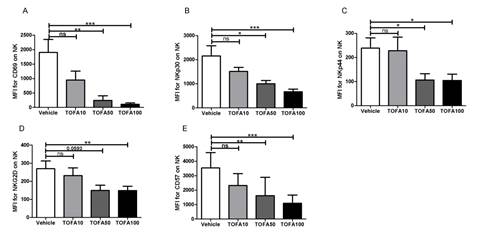
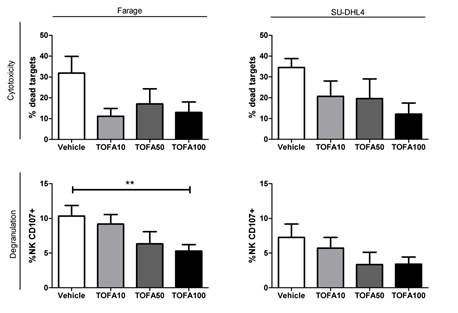
Firstly, we did not observe difference concerning the survival of NK cells in presence of tofacitinib or controls after 6 days culture. Secondly, we observed that culture in presence of tofacitinib was associated with a modification of NK phenotype with a decreased level of activation with a dose effect (Figure 1A). In addition we observed a decreased expression of activating receptors such as NKp30, NKp44 and NKG2D (Figure 1B-D). Last, we found that tofacitinib blocked NK cell maturation as observed with the significant decreased expression of CD57 on NK cells exposed to tofacitinib at 50 and 100 nM (Figure 1E). Conversely, CD16 expression was not modulated by tofacitinib. These phenotypic abnormalities were associated with an impaired function of NK as assessed by co-culture: degranulation was significantly decreased after exposure to tofacitinib 100nM in case of co-culture with Farage. A trend was observed with SU-DHL4. A trend for decreased NK cells cytotoxicity was observed with the 2 cell lines (Figure 2).
Conclusion:
This study demonstrates that tofacitinib treatment negatively impact the state of activation, maturation and functions of NK cells with impaired degranulation and less efficient lysis of B lymphoma cell lines . These results need to be confirmed in vivo. This negative impact of tofacitinib on NK cells activation and function might participate to the increased risk of herpes zoster infection in patients treated with tofacitinib and suggest to remains cautious about a possible increased risk of lymphoma.
Figure 1: NK phenotype after 6 days culture to tofacitinib or control (*: p<0.05, **: p<0.01, ***: p<0.001, ns: non-significant).
Figure 2: Anti lymphoma activity of tofacitinib exposed NK cells (**: p<0.01).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nocturne G, Tahmasebi F, Boudaoud S, Ly B, Mariette X. Tofacitinib Is Associated with an Impaired Function of NK Cells and a Defective Immunosurveillance Against B-Cell Lymphomas [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tofacitinib-is-associated-with-an-impaired-function-of-nk-cells-and-a-defective-immunosurveillance-against-b-cell-lymphomas/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tofacitinib-is-associated-with-an-impaired-function-of-nk-cells-and-a-defective-immunosurveillance-against-b-cell-lymphomas/