Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Depression and anxiety are common in patients (pts) with RA1 and can lead to reduced quality of life, functional capacity, and RA treatment response.2-4 Elevated IL-6 levels have been associated with depressive symptoms in pts with RA.5 The 36-Item Short Form Health Survey (SF-36) Mental Component Summary score (MCS) ≤ 38 has been used as an identifier of probable major depressive disorder (pMDD) and/or probable generalized anxiety disorder (pGAD) in pts with RA.6 Tofacitinib is an oral JAK inhibitor for the treatment of RA. We assessed the prevalence of pMDD and/or pGAD by SF-36 MCS ≤ 38 status in tofacitinib clinical trials for RA, and tofacitinib efficacy by baseline (BL) pMDD and/or pGAD status.
Methods: In this post hoc analysis, data were pooled from 5 Phase (P)3 trials and 1 P3b/4 trial. Pts receiving tofacitinib 5 or 10 mg BID, adalimumab 40 mg every other week (ADA), or placebo (PBO), with a non-missing BL SF-36 MCS, were included. Demographics and BL disease characteristics were reported by BL pMDD and/or pGAD status (SF-36 MCS ≤ 38 [presence] or > 38 [absence]). At Months (M)3/6/9/12: SF-36 MCS change from BL (∆) was estimated by modeling of pooled data, and the % of pts with pMDD and/or pGAD was reported. Efficacy endpoints were estimated at M3/6/12 by linear models, comparing tofacitinib-treated pts by BL pMDD and/or pGAD status.
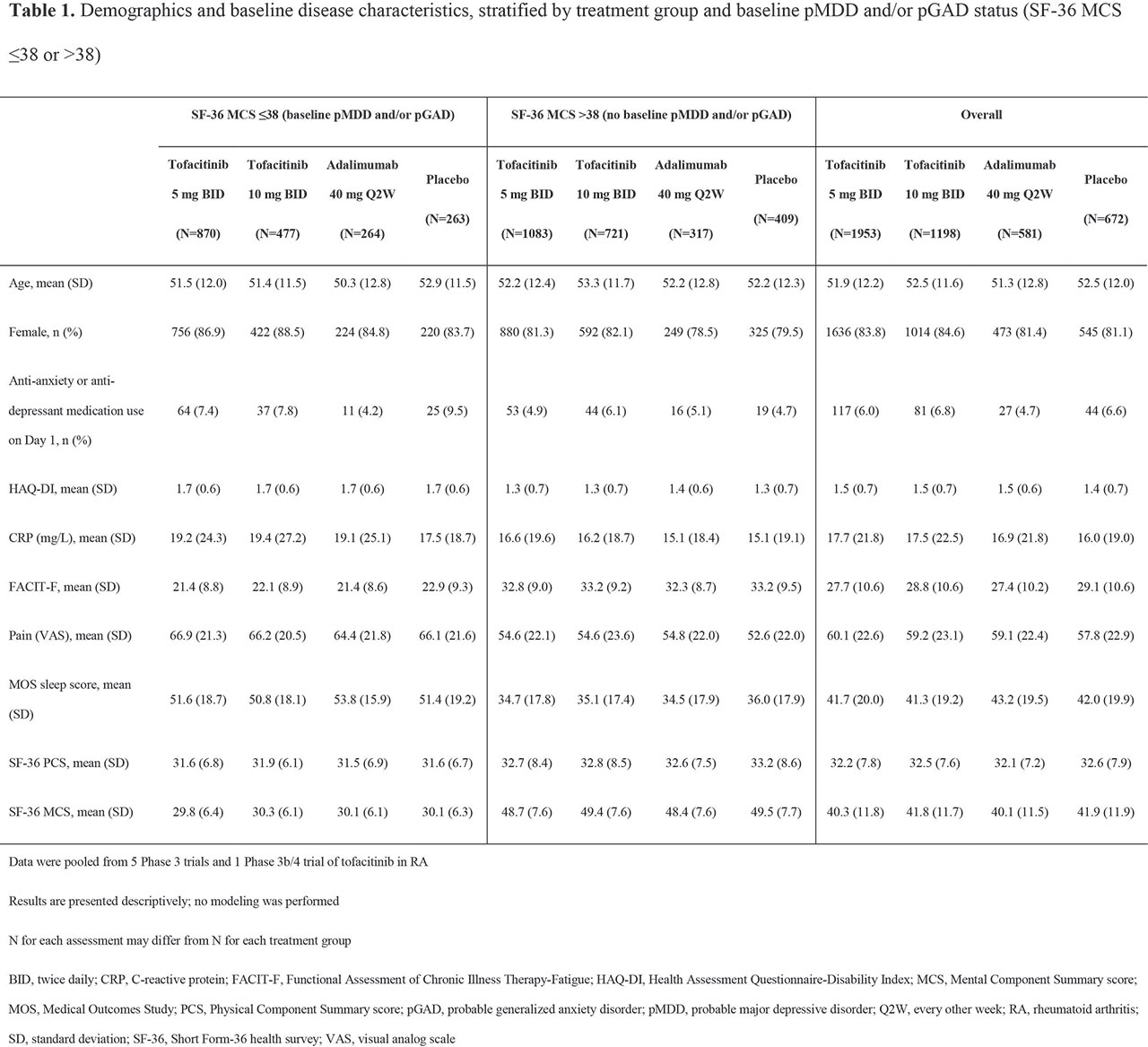
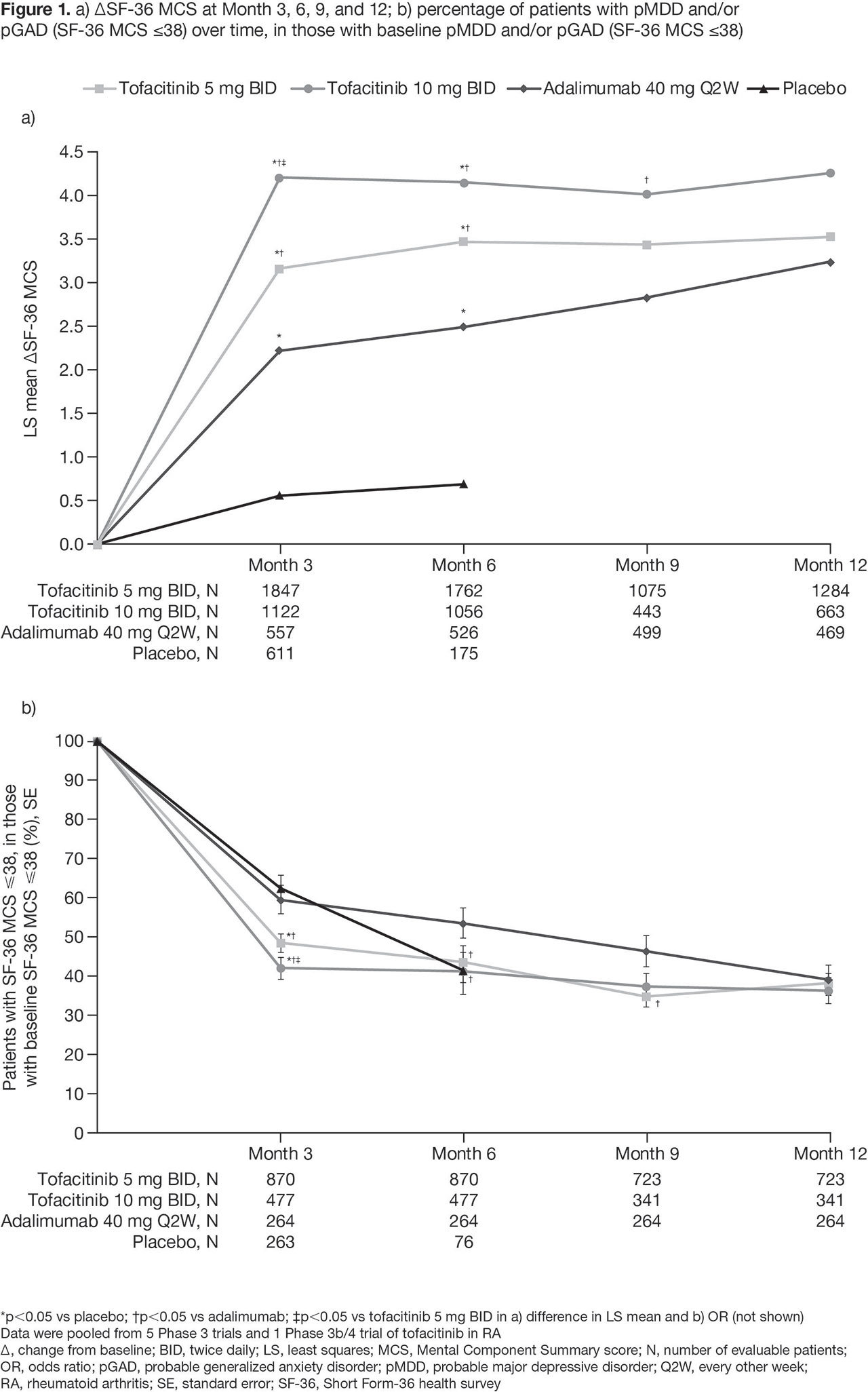
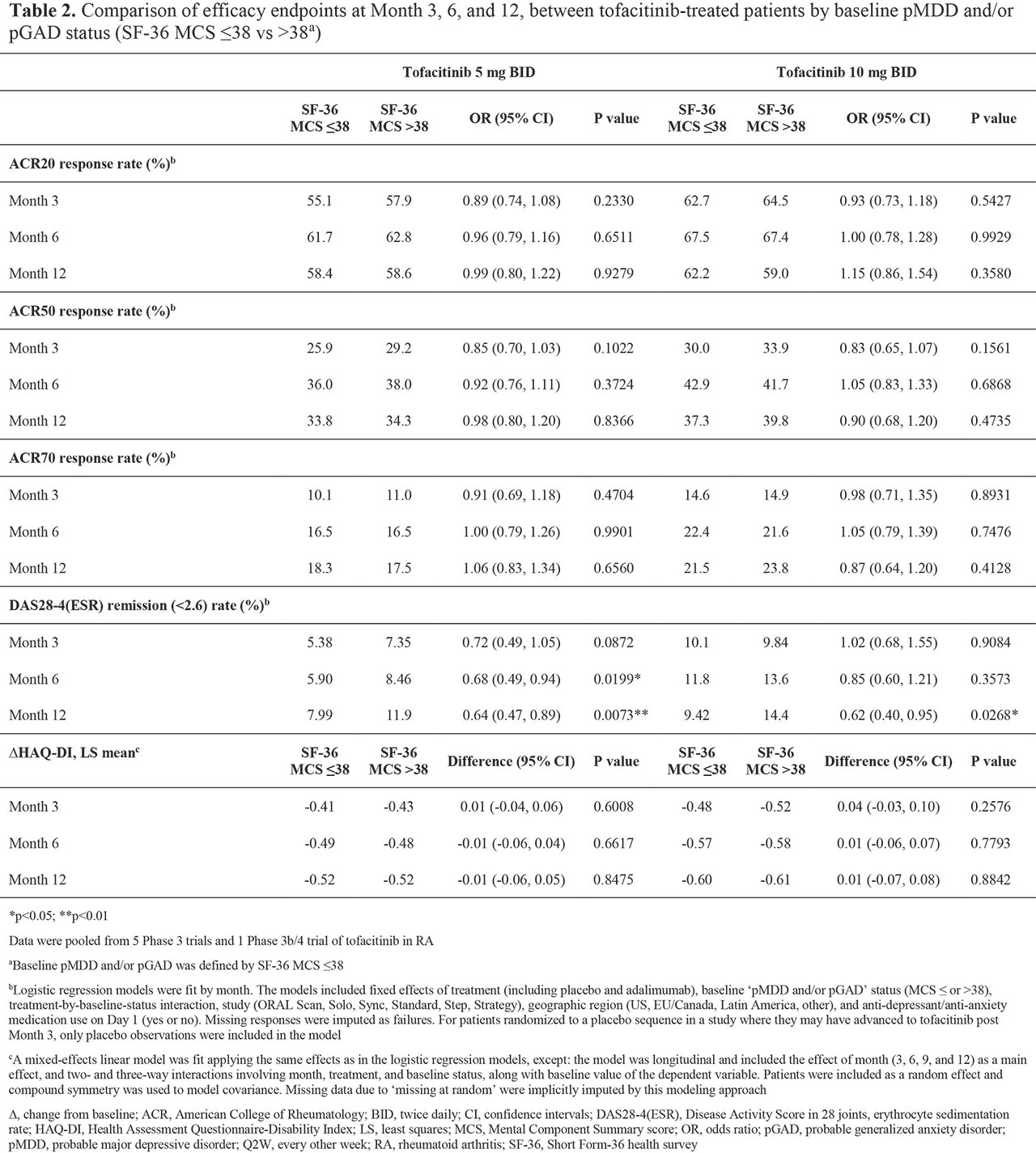
Results: BL pMDD and/or pGAD were reported in 44.5%, 39.8%, 45.4%, and 39.1% of pts receiving tofacitinib 5 mg BID, tofacitinib 10 mg BID, ADA, and PBO, respectively. At BL, higher CRP levels and worse disability, fatigue, pain, and sleep were reported in pts with pMDD and/or pGAD vs those without (Table 1). A numerically, and sometimes significantly (p < 0.05), greater increase in SF-36 MCS was reported in pts receiving tofacitinib vs PBO or ADA (Figure 1a). The % of pts with BL pMDD and/or pGAD who continued to have pMDD and/or pGAD reduced over time, and was generally lower in pts receiving tofacitinib vs PBO or ADA (Figure 1b). In tofacitinib-treated pts, efficacy was generally similar regardless of BL pMDD and/or pGAD status (Table 2).
Conclusion: In this post hoc analysis, around 40% of pts with RA had BL pMDD and/or pGAD identified by SF-36 MCS ≤ 38. Improvement in SF-36 MCS was greater in pts receiving tofacitinib vs ADA or PBO. In tofacitinib-treated pts, the % with SF-36 MCS ≤ 38 (ie identified as having pMDD and/or pGAD) reduced by around 60% at M12. Tofacitinib efficacy was similar in those with and without BL pMDD and/or pGAD (identified using SF-36 MCS). Limitations include using SF-36 MCS to identify probable rather than confirmed MDD or GAD. Future research is required to replicate the findings of this study using a gold-standard psychiatric interview against which to validate the use of SF-36 MCS ≤ 38.
- Covic T et al. BMC Psychiatry 2012; 12: 6.
- Hattori Y et al. J Clin Rheumatol 2018; 24: 308-312.
- Ayelen Isnardi C et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2018; 70 (Suppl 10) Abstract 1510.
- Matcham F et al. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2016; 55: 268-278.
- Li YC et al. Int J Rheum Dis 2019; [Epub ahead of print].
- Matcham F et al. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2016; 17: 224.
Acknowledgments: Study sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Medical writing support was provided by Sarah Piggott of CMC Connect and funded by Pfizer Inc.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Citera G, Jain R, Irazoque F, Guzman R, Madariaga H, Gruben D, Wang L, Stockert L, Hsu M, Santana K, Ebrahim A, Ponce de Leon D. Tofacitinib in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Indicative of Depression And/or Anxiety: A Post Hoc Analysis of Phase 3 and Phase 3b/4 Clinical Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tofacitinib-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-indicative-of-depression-and-or-anxiety-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-phase-3-and-phase-3b-4-clinical-trials/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tofacitinib-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-indicative-of-depression-and-or-anxiety-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-phase-3-and-phase-3b-4-clinical-trials/