Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Spondyloarthropathies and Psoriatic Arthritis – Clinical Aspects and Treatment Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor under investigation for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis (PsA). PsA is a heterogeneous disease and composite endpoints allow assessment of multiple clinical outcomes in one instrument. We examined the effects of tofacitinib treatment on several composite endpoints in patients (pts) with PsA.
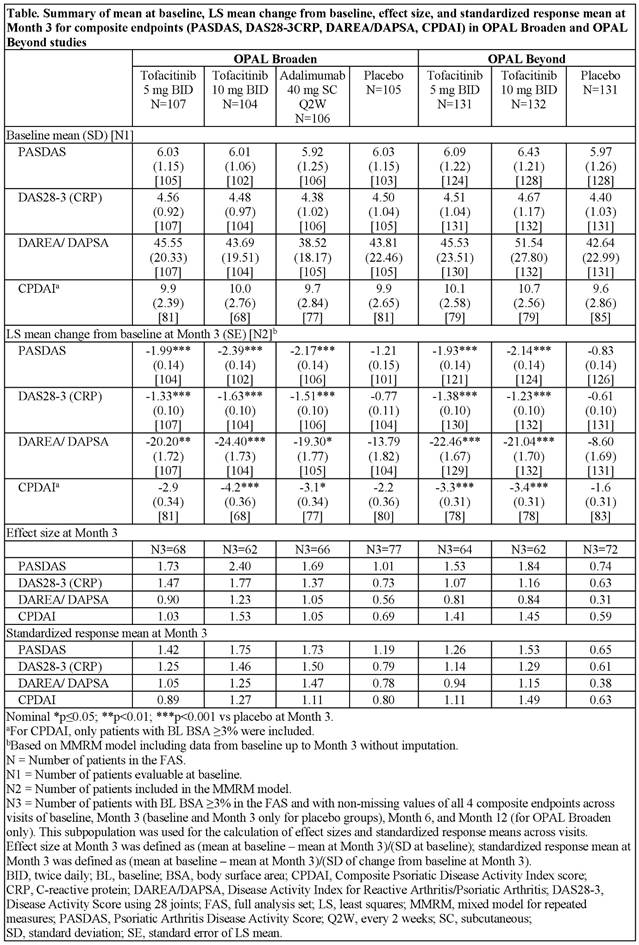
Methods: In 2 placebo (PBO)-controlled, double-blind, multicenter, global Phase 3 studies, pts had active PsA and either had an inadequate response (IR) to ≥1 conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (csDMARD) and were tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi)-naïve (OPAL Broaden [N=422; 12 months; NCT01877668]), or had an IR to ≥1 TNFi (OPAL Beyond [N=394; 6 months; NCT01882439]). Pts were randomized to receive tofacitinib 5 mg BID, tofacitinib 10 mg BID, adalimumab 40 mg subcutaneous injection once every 2 weeks (OPAL Broaden only), or PBO (advancing to tofacitinib 5 or 10 mg BID at Month 3, OPAL Broaden and OPAL Beyond), in addition to continuing on a single, stable csDMARD. Composite endpoints assessed: Psoriatic Arthritis Disease Activity Score (PASDAS), Disease Activity Score using 28 joints with C‑reactive protein, Disease Activity Index for Reactive Arthritis/Psoriatic Arthritis (DAREA/DAPSA), and Composite Psoriatic Disease Activity Index score.
Results: Demographics and baseline disease characteristics were generally similar between treatment groups within the 2 studies, except for duration of PsA disease (longer in OPAL Beyond) and geographic distribution (OPAL Broaden having more Eastern EU pts). Baseline values for composite endpoints were generally similar across treatment groups and studies (Table). Both doses of tofacitinib showed improvements in composite endpoints vs PBO at Month 3 in both studies (Table). In OPAL Broaden, the effects of adalimumab were similar to both doses of tofacitinib across composite endpoints. Effect size for the composite endpoints (using a subpopulation of pts who had all available data for all endpoints) was highest for PASDAS and typically lowest for DAREA/DAPSA; this rank order of effect size was similar across treatment arms and studies. At Month 3, effect sizes in pts receiving active treatment ranged from 0.90 (DAREA/DAPSA for tofacitinib 5 mg BID) to 2.40 (PASDAS for tofacitinib 10 mg BID) in OPAL Broaden, and 0.81 (DAREA/DAPSA for tofacitinib 5 mg BID) to 1.84 (PASDAS for tofacitinib 10 mg BID) in OPAL Beyond (Table). Standardized response means generally followed the same pattern as effect size across studies with both doses of tofacitinib (Table).
Conclusion: In 2 Phase 3 studies, tofacitinib 5 mg and 10 mg BID improved composite endpoint scores vs PBO over 3 months in pts with PsA. The largest effect size and standardized response means were observed for PASDAS. Effect sizes and standardized response means varied across endpoints but were consistent across studies.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Helliwell PS, Coates LC, FitzGerald O, Nash P, Soriano ER, Husni ME, Hsu MA, Kanik KS, Hendrikx T, Wu J, Kudlacz E. Tofacitinib Improves Composite Endpoint Measures of Disease in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tofacitinib-improves-composite-endpoint-measures-of-disease-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tofacitinib-improves-composite-endpoint-measures-of-disease-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/