Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0510–0542) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment: AxSpA Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Elevated baseline (BL) CRP levels can predict treatment response in patients (pts) with AS. Tofacitinib is a Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of AS. This post hoc analysis evaluated the impact of BL CRP levels on tofacitinib efficacy and safety in pts with AS.
Methods: Post hoc analysis of pooled data from placebo (PBO)-controlled, randomized, double-blind trials (NCT01786668, Phase [P]2, 16 weeks; NCT03502616, P3, 48 weeks) in pts with AS on ≥ 1 dose of tofacitinib or PBO (P3: PBO-treated pts switched to tofacitinib after Week [W]16), by BL CRP: normal (NML) < 5 mg/L; elevated (ELV) ≥ 5 mg/L. Tofacitinib 5 mg twice daily (BID) efficacy was assessed to W12/W16–48 (P3). Endpoints: Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society (ASAS) 20/40, Bath AS Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) 50, AS-Disease Activity Score-CRPinactive disease (ASDAS-CRP ID), and least squares mean change from BL (∆) in nocturnal pain and Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue (FACIT-F). Safety was assessed to W16 and W48.
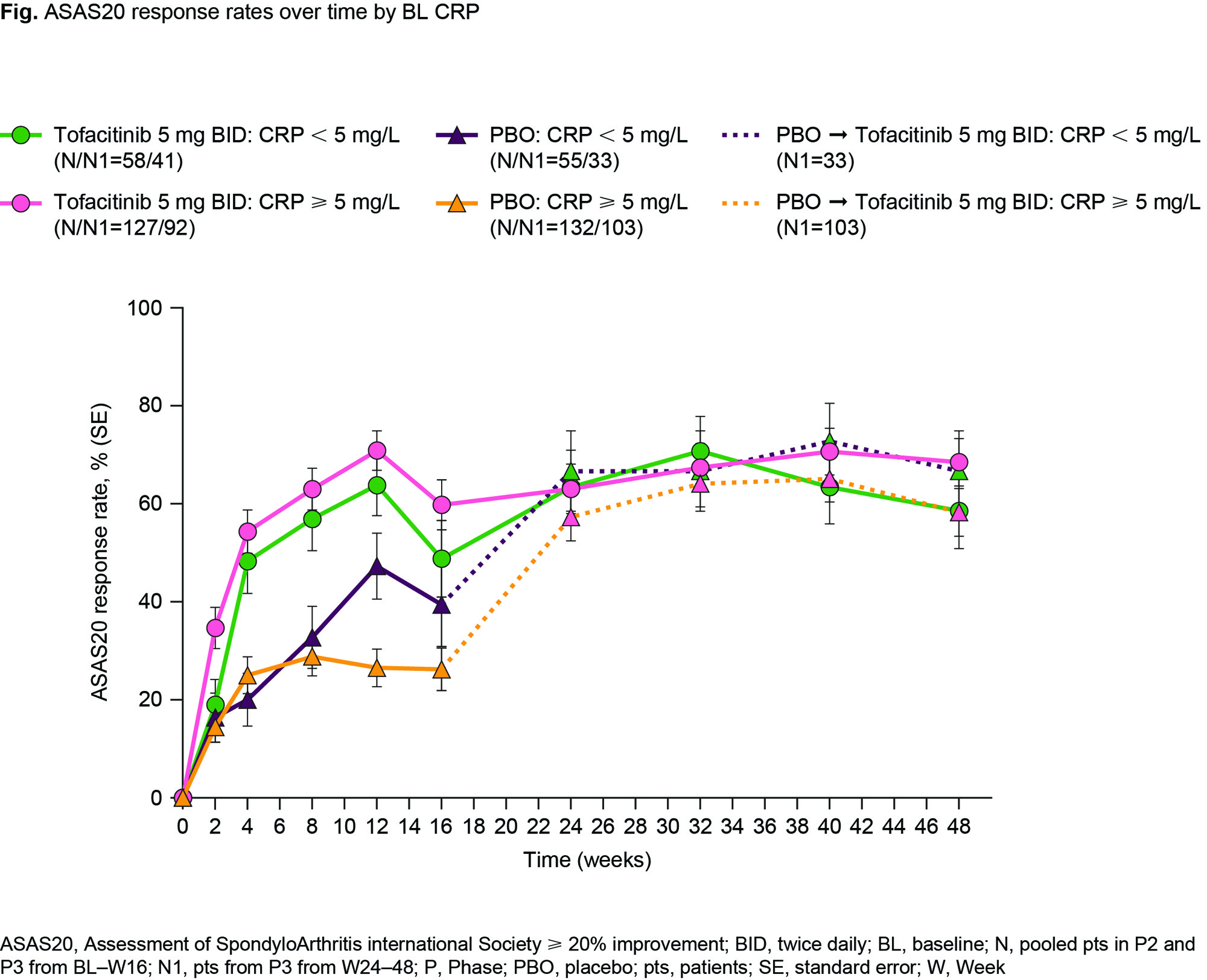
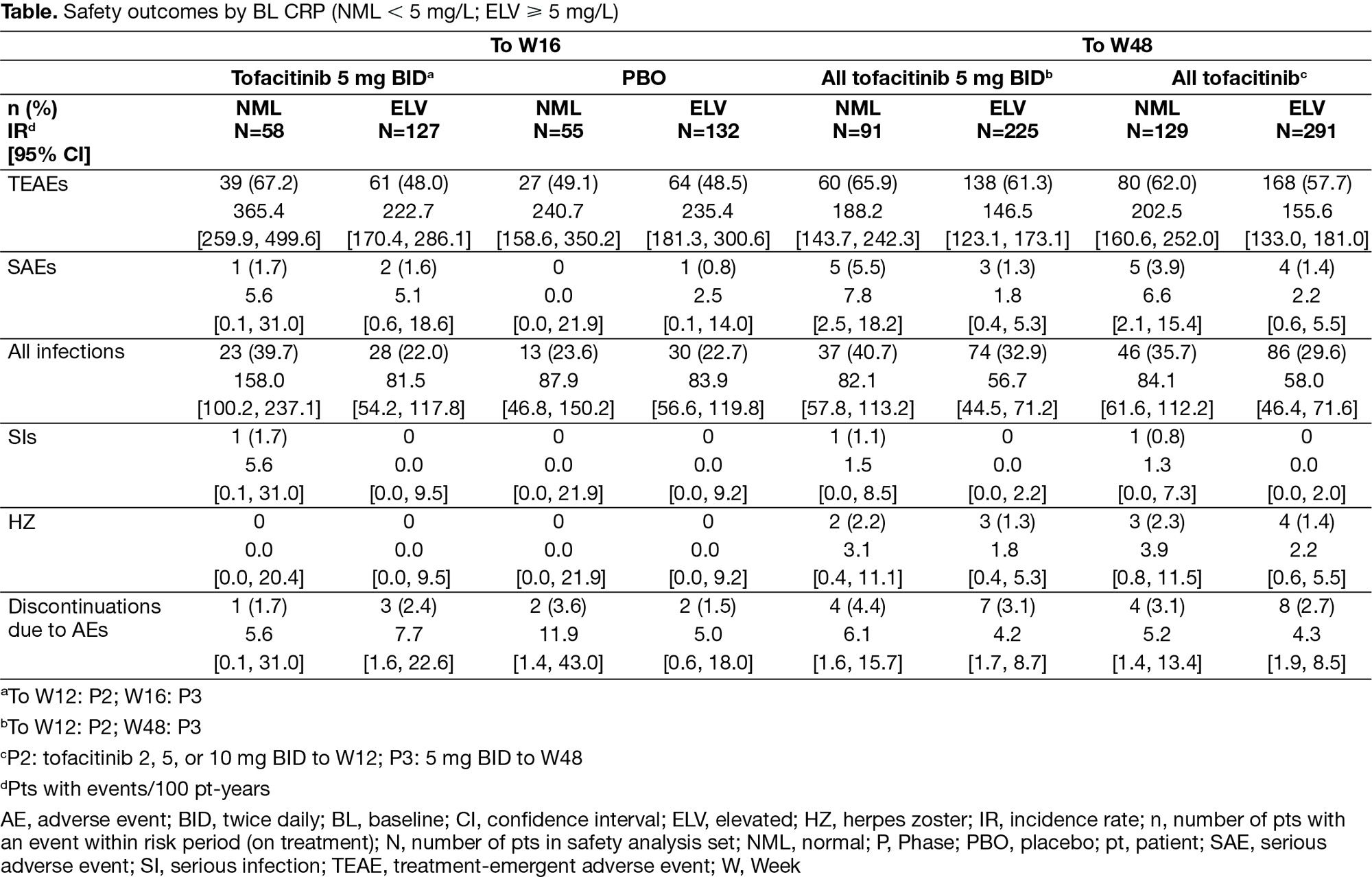
Results: Of 372 pts, 30.4/69.6% had NML/ELV BL CRP. Both groups had generally similar BL characteristics; more pts with ELV CRP were male, current smokers, and had prior biologic DMARD use. At W12, ASAS20 response was greater for tofacitinib vs PBO in both groups (Fig); efficacy maintained to W48. At W12, the difference in response from PBO for tofacitinib was numerically greater for ELV vs NML CRP for ASAS20 (44.7% vs 15.9%), ASAS40 (34.6% vs 17.3%), BASDAI50 (33.8% vs 15.3%), ASDAS-CRP ID (9.5% vs 8.2%), Δnocturnal spinal pain (-2.1 vs -1.4), and ΔFACIT-F (5.2 vs 3.5). For tofacitinib, rates of treatment-emergent adverse events and infections to W16 trended numerically higher for tofacitinib vs PBO in pts with NML CRP, but were similar to PBO in pts with ELV CRP (Table). There were few serious adverse events, serious infections, or herpes zoster across groups and no deaths. Limitations: small sample size, differences in BL characteristics.
Conclusion: Regardless of BL CRP, at W12, tofacitinib was more efficacious vs PBO; and across endpoints, the differences in response from PBO for tofacitinib were numerically greater in pts with ELV vs NML CRP. Tofacitinib safety rates were consistent with PBO in pts with ELV CRP, but trended higher for tofacitinib vs PBO in pts with NML CRP.
Study sponsored by Pfizer. Medical writing support provided by L Manjunatha and J Arnold, CMC Connect; funded by Pfizer.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Deodhar A, Baraliakos X, Magrey M, Gensler L, Thorat A, Pemmaraju S, Cadatal M, Nash P. Tofacitinib Efficacy and Safety in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis by Baseline C-Reactive Protein Levels: A Post Hoc Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tofacitinib-efficacy-and-safety-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis-by-baseline-c-reactive-protein-levels-a-post-hoc-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tofacitinib-efficacy-and-safety-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis-by-baseline-c-reactive-protein-levels-a-post-hoc-analysis/