Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients (pts) are at increased risk for cardiovascular (CV) disease. Although analysis of lipids such as LDL-C and HDL-C is useful in the general population to estimate CV risk, disease-associated inflammation also contributes to CV risk among RA pts. Chronic inflammation in RA is associated with low HDL-C and altered HDL composition. HDL particles may become atherogenic due to association with acute-phase reactants (ie, serum amyloid A [SAA] and secretory phospholipase A2 [sPLA2]), thereby losing their ability to protect LDL from oxidation. Elevated serum HDL-associated SAA (HDL-SAA) and sPLA2 have been identified as markers of increased CV risk.1 We conducted a post hoc analysis of HDL-SAA and sPLA2 to investigate changes in HDL composition in RA pts after initiation of 2 biological therapies with different mechanisms of action.
Methods: ADACTA was a phase 4, randomized, double-blind study in RA pts (tocilizumab [TCZ], n=163; adalimumab [ADA], n=163).2 Pts received TCZ 8 mg/kg IV Q4W or ADA 40 mg SC Q2W for 24 wks, both as monotherapy. Available serum samples were analyzed at baseline (BL) and wk 8 for HDL-C, HDL-SAA, and sPLA2. Change from BL to wk 8 was analyzed by ACR20 response (responders [R]/nonresponders [NR]) at wk 24. Change from BL to wk 8 in median HDL-SAA and sPLA2 was compared using nonparametric Kruskal-Wallis analyses. Spearman rank correlation coefficients were used to determine associations between changes in these parameters and C-reactive protein (CRP) and apolipoprotein A-1 (apoA-1) collected during the trial.
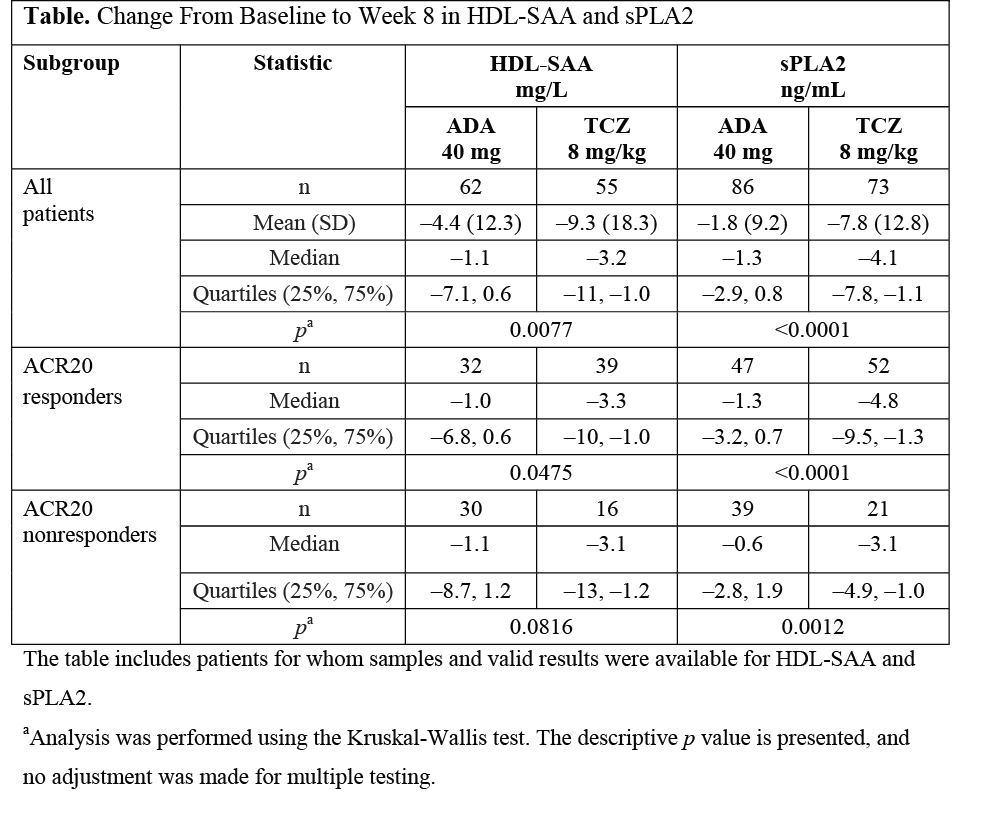
Results: A greater increase in HDL-C was observed after treatment with TCZ vs ADA (TCZ, 0.14 mmol/L, n=129; ADA, 0.07 mmol/L, n=137). Reductions in HDL-SAA and sPLA2 were seen in both arms, with a greater response with TCZ (Table). Larger reductions in sPLA2 were seen with TCZ for ACR20-R. For ACR20-NR, smaller reductions were seen in both arms, also in favor of TCZ. There were similar reductions in HDL-SAA for ACR20-R and -NR, but again reductions were greater with TCZ (Table); the same effect was seen for EULAR good responders (data not shown). In both arms, a moderate positive correlation was seen between HDL-SAA and sPLA2 (TCZ, r=0.57, p<0.0001; ADA, r=0.54, p<0.0001). A stronger correlation was observed between HDL-SAA and CRP (TCZ, r=0.58, p<0.0001; ADA, r=0.69, p<0.0001) and sPLA2 and CRP (TCZ, r=0.66, p<0.0001; ADA, r=0.74, p<0.0001). There was a weak negative correlation between HDL-SAA or sPLA2 and apoA-1 with TCZ (HDL-SAA, r=–0.27, p=0.05; sPLA2, r=–0.25, p=0.04) and a weaker correlation with ADA (HDL-SAA, r=–0.19, p=0.13; sPLA2, r=–0.16, p=0.14).
Conclusion: TCZ had a greater effect than ADA on reducing HDL-SAA and sPLA2 levels, suggesting a greater positive impact of TCZ on the antiatherogenic properties of HDL.
References: 1. Rohrer L et al. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2004;15:269-278. 2. Gabay C et al. Lancet. 2013;381:1541-1550.
Disclosure:
C. Gabay,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
2,
Roche, Abbvie, Pfizer, UCB, BMS, MSD,
5;
K. Tuckwell,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
3;
J. Green,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
3;
M. Klearman,
Genentech and Biogen IDEC Inc.,
3;
A. Kavanaugh,
Roche, Abbott, Amgen, UCB, BMS, Pfizer, Janssen,
2.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tocilizumab-monotherapy-compared-with-adalimumab-monotherapy-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-an-evaluation-of-high-density-lipoprotein-composition/