Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster III: Psoriatic Arthritis II (1801–1835)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Guselkumab (GUS), a human monoclonal antibody targeting the interleukin-23p19-subunit, has demonstrated efficacy across joint and skin endpoints at Week 24 (W24) in the Phase 3 DISCOVER-1 and -2 clinical trials of patients with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA).1,2 The aim of this post hoc analysis was to identify clinical phenotypic predictors of minimal disease activity (MDA) response to GUS treatment at W24 in patients with active PsA.
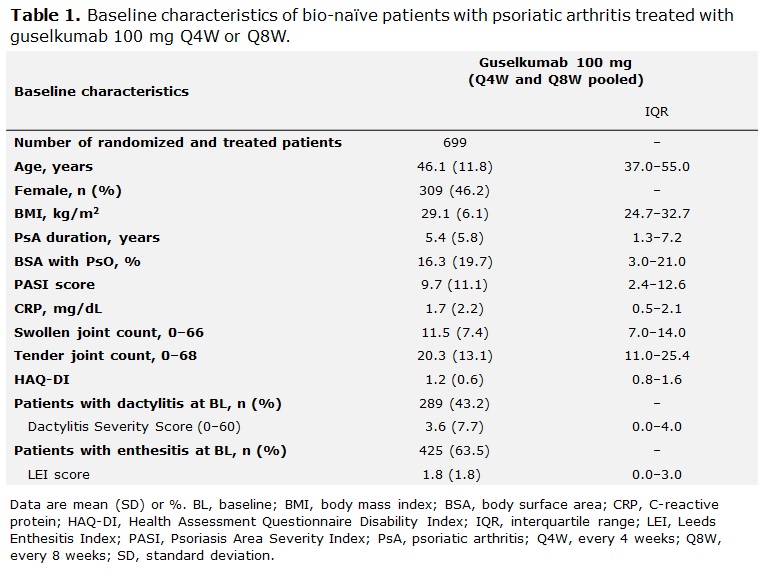
Methods: Data from bio-naïve patients with active PsA who were treated with GUS 100 mg every 4 or 8 weeks (Q4W; Q8W) were pooled across DISCOVER-1 and -2. Patients in DISCOVER-1 were required to have ≥3 swollen and ≥3 tender joints and C-reactive protein (CRP) ≥0.3 mg/dL; patients in DISCOVER-2 were required to have ≥5 swollen and ≥5 tender joints and CRP ≥0.6 mg/dL. Logistic regression analysis was performed to identify potential predictors of MDA response to GUS at W24; odds ratios, 95% confidence intervals and p-values were calculated. Missing data for MDA at W24 were imputed as non-response; a few missing baseline (BL) values in 4 patients were imputed. Potential predictors of response were characterized by patients’ baseline clinical features, including swollen and tender joint counts, affected joint location (including temporomandibular joint, hands, feet, wrist, elbow, shoulder, hip, and knee), BL dactylitis and enthesitis, Psoriasis Area Severity Index (PASI) score, and psoriasis (PsO) localization (including hands and feet, scalp, or nail involvement). Other selected BL characteristics are also described (Table 1).
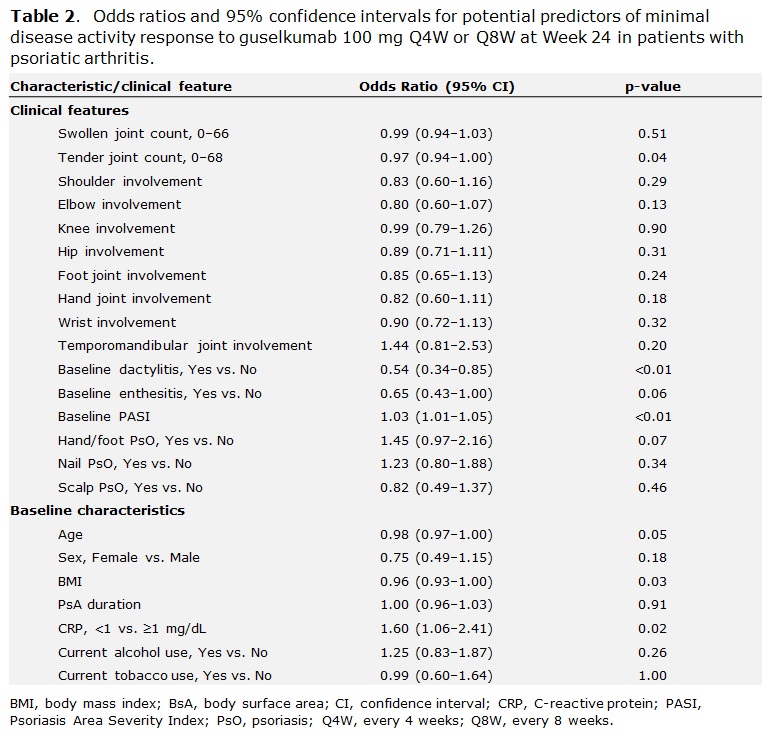
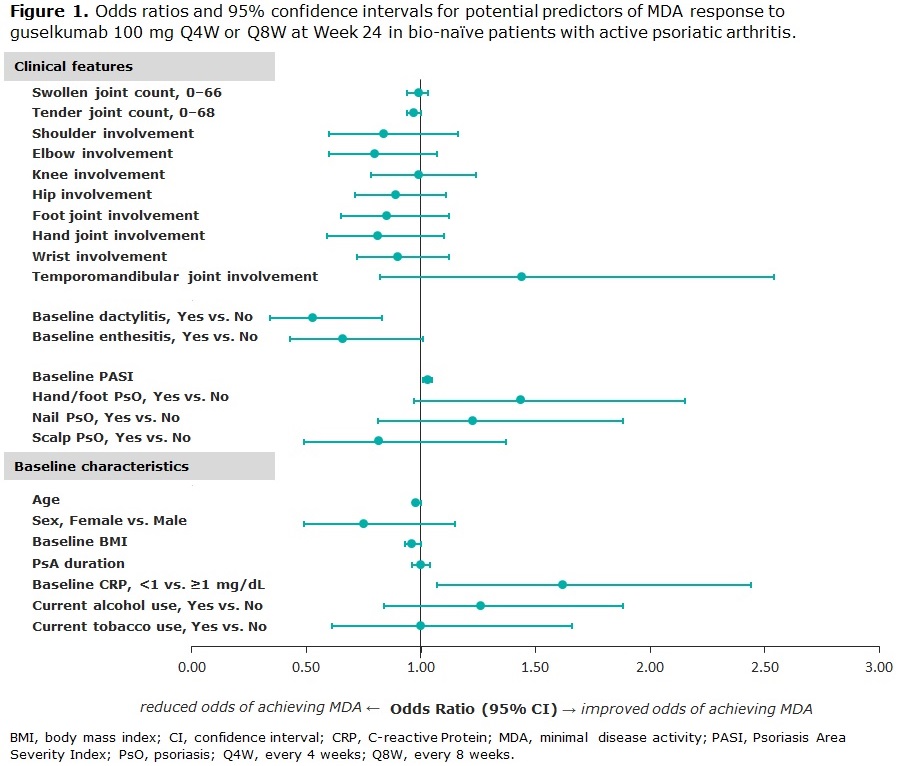
Results: Clinical characteristics of 669 bionaïve, GUS-treated patients, which were generally consistent across DISCOVER-1 (n=176) and DISCOVER-2 (n=493), indicated substantial disease burden at BL. Patients had a mean tender and swollen joint count of 20.3 and 11.5, respectively, and a mean PASI score of 9.7; 63.5% had enthesitis, and 43.2% had dactylitis at BL (Table 1). At W24, MDA was achieved by 24.4% (163/669) of pooled GUS Q4W- and Q8W-treated patients. Lower body mass index (BMI) and tender joint count, CRP < 1 mg/dL, and higher PASI at BL (all p< 0.05) were significant predictors of MDA response at W24. Patients with presence of dactylitis at BL were significantly less likely than those without this manifestation to achieve MDA at W24 (Table 2; p< 0.01). The localization of PsO, affected joint location, or current tobacco use were not predictive of MDA response at W24 (Figure 1).
Conclusion: PsA phenotypes at BL are significant positive (lower tender joint count, higher PASI) or negative (presence of dactylitis) predictors of achieving the multidomain composite endpoint MDA at W24. BL BMI and CRP may also affect the prospect of reaching MDA. These data emphasize that all domains of PsA should be taken into account, and that more complex disease requires particular attention.
1. Deodhar A et al. Lancet 2020; 395: 1115–1125.
2. Mease PJ et al. Lancet 2020; 395: 1126–1136.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Vis M, Richette P, Julio R, Neuhold M, Wapenaar R, Theander E, Noel W, Shawi M, Kollmeier A, Tillett W. To What Extent Do Clinical Features of PsA Predict Achievement of Minimal Disease Activity at Week 24: A Post Hoc Analysis of the Phase III Clinical Trial Program of Guselkumab in a Bio-naïve Patient Population [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/to-what-extent-do-clinical-features-of-psa-predict-achievement-of-minimal-disease-activity-at-week-24-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-the-phase-iii-clinical-trial-program-of-guselkumab-in-a-bio-naive-patient/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/to-what-extent-do-clinical-features-of-psa-predict-achievement-of-minimal-disease-activity-at-week-24-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-the-phase-iii-clinical-trial-program-of-guselkumab-in-a-bio-naive-patient/