Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 7, 2020
Title: RA – Treatments Poster II: Comparative Effectiveness, Biosimilars, Adherence & the Real World
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib (TOFA) is an oral, small molecule drug used for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) treatment and is prescribed alone or with methotrexate (MTX). TOFA can be used as an alternative to biologic disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) including tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi). We aimed to evaluate the discontinuation rate of this drug, with and without concurrent MTX in comparison with TNFi, in patients with RA in the Ontario Best Practices Research Initiative (OBRI).
Methods: RA patients enrolled in the OBRI initiating their TOFA or TNFi (adalimumab, certolizumab, etancercept, golimumab, and infliximab) between 1st June 2014 (TOFA approval date in Canada) and 31st Dec 2018 were included. Time to discontinuation (due to any reason) were assessed using Kaplan-Meier survival (adjusted for propensity score using inverse probability of treatment weight) to compare patients with and without MTX use at initiation of TOFA or TNFi. We used multiple imputation (N=20) to deal with missing data for covaraites at treatment initiation.
Results: A total of 565 patients initiated TOFA (n=208) or TNFi (n=357). Of those, 106 (51%) and 222 (62%) were treated with MTX in the TOFA and TNFi group, respectively. There was no significant difference for sociodemographic , comorbidity, and disease profile between MTX groups in TOFA users. In TNFi users, compared with no MTX group, patients with MTX were significantly less likely to be women (77.9% vs. 88.9%) and to have prior bDMARDs use (24.3% vs. 42.4%).
Over a mean of 17.3 month follow-up, discontinuation was reported in 75 (36%) and 103 (29%) of all TOFA and TNFi patients, respectively. After adjusting for propensity score, patients treated with TNFi and MTX remained on treatment longer than those treated without MTX (Logrank p=0.002) (Figure 1A) while there was no significant difference in TOFA discontinuation in patients with and without MTX (Logrank p=0.31) (Figure 1B).
Conclusion: In this real world data study, we found that TOFA retention is similar in patients with and without MTX, while patients treated with TNFi and MTX remained on treatment longer than those treated without MTX. Merging data with other RA registries in Canada is proposed to increase study power and to provide more robust results.
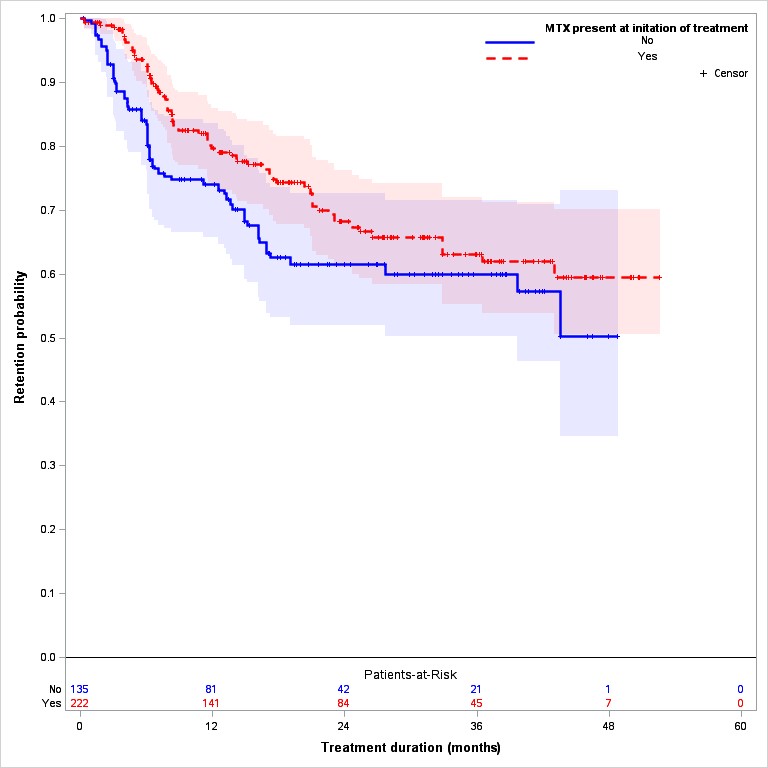 Figure 1. Drug discontinuation TNFi and TOFA; with and without MTX A. TNFi
Figure 1. Drug discontinuation TNFi and TOFA; with and without MTX A. TNFi
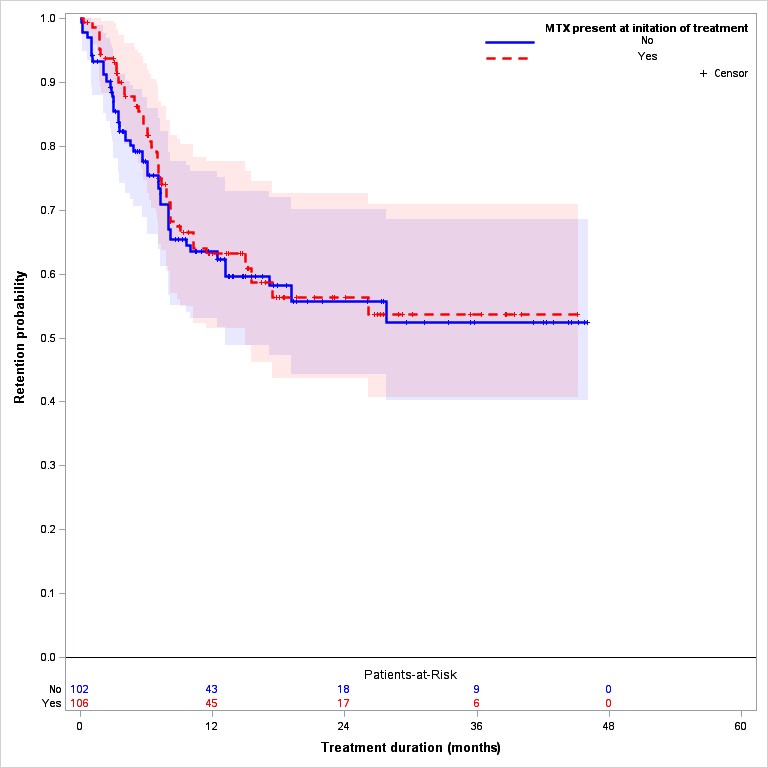 Figure 1. Drug discontinuation TNFi and TOFA; with and without MTX B. TOFA
Figure 1. Drug discontinuation TNFi and TOFA; with and without MTX B. TOFA
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Movahedi M, Cesta A, Li X, Keystone E, Bombardier C. Time to Discontinuation of Tofacitinib and TNF Inhibitors in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients with and Without Methotrexate: Real World Results from a Rheumatoid Arthritis Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/time-to-discontinuation-of-tofacitinib-and-tnf-inhibitors-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-with-and-without-methotrexate-real-world-results-from-a-rheumatoid-arthritis-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/time-to-discontinuation-of-tofacitinib-and-tnf-inhibitors-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-with-and-without-methotrexate-real-world-results-from-a-rheumatoid-arthritis-cohort/
