Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2095–2140) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: We analyzed trends in the incidence and severity of novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) from the first wave to early 2023 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods: Cases who were diagnosed according to ACR/EULAR 2010 classification criteria were recruited to SHin-yokohama Arthritis REgister (SHARE) between 2020 and 2023. We conducted a retrospective cohort study investigating COVID-19 outcomes in clinic-confirmed rheumatoid arthritis patients from March 1, 2020 to February 28, 2023. We aggregated the total number of COVID-19 cases and the number of critically ill cases (hospitalized or died) and calculated the number of severe cases of COVID-19 by calendar period. compared the proportions. We estimated the clinical features of severe COVID-19 in each period. Rheumatic Disease Comorbidity Index (RDCI) were analyzed to detect the clinical features of severe COVID-19 in RA patients.
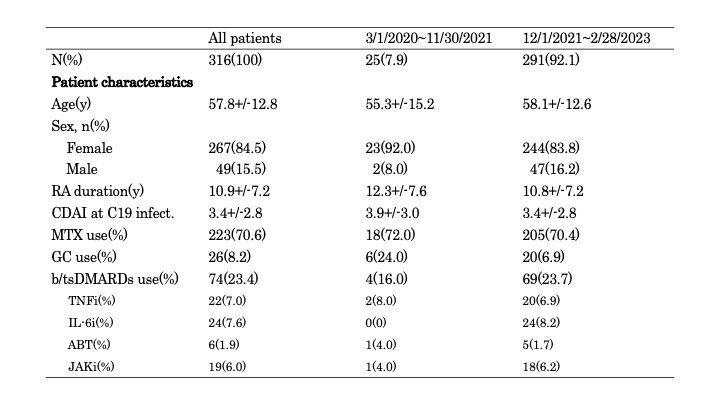
Results: 2,481 RA patients were enrolled. 316 cases were diagnosed as COVID-19 (12.8%, average age 57.8+/-12.8 years, female 84.5%). There were 7 cases of severe COVID-19 (2.2%). The proportion of serious outcomes due to COVID-19 decreased over calendar time (p < 0.0001). 16% of cases were severe in the early stage of COVID-19 (March 1, 2020-November 30, 2021), compared with after omicron stages (December 1, 2021-February 28, 2023) was 1.0%.
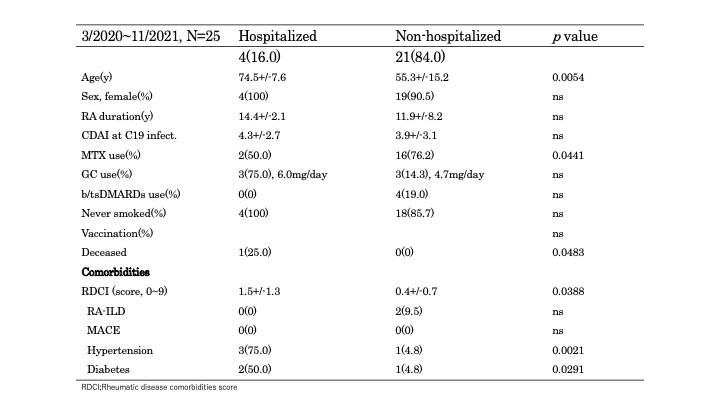
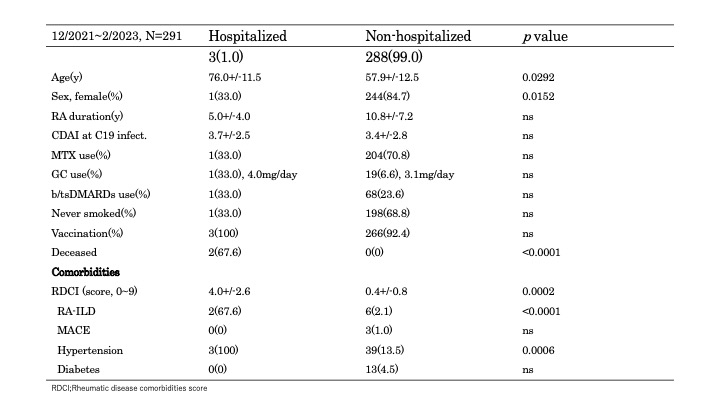
In the early stage of COVID-19, elderly age (p=0.0054), hypertension (p=0.0021), diabetes (p=0.0291) and RDCI (1.5+/-1.3 vs. 0.4+/-0.7, p=0.0388) were associated with critical ill cases. After omicron stages of COVID-19, elderly age (p=0.0292), hypertension (p=0.0006), RA-ILD (p< 0.0001) and RDCI (4.0+/-2.6 vs. 0.4+/-0.8, p=0.0002) were associated with critical ill cases.
Conclusion: CONCLUSIONS Although the proportion of severe COVID-19 RA cases has decreased in after omicron stages compared to early stages of COVID-19, the clinical features of severe COVID-19 were very similar between two groups.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
YAMASAKI M. Time-course Analysis from the First Wave to Early 2023 in Critically Ill Patients with Novel Coronavirus Infection in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/time-course-analysis-from-the-first-wave-to-early-2023-in-critically-ill-patients-with-novel-coronavirus-infection-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/time-course-analysis-from-the-first-wave-to-early-2023-in-critically-ill-patients-with-novel-coronavirus-infection-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/