Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0593–0640) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Renal involvement is a major prognostic factor in systemic lupus erythematosus. Pure lupus membranous nephropathy (PLMN, class V) represents 5–20% of lupus nephritis cases, with up to 30% progressing to end-stage kidney disease. Unlike proliferative forms, the benefit-risk profile of immunosuppressive therapy in PLMN remains poorly defined. Accordingly, real-world data from unselected patients treated with contemporary therapeutic regimens are critical to delineate response patterns, identify predictors of treatment failure, and establish clinically meaningful therapeutic targets.
Methods: We conducted a nationwide, population-based observational study between 2000 and 2020, involving 25 centers across France (IRB registration: 00012437). Patients experiencing a first flare of PLMN were classified into four treatment groups: (i) supportive care, receiving no immunosuppressive therapy; (ii) mycophenolate mofetil (MMF), treated with MMF combined with low- or high-dose corticosteroids; (iii) rituximab (RTX), treated with RTX and corticosteroids; and (iv) other treatments, receiving immunosuppressive agents excluding MMF and RTX. Renal responses were defined according to the 2024 KDIGO guidelines. Treatment failure was defined as failure to achieve complete or partial response by month 12, occurrence of a relapse, or need for a change in therapeutic class before month 12—excluding initiation of maintenance therapy.
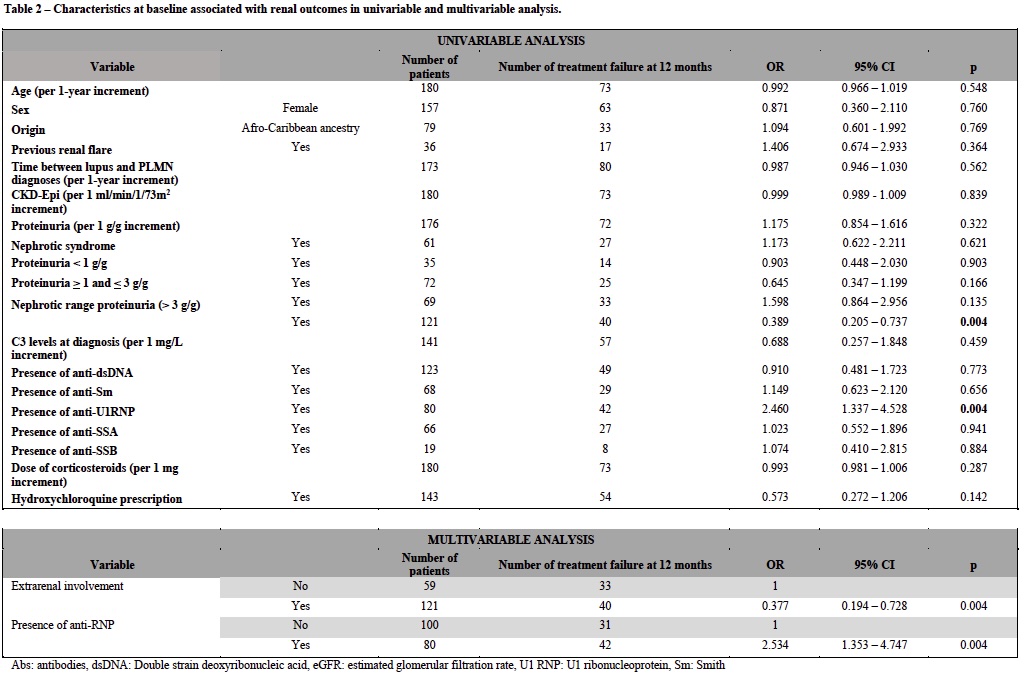
Results: A total of 194 patients with a first flare of PLMN were analyzed. At the time of PLMN diagnosis, 53 patients (27.3%) received supportive care only, while 141 (72.7%) were treated with at least one immunosuppressive agent. Among them, 54 (38.3%) received a mycophenolate mofetil (MMF)-based regimen, 26 (18.4%) a rituximab (RTX)-based regimen, and 61 (43.2%) other types of immunosuppressive treatment (Table 1). Complete renal response (CRR) at 6 and 12 months was achieved in 1/47 (2.1%) and 18/49 (36.7%) patients in the supportive care group, 11/50 (22%) and 31/51 (60.8%) patients treated with MMF, 5/23 (21.7%) and 16/25 (64.0%) patients treated with RTX, and 14/51 (27.4%) and 25/55 (45.4%) patients treated with other regimens, respectively. Treatment with steroids was not associated with treatment response (p = 0.3). Patients treated by RTX had a shorter duration treatment (p< 0.01) and a lower corticosteroids exposure (p=0.02) than patients treated by other regimens (Figure 1). Independent risk-factors for treatment failure were the presence of anti-U1RNP antibodies (OR=2.5 [95% CI: 1.35-4.75]) and the absence of extra-renal involvement (OR=0.34 [95% CI: 0.19 – 0.73]) (Table 2).
Conclusion: While 22–27% of patients achieve CRR by 6 months, this proportion increased substantially without treatment modification to 45–64% at 12 months, underscoring that premature modification of therapy may be unwarranted in PLMN patients. RTX was associated with a lower corticosteroid exposure and a shorter treatment duration. Anti-U1RNP was independently associated with treatment response, suggesting its potential to stratify the risk of treatment failure in PLMN patients and foster individualized follow-up.
.jpg) Figure 1 – Evolution of (A) proteinuria (urine protein creatinine ratio), (B) serum albumin and (C) corticosteroids dosage at month 0, 6 and 12 according to the initial immunosuppressant group of treatment.
Figure 1 – Evolution of (A) proteinuria (urine protein creatinine ratio), (B) serum albumin and (C) corticosteroids dosage at month 0, 6 and 12 according to the initial immunosuppressant group of treatment.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chevalier K, Brousse R, karras a, Costedoat-Chalumeau N, Dang J, Taillar M, JOURDE-CHICHE N, Ronsin C, Le Quintrec-Donnette M, Julien M, Huart A, Couturier A, Pommerolle P, Lebas C, Coussement A, Chapal M, Barba C, Gauffre A, Teisseyre M, Noble J, Comarmond C, Vilaine E, Augusto J, Hummel A, Pillebout E, Halami J, Moranne O, Daugas E, Boffa J, Esteve E. Therapeutic landscape of systemic lupus erythematosus pure membranous nephropathy: a nationwide population-based study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/therapeutic-landscape-of-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-pure-membranous-nephropathy-a-nationwide-population-based-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/therapeutic-landscape-of-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-pure-membranous-nephropathy-a-nationwide-population-based-study/

.jpg)