Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Oligoarticular psoriatic arthritis (PsA, ≤4 joints affected) is common but understudied, as most clinical trials enroll patients (pts) with ≥3 swollen and tender joints. FOREMOST (NCT03747939) is the first phase 4, multicenter, randomized, placebo (PBO)-controlled trial to demonstrate efficacy of apremilast (APR) in pts with early oligoarticular PsA and investigate clinical outcomes in this pt population. The PsA Impact of Disease (PsAID-12) Questionnaire, a 12-item pt-reported outcome measure with recently described cutoff values, can be used to understand the burden of PsA from the pt’s perspective. Here, we evaluate the efficacy of APR on the impact of disease, as measured by PsAID-12 total score in pts with early oligoarticular PsA.
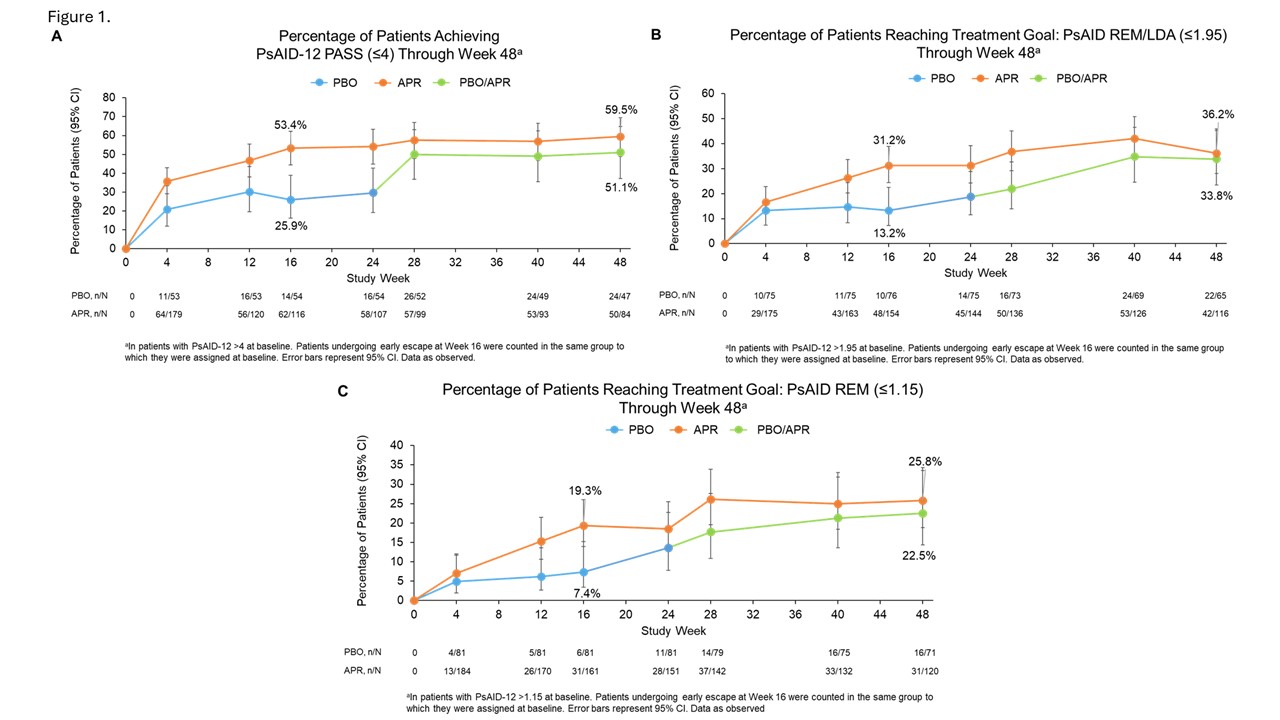
Methods: FOREMOST included pts with early PsA (duration ≤5 years) and limited joint involvement ( >1 but ≤4 swollen and >1 but ≤4 tender joint count, 66–68 joints assessed). Pts were randomized 2:1 to APR (30 mg twice daily) or PBO for 24 wks (early escape at Wk 16), followed by an extension phase in which all pts received APR through Wk 48. Change in PsAID-12 from baseline was calculated at Wks 16 and 48 in both groups. Percentage of pts achieving a Patient Acceptable Symptom State (PASS) according to PsAID-12 (PsAID-12 ≤4) through Wk 48 was assessed in pts not in PASS (PsAID-12 >4) at baseline. We also assessed the percentages of pts reaching PsAID-defined remission or low disease activity (REM/LDA: PsAID-12 ≤1.95) and remission (REM: PsAID-12 ≤1.15) through Wk 48 in pts not in REM/LDA (PsAID-12 >1.95) and REM (PsAID-12 >1.15) at baseline1. Data are as observed.
Results: In 308 randomized pts (APR: n=203; PBO: n=105), mean (standard deviation [SD]) PsA duration at baseline was 10 (10.18) months and mean (SD) PsAID-12 was 4.72 (2.09). At Wk 16, mean (SD) change in PsAID-12 from baseline was −1.51 (1.9) in APR and −0.44 (1.9) in PBO; during the extension phase, pts continuing APR (APR/APR) and pts who switched from PBO to APR (PBO/APR) improved through Wk 48 (−1.63 [2.1] and −1.59 [1.8], respectively). At Wk 16, 53.4% (62/116) of pts not in PsAID-12 PASS at baseline achieved PsAID-12 PASS with APR compared with 25.9% (14/54) with PBO (Figure 1A). At Wk 16, 31.2% (48/154) of pts not in PsAID-REM/LDA at baseline reached the treatment goal of PsAID-REM/LDA with APR compared with 13.2% (10/76) with PBO (Figure 1B), and 19.3% (31/161) of pts not in PsAID-REM at baseline achieved PsAID-REM with APR vs 7.4% (6/81) with PBO (Figure 1C). Through Wk 48, the APR/APR and PBO/APR groups maintained achievement of or improved in PsAID-12 PASS, REM/LDA, and REM (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Greater percentages of pts with oligoarticular PsA receiving APR achieved the acceptable symptom state, symptom-based low disease activity, or symptom based-remission at Wk 16 compared with PBO; this was maintained through Wk 48. These results demonstrate the efficacy of APR on reducing the burden of oligoarticular PsA disease from the pt’s perspective. These results might inform shared decision-making for pts with early PsA.
REFERENCE
1. Gossec L, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2023;82(Suppl 1):565-566. (abstract).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gossec L, Coates L, Gladman D, Ogdie A, Nash P, Poddubnyy D, Kavanaugh A, Armstrong A, Selmi C, Queiro Silva R, Deignan C, Wang R, Reddy J, Brunori M, Mease P. The Use of Disease Activity Thresholds for the Psoriatic Arthritis Impact of Disease Questionnaire to Assess Patient Perceptions of Disease Burden in Patients with Early Oligoarticular Psoriatic Arthritis Treated with Apremilast in a Phase 4 Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-use-of-disease-activity-thresholds-for-the-psoriatic-arthritis-impact-of-disease-questionnaire-to-assess-patient-perceptions-of-disease-burden-in-patients-with-early-oligoarticular-psoriatic-arthr/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-use-of-disease-activity-thresholds-for-the-psoriatic-arthritis-impact-of-disease-questionnaire-to-assess-patient-perceptions-of-disease-burden-in-patients-with-early-oligoarticular-psoriatic-arthr/